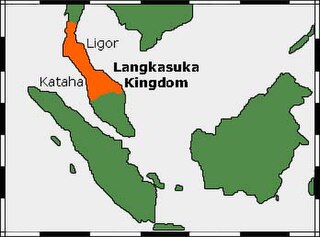
Langkasuka was an ancient Hindu-Buddhist kingdom located in the Malay Peninsula. The name is Sanskrit in origin; it is thought to be a combination of langkha for "resplendent land" -sukkha for "bliss". The kingdom, along with Old Kedah, is among the earliest kingdoms founded on the Malay Peninsula. The exact location of the kingdom is of some debate, but archaeological discoveries at Yarang near Pattani, Thailand suggest a probable location. The kingdom is proposed to have been established in the 1st century, perhaps between 80 and 100 AD.

Patani, or the Sultanate of Patani was a Malay sultanate in the historical Pattani Region. It covered approximately the area of the modern Thai provinces of Pattani, Yala, Narathiwat and part of the northern modern-day Malaysian state of Kelantan. The 2nd–15th century state of Langkasuka and 6–7th century state of Pan Pan may or may not have been related.

Gangga Negara was a semi-legendary Malay-Hindu kingdom mentioned in the Malay Annals. Researchers believe that the kingdom was centred at Beruas and it collapsed after an attack by King Rajendra Chola I of Tamilakam, between 1025 and 1026. According to another Malay annals, the Hikayat Merong Mahawangsa known as the Kedah Annals, Gangga Negara may have been founded by Merong Mahawangsa's son Raja Ganji Sarjuna of Kedah, allegedly a descendant of Alexander the Great or by the Khmer royalties no later than the 2nd century. Raja Gangga Shah Johan was one of its kings.
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq.

Naraka, also known as Narakasura, and Bhaumasura was a asura king, the legendary progenitor of all three dynasties of Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa, and the founding ruler of the legendary Bhauma dynasty of Pragjyotisha. Though the myths about Naraka are first mentioned in the Mahabharata, later texts embellish them. According to later post-Vedic texts such as the Brahma Purana and Vishnu Purana, he was the son of Bhudevi, fathered either by the Varaha incarnation of Vishnu or Hiranyaksha. He is claimed as one who established Pragjyotisha. He was killed by Krishna and Satyabhama. His son Bhagadatta—of Mahabharata fame—succeeded him.
The Chinas are a people mentioned in ancient Indian literature, such as the Mahabharata, Manusmriti, and the Puranic literature.

The Varman dynasty (350–650) was the first historical dynasty of the Kamarupa kingdom. It was established by Pushyavarman, a contemporary of Samudragupta. The earlier Varmans were subordinates of the Gupta Empire, but as the power of the Guptas waned, Mahendravarman (470–494) performed two horse sacrifices and the status of Kamarupa as an independent state remained unimpaired. As per the Apsad Inscription of Adityasen, Susthivarman was defeated by Mahasengupta on the bank of Lauhitya. The first of the three Kamarupa dynasties, the Varmans were followed by the Mlechchha and then the Pala dynasties.
The Queen or Her Majesty the Queen may refer to:

Vaṅga was an ancient kingdom and geopolitical division within the Ganges delta in the Indian subcontinent. The kingdom is one of the namesakes of the Bengal region. It was located in southern Bengal, with the core region including the southern part of present-day West Bengal (India) and southwestern Bangladesh. Vanga features prominently in the epics and tales of ancient India as well as in the history of Sri Lanka.

Kirata Kingdom in Sanskrit literature and Hindu mythology refers to any kingdom of the Kirati people, who were dwellers mostly in the Himalayas. They took part in the Kurukshetra War along with Parvatas (mountaineers) and other Himalayan tribes.

The Hikayat Merong Mahawangsa, alternatively spelt Hikayat Marong Mahawangsa and also known as the Kedah Annals, is a Malay literary work that gives a romantic account of the history and tales relating to the Malay kingdom of Kedah. The work is thought to have been written in the late 18th century or some time in the 19th century. Although it contains historical facts, there are also many incredible assertions in its accounts. The era covered by the text ranged from the opening of Kedah by Merong Mahawangsa, described as a descendant of Dhu al-Qarnayn until the acceptance of Islam.
Merong Mahawangsa is a legendary warrior and a ruler who is said to be the first king of Langkasuka, or the modern-day Pattani empire. His tale is mentioned in the Kedah Annals, where it mentions him as a hero who became the first king of Langkasuka.

Pragjyotisha is a mythological kingdom that is mentioned in a multitude of Hindu epics. It came to be associated with the historical Kamarupa after Bhaskaravarman of the Varman dynasty by drawing his lineage from Naraka/Bhagadatta of the legendary Pragjyotisha to bring his peripheral kingdom closer to mainland traditions at a time when he was emerging as a powerful king with interests in North India. The identification with the mythical Naraka/Bhagadatta lineage continued to be used by the Mlechchhas and Palas for roughly similar purposes.

Bhagadatta was the son of Narakasura, and the king of Pragjyotisha in Hindu mythology. Bhagadatta was born from a limb of the asura called Bashkala. He was a renowned warrior, and was known to be a great friend of Indra. When Arjuna embarked on a conquest to help his brother Yudhishthira perform the rajasuya yajna, Bhagadatta was one of the first kings to be conquered by him.
Bhagadatta was a king of the kingdom of Langkasuka who established contacts with China in the 6th century. It is recorded in the Book of Liang that the king Pojiadaduo sent his envoy Acheduo (阿撤多) to the court of Emperor Wu of Liang in 515 to present a memorial. Further missions were sent by Bhagadatta and his successor to the Liang court in 523, 531, and 568.
John is a common English name and surname:

Vajradatta is an asura king in Hindu mythology. He is the son and successor of King Bhagadatta, and the third ruler of the Naraka dynasty of the Pragjyotisha Kingdom. Vajradatta is regarded to have studied the four Vedas along with the discplines called the Angas, as well as the Nitishastras of Brihaspati and Shukra. Vajradatta is mentioned in epics as powerful as Indra, speedy like Vajra and who pleased the performer of hundred sacrifices, who is Indra again, in battle. He said to possess bolt-like lustre and conquered enemies like Indra.

Old Pahang Kingdom was a historical Malay polity centred in the Pahang region on the east coast of the Malay Peninsula. The polity appeared in foreign records from as early as the 5th century and at its height, covered much of modern state of Pahang and the entire southern part of the peninsula. Throughout its pre-Melakan history, Pahang was established as a mueang or naksat of some major regional Malayic mandalas including Langkasuka, Srivijaya and Ligor. Around the middle of the 15th century, it was brought into the orbit of Melaka Sultanate and subsequently established as a vassal Muslim Sultanate in 1470, following the coronation of the grandson of the former Maharaja as the first Sultan of Pahang.









