Kerberos is a computer-network authentication protocol that works on the basis of tickets to allow nodes communicating over a non-secure network to prove their identity to one another in a secure manner. The protocol was named after the character Kerberos from Greek mythology, the ferocious three-headed guard dog of Hades. Its designers aimed it primarily at a client–server model and it provides mutual authentication—both the user and the server verify each other's identity. Kerberos protocol messages are protected against eavesdropping and replay attacks.

A subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module (SIM), widely known as a SIM card, is an integrated circuit that is intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices. It is also possible to store contact information on many SIM cards. SIM cards are always used on GSM phones; for CDMA phones, they are needed only for LTE-capable handsets. SIM cards can also be used in satellite phones, smart watches, computers, or cameras.
Non-access stratum (NAS) is a functional layer in the UMTS and LTE wireless telecom protocol stacks between the core network and user equipment. This layer is used to manage the establishment of communication sessions and for maintaining continuous communications with the user equipment as it moves. The NAS is defined in contrast to the Access Stratum which is responsible for carrying information over the wireless portion of the network. A further description of NAS is that it is a protocol for messages passed between the User Equipment, also known as mobiles, and Core Nodes that is passed transparently through the radio network. Examples of NAS messages include Update or Attach messages, Authentication Messages, Service Requests and so forth. Once the User Equipment (UE) establishes a radio connection, the UE uses the radio connection to communicate with the core nodes to coordinate service. The distinction is that the Access Stratum is for dialogue explicitly between the mobile equipment and the radio network and the NAS is for dialogue between the mobile equipment and core network nodes. For LTE, the Technical Standard for NAS is 3GPP TS 24.301.
+- – - – - -+ +- – - – - – -+ | HTTP | | Application | +- – - – - -+ +- – - – - – -+ | TCP | | Transport | +- – - – - -+ +- – - – - – -+ | IP | | Internet | +- – - – - -+ +- – - – - – -+ | NAS | | Network | +- – - – - -+ +- – - – - – -+ | AS | | Link | +- – - – - -+ +- – - – - – -+ | Channels | | Physical | +- – - – - -+ +- – - – - – -+
The GPRS core network is the central part of the general packet radio service (GPRS) which allows 2G, 3G and WCDMA mobile networks to transmit IP packets to external networks such as the Internet. The GPRS system is an integrated part of the GSM network switching subsystem.
Network switching subsystem (NSS) is the component of a GSM system that carries out call out and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations. It is owned and deployed by mobile phone operators and allows mobile devices to communicate with each other and telephones in the wider public switched telephone network (PSTN). The architecture contains specific features and functions which are needed because the phones are not fixed in one location.
Diameter is an authentication, authorization, and accounting protocol for computer networks. It evolved from the earlier RADIUS protocol. It belongs to the application layer protocols in the internet protocol suite.
The IP Multimedia Subsystem or IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) is an architectural framework for delivering IP multimedia services. Historically, mobile phones have provided voice call services over a circuit-switched-style network, rather than strictly over an IP packet-switched network. Alternative methods of delivering voice (VoIP) or other multimedia services have become available on smartphones, but they have not become standardized across the industry. IMS is an architectural framework to provide such standardization.
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is an authentication framework frequently used in network and internet connections. It is defined in RFC 3748, which made RFC 2284 obsolete, and is updated by RFC 5247. EAP is an authentication framework for providing the transport and usage of material and parameters generated by EAP methods. There are many methods defined by RFCs and a number of vendor specific methods and new proposals exist. EAP is not a wire protocol; instead it only defines the information from the interface and the formats. Each protocol that uses EAP defines a way to encapsulate by the user EAP messages within that protocol's messages.
Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA) is a security protocol used in 3G networks. AKA is also used for one-time password generation mechanism for digest access authentication. AKA is a challenge-response based mechanism that uses symmetric cryptography.
The IEEE 802.21 refers to Media Independent Handoff (MIH) and is an IEEE standard published in 2008. The standard supports algorithms enabling seamless handover between wired and wireless networks of the same type as well as handover between different wired and wireless network types also called Media independent handover (MIH) or vertical handover. Vertical handover was first introduced by Mark Stemn and Randy Katz at U C Berkeley. The standard provides information to allow handing over to and from wired 802.3 network to wireless 802.11, 802.15, 802.16, 3GPP and 3GPP2 networks through different handover mechanisms.
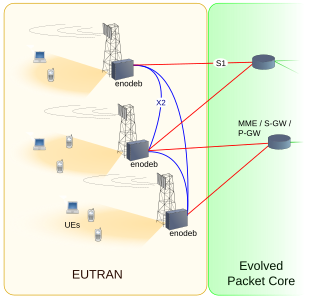
E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) Terrestrial Radio Access, also referred to as the 3GPP work item on the Long Term Evolution (LTE) also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the initialism of Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network and is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and E-UTRAN Node B or Evolved Node B (EnodeB).
Generic Authentication Architecture (GAA) is a standard made by 3GPP defined in TR 33.919. Taken from the document:
"This Technical Report aims to give an overview of the different mechanisms that mobile applications can rely upon for authentication between server and client. Additionally it provides guidelines related to the use of GAA and to the choice of authentication mechanism in a given situation and for a given application".
System Architecture Evolution (SAE) is the core network architecture of 3GPP's LTE wireless communication standard.

Video Share is an IP Multimedia System (IMS) enabled service for mobile networks that allows users engaged in a circuit switch voice call to add a unidirectional video streaming session over the packet network during the voice call. Any of the parties on the voice call can initiate a video streaming session. There can be multiple video streaming sessions during a voice call, and each of these streaming sessions can be initiated by any of the parties on the voice call. The video source can either be the camera on the phone or a pre-recorded video clip.

Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA) is a technology that enables the authentication of a user. This authentication is possible if the user owns a valid identity on an HLR or on an HSS.
Mobile data offloading is the use of complementary network technologies for delivering data originally targeted for cellular networks. Offloading reduces the amount of data being carried on the cellular bands, freeing bandwidth for other users. It is also used in situations where local cell reception may be poor, allowing the user to connect via wired services with better connectivity.
Access network discovery and selection function (ANDSF) is an entity within an evolved packet core (EPC) of the system architecture evolution (SAE) for 3GPP compliant mobile networks. The purpose of the ANDSF is to assist user equipment (UE) to discover non-3GPP access networks – such as Wi-Fi or WIMAX – that can be used for data communications in addition to 3GPP access networks and to provide the UE with rules policing the connection to these networks.
IMS is a set of specifications to offer multimedia services through IP protocol. This makes it possible to incorporate all kinds of services, such as voice, multimedia and data, on an accessible platform through any Internet connection.
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is the signaling protocol selected by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) to create and control multimedia sessions with two or more participants in the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS), and therefore is a key element in the IMS framework.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.




