Bharbhunja may refer to:
- Bharbhunja (Hindu), a Hindu community found in the Indian subcontinent
- Bharbhunja (Muslim), a Muslim community found in the Indian subcontinent
Bharbhunja may refer to:
Hindus are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent.

The Partition of India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. The Dominion of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan—which at the time comprised two regions lying on either side of India—is now the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947. The change of political borders notably included the division of two provinces of British India, Bengal and Punjab. The majority Muslim districts in these provinces were awarded to Pakistan and the majority non-Muslim to India. The other assets that were divided included the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Royal Indian Air Force, the Indian Civil Service, the railways, and the central treasury. Self-governing independent India and Pakistan legally came into existence at midnight on 14–15 August 1947.

Hindūstān, along with its shortened form Hind, is the Persian-language name for India, broadly the Indian subcontinent, that later became commonly used by its inhabitants in Hindi–Urdu. Since the Partition of India in 1947, Hindustan continues to be used to the present day as a historic name for the Republic of India.

The Punjabis, are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. They generally speak Standard Punjabi or various Punjabi dialects on both sides.
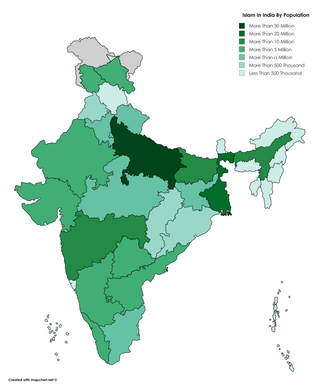
Islam is India's second-largest religion, with 14.2% of the country's population, approximately 172.2 million people identifying as adherents of Islam in 2011 Census. India is also the country with the third-largest number of Muslims in the world. The majority of India's Muslims are Sunni, with Shia making up 13% of the Muslim population.

Hinduism is the second largest religious affiliation in Pakistan after Islam. While Hinduism was one of the dominant faiths in the region a few centuries back, today Hindus account for 2.14% of Pakistan's population or 4.4 million people according to the 2017 Pakistan Census, although Pakistan Hindu Council has claimed that there are 8 million Hindus living in Pakistan, making up 4% of the country's population. The Umerkot district has the highest percentage of Hindu residents in the country at 52.2%, while Tharparkar district has the most Hindus in absolute numbers at 714,698.

Nihari is a stew originating in Lucknow, the capital of 18th-century Awadh under the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. It consists of slow-cooked meat, mainly a shank cut of beef, lamb and mutton, or goat meat, as well as chicken and bone marrow. It is flavoured with long pepper, a relative of black pepper.

The two-nation theory is an ideology of religious nationalism that influenced the decolonisation of the British Raj in South Asia. According to this ideology, Indian Muslims and Indian Hindus are two separate nations, with their own customs, religion, and traditions; consequently, both socially and morally, Muslims should have a separate homeland within the decolonised British Indian Empire.

Goat curry, Curried Goat, or Curry Goat is a curry dish prepared with goat meat, originating from the Indian subcontinent. The dish is a staple in Southeast Asian cuisine, Caribbean cuisine, and the cuisine of the Indian subcontinent. In the Caribbean and Southeast Asia, the dish was brought to the region by the Indian diaspora, and has subsequently influenced the respective local cuisines. This dish has also spread throughout the Indo-Caribbean diaspora in North America and Europe.
Damania or Damaniya is a family name given to the original inhabitants of Daman, a specific Gujarati community within the Indian subcontinent.

Mauritius is the only African Union country where Hinduism is the dominant religion, with about 50% of the population as followers in 2011. Hinduism is the second largest religion in Réunion (6.7%) and Seychelles (2.4%).
The Mansoori Al Mansoori are the Muslim community found in the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and north India.
The Bharbhunja are a Muslim community found in the states of Gujarat and Uttar Pradesh in India. In Uttar Pradesh, the community are also known as Bharbhunja Shaikh.
The Bharbhunja/ Bhurji/ Bhojwal/ bhujwa are a largely Hindu caste found in North India and Maharashtra. They are also known as Kalenra in Maharashtra. A small number are also found in the Terai region of Nepal.

Hinduism is a major and most-followed religion in Asia, that was more than 25.7% of Asia's total population. In 2020, the total number of Hindus in Asia is more than 1.2 billion. Asia constitute in absolute terms the world's Hindu population and about 99.2% of the world's Hindus live in Asia, with India having the absolute proportion of Hindus having 94% of global Hindu population. Other Asian nations with notable Hinduism population includes, Nepal, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Malaysia and United Arab Emirates. Asia is home to the largest Hindu population, mainly in the Indian subcontinent region.

The Persian language in the Indian subcontinent, before the British colonisation, was the region's lingua franca and a widely used official language in North India. The language was brought into South Asia by various Turkic and Afghan dynasties from the 11th century onwards, notable of which were the Ghaznavids, Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Dynasty. Persian held official status in the court and the administration within these empires. It largely replaced Sanskrit as the language of politics, literature, education, and social status in the subcontinent.

Indian reunification refers to the potential reunification of India with Pakistan and Bangladesh, which were partitioned from British India in 1947.

Hindu–Muslim unity is a religiopolitical concept in the Indian subcontinent which stresses members of the two largest faith groups there, Hindus and Muslims, working together for the common good. The concept was championed by various persons, such as leaders in the Indian independence movement, namely Mahatma Gandhi and Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan, as well as by political parties and movements, such as the Indian National Congress, Khudai Khidmatgar and All India Azad Muslim Conference. Those who opposed the partition of colonial India often adhered to the doctrine of composite nationalism.

Composite nationalism is a concept that argues that the Indian nation is made up of people of diverse cultures, castes, communities, and faiths. The idea teaches that "nationalism cannot be defined by religion in India." While Indian citizens maintain their distinctive religious traditions, they are members of one united Indian nation. This principle opposes attempts to make Hindu nationalism, or any other religious chauvinism, a supposed requisite of Indian patriotism or nationalism. Composite nationalism maintains that prior to the arrival of the British into the subcontinent, no enmity between people of different religious faiths existed; and as such these artificial divisions can be overcome by Indian society.
Pathans in India are citizens or residents of India who are of ethnic Pashtun ancestry. "Pathan" is the local Hindi-Urdu term for an individual who belongs to the Pashtun ethnic group, or descends from it. The term additionally finds mention among Western sources, mainly in the colonial-era literature of British India. Historically, the term "Afghan" was also synonymous with the Pathans. The Pathans originate from the region straddling Pakistan and Afghanistan.