Related Research Articles
Spasticity is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles.
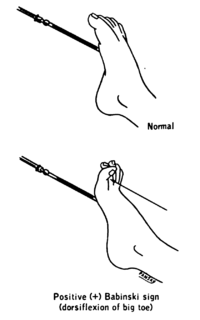
The plantar reflex is a reflex elicited when the sole of the foot is stimulated with a blunt instrument. The reflex can take one of two forms. In healthy adults, the plantar reflex causes a downward response of the hallux (flexion). An upward response (extension) of the hallux is known as the Babinski response or Babinski sign, named after the neurologist Joseph Babinski. The presence of the Babinski sign can identify disease of the spinal cord and brain in adults, and also exists as a primitive reflex in infants.

Minolta Co., Ltd. was a Japanese manufacturer of cameras, camera accessories, photocopiers, fax machines, and laser printers. Minolta Co., Ltd., which is also known simply as Minolta, was founded in Osaka, Japan, in 1928 as Nichi-Doku Shashinki Shōten. It made the first integrated autofocus 35 mm SLR camera system. In 1931, the company adopted its final name, an acronym for "Mechanism, Instruments, Optics, and Lenses by Tashima".
Clonus is a set of involuntary and rhythmic muscular contractions and relaxations. Clonus is a sign of certain neurological conditions, particularly associated with upper motor neuron lesions involving descending motor pathways, and in many cases is accompanied by spasticity. Unlike small spontaneous twitches known as fasciculations, clonus causes large motions that are usually initiated by a reflex. Studies have shown clonus beat frequency to range from three to eight Hz on average, and may last a few seconds to several minutes depending on the patient’s condition.

Joseph Jules François Félix Babinski was a French-Polish professor of neurology. He is best known for his 1896 description of the Babinski sign, a pathological plantar reflex indicative of corticospinal tract damage.
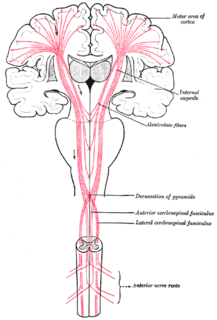
An upper motor neuron lesion Is an injury or abnormality that occurs in the neural pathway above the anterior horn cell of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. Conversely, a lower motor neuron lesion affects nerve fibers traveling from the anterior horn of the spinal cord or the cranial motor nuclei to the relevant muscle(s).

Russell's sign, named after British psychiatrist Gerald Russell, is a sign defined as calluses on the knuckles or back of the hand due to repeated self-induced vomiting over long periods of time. The condition generally arises from the afflicted's knuckles making contact with the incisor teeth during the act of inducing the gag reflex at the back of the throat with their finger(s).
Pyramidal signs indicate that the pyramidal tract is affected at some point in its course. Pyramidal tract dysfunction can lead to various clinical presentations such as spasticity, weakness, slowing of rapid alternating movements, hyperreflexia, and a positive Babinski sign.
Toe Fat were an English rock band, active from June 1969 to 1971, notable for including two future members of Uriah Heep and a future member of Jethro Tull.
Primitive reflexes are reflex actions originating in the central nervous system that are exhibited by normal infants, but not neurologically intact adults, in response to particular stimuli. These reflexes are suppressed by the development of the frontal lobes as a child transitions normally into child development. These primitive reflexes are also called infantile, infant or newborn reflexes.

Westphal's sign is the clinical correlate of the absence or decrease of patellar reflex or knee jerk. Patellar reflex or knee jerk is a kind of deep or stretch reflex where an application of a stimulus to the patellar tendon such as strike by a solid object or hammer caused the leg to extend due to such stimulus causes the quadriceps femoris muscle to contract.
The Chaddock reflex is a diagnostic reflex similar to the Babinski reflex. Chaddock's sign is present when stroking of the lateral malleolus causes extension of the great toe, indicating damage to the corticospinal tract.
The Bekhterev–Mendel reflex, also known as the Mendel reflex or Mendel–Bekhterev reflex, is a clinical sign found in patients with pyramidal tract lesions. Percussion of the dorsum of the foot causes flexion, or downward movement, of the second to the fifth toes in patients with pyramidal tract lesions, whereas percussion of the dorsum of the foot in normal patients causes extension of the toes.
Brissaud's reflex is a clinical sign in which stroking the sole of the foot elicits contraction of tensor fasciae latae. This can occur when there is no movement of the toes, and is part of the extensor plantar response.
Stransky's sign is a clinical sign in which vigorous abduction followed by the sudden release of the little toe causes an extensor plantar reflex. It is found in patients with pyramidal tract lesions, and is one of a number of Babinski-like responses.
Gonda's sign is a clinical sign in which flexing and then suddenly releasing the fourth toe elicits an extensor plantar reflex. It is found in patients with pyramidal tract lesions, and is one of a number of Babinski-like responses.
Throckmorton's reflex is a clinical sign in which pressure over the dorsal side of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe elicits a plantar reflex. It is found in patients with pyramidal tract lesions, and is one of a number of Babinski-like responses.
Rossolimo's sign is a clinical sign in which percussion of the tips of the toes causes an exaggerated flexion of the toes. It is found in patients with pyramidal tract lesions, and is one of a number of Babinski-like responses.
Schaeffer's sign is a clinical sign in which squeezing the Achilles tendon elicits an extensor plantar reflex. It is found in patients with pyramidal tract lesions, and is one of a number of Babinski-like responses.
Babinski–Nageotte syndrome is an alternating brainstem syndrome. It occurs when there is damage to the dorsolateral or posterior lateral medulla oblongata, likely syphilitic in origin. Hence it is also called the alternating medulla oblongata syndrome.
References
- ↑ Barry G. Firkin, Judith A. Whitworth. Dictionary of Medical Eponyms. Informa Health Care, 2001, page 35. ISBN 978-1-85070-333-4.