Related Research Articles
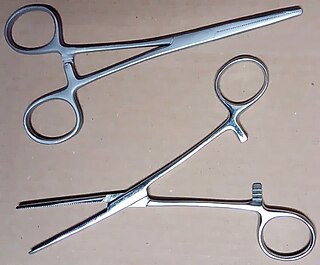
A hemostat is a tool used to control bleeding during surgery. Similar in design to both pliers and scissors, it is used to clamp exposed blood vessels shut.

Forceps are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forceps are used when fingers are too large to grasp small objects or when many objects need to be held at one time while the hands are used to perform a task. The term "forceps" is used almost exclusively in the fields of biology and medicine. Outside biology and medicine, people usually refer to forceps as tweezers, tongs, pliers, clips or clamps.

A surgical instrument is a medical device for performing specific actions or carrying out desired effects during a surgery or operation, such as modifying biological tissue, or to provide access for viewing it. Over time, many different kinds of surgical instruments and tools have been invented. Some surgical instruments are designed for general use in all sorts of surgeries, while others are designed for only certain specialties or specific procedures.
Dilation and evacuation (D&E) or dilatation and evacuation is the dilation of the cervix and surgical evacuation of the uterus after the first trimester of pregnancy. It is a method of abortion as well as a common procedure used after miscarriage to remove all pregnancy tissue.

There are many different surgical specialties, some of which require very specific kinds of surgical instruments to perform.

The coracohumeral ligament is a broad ligament of the shoulder. It attaches to the coracoid process at one end, and to the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus at the other. It strengthens the upper part of the joint capsule of the shoulder joint.

Dental instruments are tools that dental professionals use to provide dental treatment. They include tools to examine, manipulate, treat, restore, and remove teeth and surrounding oral structures.

The intertransverse ligaments are weak, sheet-like ligaments interconnecting adjacent transverse processes in the thoracic spine, and adjacent accessory processes in the lumbar spine. They act to limit lateral flexion and rotation of the spine.

The extensor retinaculum is a thickened portion of the antebrachial fascia that holds the tendons of the extensor muscles in place. It is located on the back of the forearm, just proximal to the hand. It is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament.

Howard Atwood Kelly was an American gynecologist. He obtained his B.A. degree and M.D. degree from the University of Pennsylvania. He, William Osler, William Halsted, and William Welch together are known as the "Big Four", the founding professors at the Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Maryland. He is credited with establishing gynecology as a specialty by developing new surgical approaches to gynecological diseases and pathological research. He also developed several medical innovations, including the improved cystoscope, Kelly's clamp, Kelly's speculum, and Kelly's forceps. Because Kelly was a famous prohibitionist and Fundamentalist Christian, many of his contemporaries expressed skepticism towards his medical professionalism.

Obstetrical forceps are a medical instrument used in childbirth. Their use can serve as an alternative to the ventouse method.

The artery of the round ligament of the uterus, also known as Sampson's artery, is a branch of the inferior epigastric artery. It runs under, and supplies, the round ligament of the uterus. It constitutes an anastomosis of the uterine artery and ovarian artery. It was originally named after John A. Sampson (1873–1946), an American gynecologist who studied endometriosis.

The following is a list of instruments that are used in modern obstetrics and gynaecology.

Ovarian torsion (OT) or adnexal torsion is an abnormal condition where an ovary twists on its attachment to other structures, such that blood flow is decreased. Symptoms typically include pelvic pain on one side. While classically the pain is sudden in onset, this is not always the case. Other symptoms may include nausea. Complications may include infection, bleeding, or infertility.

A tenaculum is a surgical instrument, usually classified as a type of forceps. It consists of a slender sharp-pointed hook attached to a handle and is used mainly in surgery for seizing and holding parts, such as blood vessels.
The Manchester operation, Manchester repair or simply Fothergill operation is a technique used in gynaecologic surgeries. It is an operation for uterine prolapse by fixation of the cardinal ligaments. Its purpose is to reduce the cystourethrocele and to reposition the uterus within the pelvis. The major steps of the intervention are listed below:
- Preliminary dilatation and curettage
- Amputation of cervix
- strengthening the cervix by suturing cut end of Mackenrodt ligament in front of cervix
- Anterior colporrhaphy
- Posterior colpoperineorrhaphy

An Allis clamp is a commonly used surgical instrument. It was invented by Oscar Allis.

William Francis Victor Bonney FRCP FRCS was a prominent British gynaecological surgeon. He was described by Geoffrey Chamberlain as "a primary influence on world gynaecology in the years between the wars".
The Bonney myomectomy clamp is a surgical clamp developed in the interwar years by gynaecologist Victor Bonney to provide a blood free environment when performing a myomectomy to remove uterine fibroids. It allowed the conservation of the uterus and the resulting preservation of fertility in women of reproductive age who wished to have children. It is seldom used now.
An invasive test is a type of medical procedure that requires trained medical providers to use instruments that cut skin or that are inserted into a body opening. Examples of invasive tests include biopsy, excision, cryotherapy, and endoscopy.
References
- ↑ Vimee, Bindra (2011). Practical Manual of Obstetrics and Gynecology for Residents and Fellows. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Pvt. Ltd. p. 133. ISBN 9789350252284.
- ↑ "2. Principle of Surgery". Uterus - displacements : a colour atlas of cervicopexy (Purandare's). Nagrath, Arun., Malhotra, Narendra. New Delhi. 2012. p. 4. ISBN 9789350259757. OCLC 870339882.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link)