Related Research Articles

New Britain is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan.
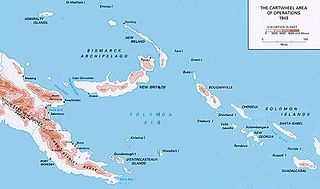
Operation Cartwheel was a major military operation for the Allies in the Pacific theatre of World War II. Cartwheel was an operation aimed at neutralising the major Japanese base at Rabaul. The operation was directed by the Supreme Allied Commander in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA), General Douglas MacArthur, whose forces had advanced along the northeast coast of New Guinea and occupied nearby islands. Allied forces from the South Pacific Area, under Admiral William Halsey, advanced through the Solomon Islands toward Bougainville. The Allied forces involved were from Australia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the US, and various Pacific Islands.

The bombing of Rabaul in November 1943 was an air attack conducted by the Allies of World War II upon a cruiser force at the major Japanese base of Rabaul. In response to the Allied invasion of Bougainville, the Japanese had brought a strong cruiser force down to Rabaul from Truk, their major naval base in the Caroline Islands about 800 miles north of Rabaul in preparation for a night engagement against the Allied supply and support shipping. Allied carrier- and land-based planes attacked the Japanese ships, airfields, and port facilities on the island of New Britain to protect the Allied amphibious invasion of Bougainville. As a result of the Rabaul raids, the Japanese naval forces could no longer threaten the landings. The success of the raid began to change the strongly held belief that carrier-based air forces could not challenge land-based air forces.

The Battle of Rabaul, also known by the Japanese as Operation R, an instigating action of the New Guinea campaign, was fought on the island of New Britain in the Australian Territory of New Guinea, from 23 January into February 1942. It was a strategically significant defeat of Allied forces by Japan in the Pacific campaign of World War II, with the Japanese invasion force quickly overwhelming the small Australian garrison, the majority of which was either killed or captured. Hostilities on the neighbouring island of New Ireland are usually considered to be part of the same battle. Rabaul was significant because of its proximity to the Japanese territory of the Caroline Islands, site of a major Imperial Japanese Navy base on Truk.

The Rabaul caldera, or Rabaul Volcano, is a large volcano on the tip of the Gazelle Peninsula in East New Britain, Papua New Guinea, and derives its name from the town of Rabaul inside the caldera. The caldera has many sub-vents, Tavurvur being the most well known for its devastating eruptions over Rabaul. The outer flanks of the highest peak, a 688-metre-high asymmetrical pyroclastic shield, are formed by thick pyroclastic flow deposits. There is no sign of a pyroclastic shield along the rim of the caldera, making the location likely underwater, on the caldera's floor.

The Solomon Islands campaign was a major campaign of the Pacific War of World War II. The campaign began with Japanese landings and capture of several areas in the British Solomon Islands and Bougainville, in the Territory of New Guinea, during the first six months of 1942. The Japanese occupied these locations and began the construction of several naval and air bases with the goals of protecting the flank of the Japanese offensive in New Guinea, establishing a security barrier for the major Japanese base at Rabaul on New Britain, and providing bases for interdicting supply lines between the Allied powers of the United States and Australia and New Zealand.

The New Britain campaign was a World War II campaign fought between Allied and Imperial Japanese forces. The campaign was initiated by the Allies in late 1943 as part of a major offensive which aimed to neutralise the important Japanese base at Rabaul, the capital of New Britain, and was conducted in two phases between December 1943 and the end of the war in August 1945.
I-177 was an Imperial Japanese Navy Kaidai-type cruiser submarine of the KD7 subclass commissioned in 1942. She served during World War II, patrolling off Australia, taking part in the New Guinea campaign, operating in the North Pacific, and participating in the Palau campaign before she was sunk by the destroyer escort USS Samuel S. Miles (DE-183) in 1944, with no survivors.
Vunakanau Airfield was an aerodrome located near Vunakanau, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. The airfield was constructed as a Royal Australian Air Force aerodrome and consisted of an unpaved single runway during World War II. The airfield was captured during the battle of Rabaul in 1942 by the Imperial Japanese and was extensively modified and expanded. Vunakanau was later neutralized by Allied air bombing in May 1944.

