Related Research Articles

The Blériot-SPAD S.34 was a French twin-seat, single-engine biplane flight training aircraft designed in 1920. The side-by-side seating arrangement was unique for its time. 150 aircraft were built, 125 for the French Air Force, who used them until 1936.

The Hanriot HD.1 was a French World War I single-seat fighter aircraft. Rejected for service with French squadrons in favour of the SPAD S.VII, the type was supplied to the Belgian Army′s Aviation Militaire Belge and the Royal Italian Army′s Corpo Aeronautico Militare, with both of which it proved highly successful. Of a total of about 1,200 examples built, 831 were produced by Italian companies under licence.

The Blériot-SPAD S.20 was a French fighter aircraft developed near the end of World War I. Too late to serve in the war, almost 100 of these aircraft equipped the French Air Force in the years immediately following. These agile aircraft were also used successfully for air racing and record-setting.

The Bleriot-SPAD S.33 was a small French airliner developed soon after World War I. The aircraft was a biplane of conventional configuration whose design owed much to the Blériot company's contemporary fighter designs such as the S.20. Four passengers could be accommodated in an enclosed cabin within the monocoque fuselage, and a fifth passenger could ride in the open cockpit beside the pilot. A great success, the S.33 dominated its field throughout the 1920s, initially on CMA's Paris-London route, and later on continental routes serviced by Franco-Roumaine.

The Blériot-SPAD S.46 was a small French airliner of the 1920s, developed from the Blériot-SPAD S.33. Like its predecessor, it was a conventional biplane that seated four passengers in an enclosed cabin while the pilot and occasionally a fifth passenger rode in an open cockpit. The S.46 had a redesigned wing of longer span and a far more powerful engine. The type was employed by Franco-Roumaine, which purchased 38 out of the 40 examples produced for use on their continental European routes.
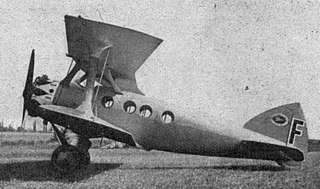
The Blériot-SPAD S.56 was a family of French airliners developed in the 1920s as various refinements of the S.33 design. All S.56 versions shared two new features: the first was a newly designed, all-metal wing, replacing the wooden wing of earlier related designs and the second was a redesigned passenger cabin, replacing the S.33's four single seats in a row with two rows of double seats. A second access door was also added.

The Blériot-SPAD S.61 was a French fighter aircraft developed in 1923. Designed by André Herbemont, the S.61 was a conventional biplane, abandoning the swept upper wing used by Herbemont in several previous designs. The prototype S.61 was evaluated by the French Air Force alongside the S.51 as a potential new fighter, but like its stablemate, was rejected. The Polish Air Force was impressed enough to order 250, as well as purchase licences for local production. The Romanian Air Force also ordered 100 aircraft. About 30 were built in Poland, by the CWL.
The Blériot-SPAD S.81 was a French fighter aircraft developed in 1923 to a requirement by the French Air Force. It was flown competitively against the Dewoitine D.1 and was selected over that aircraft due to the Dewoitine's more radical design, leading to an order for 80 aircraft. The S.81 was a single-bay biplane of conventional configuration with I-shaped interplane struts and lacking Herbemont's usual swept upper wing. It featured a wooden fuselage of monocoque construction and metal wings skinned in fabric. Production versions differed from the prototypes in having a lengthened fuselage and larger tail fin.

The SPAD S.XI or SPAD 11 was a French two-seat biplane reconnaissance aircraft of the First World War. The SPAD 11 was the work of Louis Béchereau, chief designer of the Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés (SPAD), who also designed the highly successful SPAD 7 and SPAD 13 single-seat fighter aircraft. It was developed under military specification C2, which called for a two-seat fighter aircraft. As a result of its failure to meet the levels of performance and agility demanded by the C2 specification, the SPAD 11 was used, along with the more successful Salmson 2 and Breguet 14, to replace aging Sopwith 1½ Strutter and Dorand AR reconnaissance aircraft. Persistent problems with the SPAD 11 led to its early replacement by the SPAD S.XVI or SPAD 16 variant.
The SPAD XIV was a French biplane floatplane fighter aircraft built by Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés (SPAD) and flown by the French Navy during World War I.

The Blériot-SPAD S.91 was a French light-weight fighter aircraft. It would be later developed into the Blériot-SPAD S.510, the last biplane produced by the French aeronautic industries.
The SPAD S.XV was a single-seat fighter designed and built in France and offered to fulfil a 1918 C1 specification.
The Blériot-SPAD S.41 was a French fighter aircraft developed in the early 1920s.

The SPAD S.42 was a French biplane trainer aircraft of the early 1920s, developed by Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés (SPAD) from prolific SPAD S.XIII fighter.

The SPAD S.54 was a French biplane trainer aircraft of the early 1920s, developed by Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés (SPAD).
The Blériot-SPAD S.70 was a French fighter aircraft developed in the late 1920s.
The Bleriot-SPAD S.30 was a French racer aircraft built in the early 1920s.
The Bleriot-SPAD S.36 was a French reconnaissance aircraft built in the early 1920s.
The Blériot-SPAD S.72 was a French one-seat, single-engine biplane flight training aircraft designed in the 1920s
The Blériot-SPAD S.71 was a French fighter aircraft developed in the early 1920s.
References
- ↑ "SPAD S-30 - avion de sport - Un siècle d'aviation française". aviafrance.com. Retrieved 2019-02-03.