
Khartoum or Khartum is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing north from Lake Victoria, and the Blue Nile, flowing west from Lake Tana in Ethiopia. The place where the two Niles meet is known as al-Mogran or al-Muqran. From there, the Nile continues north towards Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea.

The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer. Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About 6,650 km (4,130 mi) long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Republic of the Sudan, and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt, Sudan and South Sudan. Additionally, the Nile is an important economic river, supporting agriculture and fishing.

Sudan is located in Northeast Africa. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west and Libya to the northwest. Sudan is the third largest country in Africa, after Algeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It had been the largest country on the continent until the 2011 independence of South Sudan.

The Blue Nile is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. It travels for approximately 1,450 km (900 mi) through Ethiopia and Sudan. Along with the White Nile, it is one of the two major tributaries of the Nile and supplies about 85.6% of the water to the Nile during the rainy season.

The White Nile is a river in Africa, one of the two main tributaries of the Nile, the other being the Blue Nile. The name comes from the clay sediment carried in the water that changes the water to a pale color.

The rich and varied music of Sudan has traditional, rural, northeastern African roots and also shows Arabic, Western or other African influences, especially on the popular urban music from the early 20th century onwards. Since the establishment of big cities like Khartoum as melting pots for people of diverse backgrounds, their cultural heritage and tastes have shaped numerous forms of modern popular music. In the globalized world of today, the creation and consumption of music through satellite TV or on the Internet is a driving force for cultural change in Sudan, popular with local audiences as well as with Sudanese living abroad.

Below is a list of the 18 states of the Sudan. Prior to 9 July 2011, the Republic of the Sudan was composed of 25 states. The ten southern states now form part of the independent country of South Sudan. Two additional states were created in 2012 within the Darfur region, and one in 2013 in Kordofan, bringing the total to 18.

Gezira, also spelt Al Jazirah, is one of the 18 states of Sudan. The state lies between the Blue Nile and the White Nile in the east-central region of the country. It has an area of 27,549 km2. The name comes from the Arabic word for island. Wad Madani is the capital of the state. Gezira is known as an irrigated cotton-producing state as it is a well-populated area that is suitable for agriculture.

Khartoum State is one of the eighteen states of Sudan. Although it is the smallest state by area (22,142 km2), it is the most populous - 5,274,321 in the 2008 census, and officially estimated at 7,993,900 in 2018. It contains the country's largest city by population, Omdurman, together with the cities of North Khartoum and Khartoum; the City of Khartoum is the capital of the state as well as the national capital of Sudan. The capital city contains offices of the state, governmental and non-governmental organizations, cultural institutions, and the main airport.
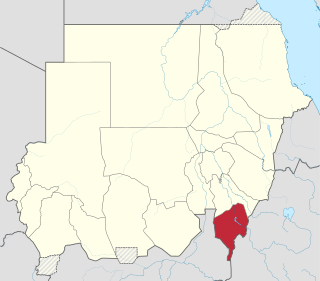
Blue Nile is one of the eighteen states of the Republic of the Sudan. It was established by presidential decree nº 3 in 1992 and it is named after the Blue Nile River.
The term Sudanese Civil War refers to at least two separate conflicts in Sudan in Northeast Africa:
Sennar typically refers to one of two adjacent cities in the eastern Sudan near the Blue Nile.

The United Nations Mission in the Sudan (UNMIS) was established by the UN Security Council under Resolution 1590 of 24 March 2005, in response to the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement between the government of the Sudan and the Sudan People's Liberation Movement on January 9, 2005 in Sudan.

The Comprehensive Peace Agreement, also known as the Naivasha Agreement, was an accord signed on January 9, 2005, by the Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM) and the Government of Sudan. The CPA was meant to end the Second Sudanese Civil War, develop democratic governance countrywide, and share oil revenues. It also set a timetable for a Southern Sudanese independence referendum.
The wazza, also referred to as al-Wazza, is a type of natural horn played in Sudanese music. The wazza is a long wind instrument, constructed by joining several wooden tubes to form an elaborate gourd trumpet, and while blown, it is also tapped for percussive effect. Characteristically, it has been used by the Berta people of the Blue Nile State in Sudan.

Sudan People's Liberation Movement–North, or SPLM–N, is a political party and militant organisation in the Republic of Sudan, based in the states of Blue Nile and South Kordofan. As of 2017, its two factions, SPLM-N (Agar) and SPLM-N (al-Hilu) were engaged in fighting each other and against the government of Sudan.

Malik Agar is a Sudanese politician and insurgent leader active in the insurgency in Blue Nile state. Since 2023 he has been the deputy chairman of the Transitional Sovereignty Council, Sudan's ruling military junta.

The Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile was an armed conflict in the Sudanese southern states of South Kordofan and Blue Nile between the Sudanese Army (SAF) and Sudan People's Liberation Movement-North (SPLM-N), a northern affiliate of the Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM) in South Sudan. After some years of relative calm following the 2005 agreement which ended the second Sudanese civil war between the Sudanese government and SPLM rebels, fighting broke out again in the lead-up to South Sudan independence on 9 July 2011, starting in South Kordofan on 5 June and spreading to the neighboring Blue Nile state in September. SPLM-N, splitting from newly independent SPLM, took up arms against the inclusion of the two southern states in Sudan with no popular consultation and against the lack of democratic elections. The conflict is intertwined with the War in Darfur, since in November 2011 SPLM-N established a loose alliance with Darfuri rebels, called Sudan Revolutionary Front (SRF).

The Sudans is a region in Northeast Africa comprising the sovereign countries of Sudan and South Sudan. Until 2011, the region was united under a state known as the Republic of the Sudan.