Operation RY was the Imperial Japanese plan to invade and occupy Nauru and Ocean islands in the south Pacific during the Pacific conflict of World War II. The operation was originally set to be executed in May 1942 immediately following Operation MO and before Operation MI, which resulted in the Battle of Midway. The primary reason for the operation was to exploit the islands' supplies of phosphate. After a postponement due to interference by enemy forces, the operation was completed in August 1942.
Vunakanau is situated on a plateau just outside Rabaul, Papua New Guinea. Vunakanau Airfield was used in World War II. In the 1970s Vunakau was proposed to be used as the new airstrip replacing Rabaul however this did not eventuate.

Lakunai Airfield, later known as Rabaul Airport, was an aerodrome located near Rabaul, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. It was located at the foot of Tavurvur volcano, near Matupit Island. The airport was destroyed by the 1994 eruption that destroyed the town of Rabaul and subsequently a new airport was built and opened at Tokua, on the opposite side of the Rabaul caldera. The former airport was located at 04°13′S152°11′E.
Rapopo Airfield was an aerodrome located at Lesson Point, Blanche Bay near Rabaul, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. The airfield was constructed by the Imperial Japanese during World War II in December 1942. Rapopo was later neutralized by Allied air bombing from 1944. The airfield was abandoned after the cessation of hostilities.
Tobera airfield was an aerodrome located near Tobera, near Keravat, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. The airfield was constructed by the imperial Japan during World War II. Tobera was later neutralized by Allied air bombing from 1944. The airfield was abandoned after the cessation of hostilities.

Kerevat Airfield was an aerodrome located near Kerevat, East New Britain province, Papua New Guinea. Situated on the northern coast, it was 13 miles (21 km) south west of Rabaul. The airfield was constructed by the Imperial Japanese in World War II during September 1943. Kerevat Airfield was neutralized by Allied Powers' air bombing from 1944, who ran missions on the airfield between June 20, 1943, and May 16, 1944. The airfield was abandoned after the cessation of hostilities; however, the airstrip is still visible.

The Warangoi River also known as the Adler River, is a river located in the eastern part of the Gazelle Peninsula in the north-eastern part of New Britain, Papua New Guinea. It flows past the village of Warangoi and out into the Warangoi Bay. It played a part in the Battle of Rabaul early in 1942. Lieutenant Colonel Ishiro Kuwada's men of the 3rd Infantry Battalion captured at least 200 Australian men between the Warangoi River and Vunakanau. Virgin rainforest lies along the river basin.

The neutralisation of Rabaul was an Allied campaign to render useless the Imperial Japanese base at Rabaul in eastern New Britain, Papua New Guinea. Japanese forces landed on Rabaul on 23 January 1942, capturing it by February 1942, after which the harbor and town were transformed into a major Japanese naval and air installation. The Japanese heavily relied on it, using it as a launching point for Japanese reinforcements to New Guinea and Guadalcanal. Throughout the Solomon Islands campaign, neutralizing Rabaul became the primary objective of the Allied effort in the Solomons.
I-4 was an Imperial Japanese Navy J1 type submarine commissioned in 1929. She was a large cruiser submarine that served in the Second Sino-Japanese War and World War II. During the latter conflict she operated in support of the attack on Pearl Harbor, conducted anti-shipping patrols in the Indian Ocean, supported the Indian Ocean raid, and took part in the Aleutian Islands campaign, Guadalcanal campaign, and New Guinea campaign before she was sunk in December 1942.

The Japanese occupation of the Solomon Islands was the period in the history of Solomon Islands between 1942 and 1945 when Imperial Japanese forces occupied Solomon Islands during World War II.
Ro-100 was an Imperial Japanese Navy Ro-100-class submarine. Completed and commissioned in September 1942, she served in World War II, operating in the Solomon Islands, Rabaul, and New Guinea areas. She sank in November 1943 when she struck a mine during her seventh war patrol.
References
- Sakaida, Henry (1996). The Siege of Rabaul. St. Paul, MN, USA: Phalanx. ISBN 1-883809-09-6.
- Gamble, Bruce (2006). Darkest Hour: The True Story of Lark Force at Rabaul. St. Paul, Minnesota: Zenith Imprint. ISBN 0-7603-2349-6.