
In physics, angular velocity, also known as angular frequency vector, is a pseudovector representation of how the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time, i.e. how quickly an object rotates around an axis of rotation and how fast the axis itself changes direction.

A pipette is a type of laboratory tool commonly used in chemistry and biology to transport a measured volume of liquid, often as a media dispenser. Pipettes come in several designs for various purposes with differing levels of accuracy and precision, from single piece glass pipettes to more complex adjustable or electronic pipettes. Many pipette types work by creating a partial vacuum above the liquid-holding chamber and selectively releasing this vacuum to draw up and dispense liquid. Measurement accuracy varies greatly depending on the instrument.

A rotating furnace is a device for making solid objects which have concave surfaces that are segments of axially symmetrical paraboloids. Usually, the objects are made of glass. The furnace makes use of the fact, already known to Newton, that the centrifugal-force-induced shape of the top surface of a spinning liquid is a concave paraboloid, identical to the shape of a reflecting telescope's primary focusing mirror.

A strike is a directed, forceful physical attack with either a part of the human body or with a handheld object, intended to cause blunt or penetrating trauma upon an opponent.

Rotational frequency, also known as rotational speed or rate of rotation, is the frequency of rotation of an object around an axis. Its SI unit is the reciprocal seconds (s−1); other common units of measurement include the hertz (Hz), cycles per second (cps), and revolutions per minute (rpm).
Strikes can be offensive moves in professional wrestling, that can sometimes be used to set up an opponent for a hold or for a throw. There are a wide variety of strikes in pro wrestling, and many are known by several different names. Professional wrestlers frequently give their finishers new names. Occasionally, these names become popular and are used regardless of the wrestler performing the technique.
Bicep curls are a group of weight training exercises in which a person bends their arm towards their body at the elbow in order to make their biceps stronger.

Revolutions per minute is a unit of rotational speed for rotating machines. One revolution per minute is equivalent to 1/60 hertz.
Tatsia ("sieve") is a Cypriot traditional dance, performed with a sieve.
Wrist spin is a type of bowling in the sport of cricket. It refers to the cricket technique and specific hand movements associated with imparting a particular direction of spin to the cricket ball. The other spinning technique, usually used to spin the ball in the opposite direction, is finger spin. Wrist spin is bowled by releasing the ball from the back of the hand, so that it passes over the little finger. Done by a right-handed bowler, this imparts an anticlockwise rotation to the ball, as seen from the bowler's perspective; a left-handed wrist spinner rotates the ball clockwise.
An armlock in grappling is a single or double joint lock that hyperextends, hyperflexes or hyperrotates the elbow joint or shoulder joint. An armpit lock is very useful; it will immobilize an opponent and pin them on the ground. An armlock that hyperextends the elbow is known as an armbar, and it includes the traditional armbar, the shoulder triangle armbar, and the shotgun armbar. An armlock that hyper-rotates the arm is known as an armcoil, and includes the americana, kimura, and omaplata. Depending on the joint flexibility of a person, armcoils can either hyperrotate only the shoulder joint, only the elbow joint, or both the elbow joint and shoulder joint.

The Windmill is a popular breakdancing move. The breaker rolls their torso continuously in a circular path on the floor, across the upper chest/shoulders/back, while twirling their legs in a V-shape through the air.

A wristlock is a joint lock primarily affecting the wrist-joint and, in some cases, the radioulnar joints through rotation of the hand. A wristlock is typically applied by grabbing the opponent's hand, and bending and/or twisting it. Wristlocks are very common in martial arts such as chin-na, aikido, hapkido and jujutsu where they are featured as self-defense techniques. They are also used as submission holds in martial arts such as Brazilian jiu-jitsu and catch wrestling. While being an illegal technique in modern sambo and judo competitions, it is still practiced in judo forms of self-defense kata kōdōkan goshinjutsu. Wristlocks are also widely used as pain compliance holds, often in police, military, and residential treatment centers.

Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes.
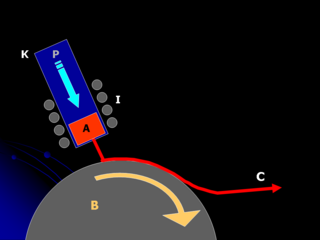
Melt spinning is a metal forming technique that is typically used to form thin ribbons of metal or alloys with a particular atomic structure.

In the sport of ten-pin bowling, there are many different ways in which to deliver the bowling ball in order to advance it toward the pins in an accurate and powerful manner. Generally, there are three basic forms of 10-pin bowling. The most basic form is known as stroking, which is the most classic form. The most powerful form is known as cranking, which imparts great leverage and maximum rotation on the ball, but sacrifices accuracy. In between the two is the domain of the tweener, who has characteristics of both, but does not truly fit into either category. A well-known variant of "tweening" is the power stroker.
A GALS screen is an examination used by doctors and other healthcare professionals to detect locomotor abnormalities and functional disability relating to gait, arms, legs and the spine.
Spinning cone columns are used in a form of low temperature vacuum steam distillation to gently extract volatile chemicals from liquid foodstuffs while minimising the effect on the taste of the product. For instance, the columns can be used to remove some of the alcohol from wine, 'off' smells from cream, and to capture aroma compounds that would otherwise be lost in coffee processing.
The rear delt raise, also known as the rear deltoid raise, or rear shoulder raise is an exercise in weight training. This exercise is an isolation exercise that heavily works the posterior deltoid muscle. The movement is primarily limited to the two shoulder joints: the glenohumeral joint and the scapulothoracic joint. Scapular movement will also cause movement in the sternoclavicular joint and acromioclavicular joint. If the elbow bends during the extension exercises, it gravitates into a rowing motion.










