| Abbreviation | MXP |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1996 |
| Location | Boston, United States |
| Website | www.bmxp.net |
| Peers | 8 As of August 2009 [update] |
| Peak | 40 Mbit/s As of August 2009 [update] |
| Daily (avg.) | 40 Mbit/s As of August 2009 [update] |
The Boston MXP was an Internet Exchange Point in Boston, Massachusetts and Quincy, Massachusetts. It was founded by MAI in 1996. It supports 10 megabit and 100 megabit connections on copper, and gigabit connections on fiber. Global NAPs, the main sponsor of the Boston MXP, was sold on February 29, 2012. The Boston MXP is no longer operational and was replaced by the Boston Internet Exchange.

In computer networking, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a data link layer communication protocol between two routers directly without any host or any other networking in between. It can provide loop detection, authentication, transmission encryption, and data compression.

Ethernet over twisted-pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. They are a subset of all Ethernet physical layers.

A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a computer network that interconnects users with computer resources in a geographic region of the size of a metropolitan area. The term MAN is applied to the interconnection of local area networks (LANs) in a city into a single larger network which may then also offer efficient connection to a wide area network. The term is also used to describe the interconnection of several LANs in a metropolitan area through the use of point-to-point connections between them.

The London Internet Exchange (LINX) is a mutually governed Internet exchange point (IXP) providing peering services and public policy representation to network operators, encompassing over 950 different autonomous systems (ASNs). Established in 1994 in London, LINX operates IXPs in London, Manchester, Scotland, and Wales in the United Kingdom, as well as in Northern Virginia, United States.

In telecommunications, broadband or high speed is the wide-bandwidth data transmission that exploits signals at a wide spread of frequencies or several different simultaneous frequencies, and is used in fast Internet access. The transmission medium can be coaxial cable, optical fiber, wireless Internet (radio), twisted pair cable, or satellite.
The megabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information. The prefix mega (symbol M) is defined in the International System of Units (SI) as a multiplier of 106 (1 million), and therefore

JFK/UMass station is a Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) intermodal transfer station, located adjacent to the Columbia Point area of Dorchester, Boston, Massachusetts. It is served by the rapid transit Red Line; the Greenbush Line, Kingston/Plymouth Line, and Middleborough/Lakeville Line of the MBTA Commuter Rail system, and three MBTA bus routes. The station is named for the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum and the University of Massachusetts Boston, both located nearby on Columbia Point.

State station is an underground Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) rapid transit station located in downtown Boston, Massachusetts. It is the transfer point between the Orange Line and the Blue Line, and one of four "hub stations" on the MBTA subway system. The Orange Line has two side platforms on two levels, while the Blue Line has two side platforms on a single level. The station is fully accessible.

Boston College station is a light rail station on the MBTA Green Line B branch. It is located at St. Ignatius Square on the Boston College campus near the intersection of Commonwealth Avenue and Lake Street, on the border between the Brighton neighborhood of Boston and the Chestnut Hill neighborhood of Newton, Massachusetts. Originally opened in 1896, it has been the terminus of the Commonwealth Avenue line since 1900. The current station is planned to be replaced by a new station located in the median of Commonwealth Avenue just east of Lake Street.

Bragg Communications Inc., doing business as Eastlink, is a Canadian cable television and telecommunications company. The privately held company was founded in Nova Scotia in 1969 by the Bragg family, and has grown since through the amalgamation of several telecommunications companies.
A dedicated hosting service, dedicated server, or managed hosting service is a type of Internet hosting in which the client leases an entire server not shared with anyone else. This is more flexible than shared hosting, as organizations have full control over the server(s), including choice of operating system, hardware, etc.
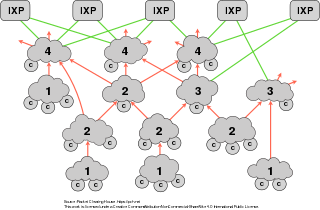
Internet transit is the service of allowing network traffic to cross or "transit" a computer network, usually used to connect a smaller Internet service provider (ISP) to the larger Internet. Technically, it consists of two bundled services:

A digital subscriber line (DSL) modem is a device used to connect a computer or router to a telephone line which provides the digital subscriber line (DSL) service for connection to the Internet, which is often called DSL broadband. The modem connects to a single computer or router, through an Ethernet port, USB port, or is installed in a computer PCI slot.

The Toronto Internet Exchange Community (TorIX) is a not-for-profit Internet Exchange Point (IXP) located in a carrier hotel at 151 Front Street West, Equinix's TR2 data centre at 45 Parliament Street and 905 King Street West in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. As of March 2021, TorIX has 259 unique autonomous systems representing 285 peer connections and peak traffic rates of 1.344 Tbps, making it the largest IXP in Canada. According to Wikipedia's List of Internet Exchange Points by Size, TorIX is the 16th largest IXP in the world in numbers of peers, and 17th in the world in traffic averages. The Exchange is organized and run by industry professionals in voluntary capacity.
MXP may refer to:
In telecommunications, data transfer rate is the average number of bits (bitrate), characters or symbols (baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are multiples of bits per second (bit/s) and bytes per second (B/s). For example, the data rates of modern residential high-speed Internet connections are commonly expressed in megabits per second (Mbit/s).
Microwave Bypass, Inc. launched the world's first fixed wireless internet access technology in 1987, a decade before Wi-Fi. It enabled local and remote networks to connect at the then full Ethernet (802.3) data rate of 10 megabits per second, and for up to 4.3 miles.

A mobile broadband modem, also known as wireless modem or cellular modem, is a type of modem that allows a personal computer or a router to receive wireless Internet access via a mobile broadband connection instead of using telephone or cable television lines. A mobile Internet user can connect using a wireless modem to a wireless Internet Service Provider (ISP) to get Internet access.
The Boston Internet Exchange is an Internet exchange point in Boston, Massachusetts, USA. The Boston IX is owned and operated by Markley Group, hosted in Markley's One Summer Street, Boston datacenter and their Prince Avenue, Lowell datacenter.

Stockholm Internet eXchange (STHIX) manages multiple carrier- and data center-neutral internet exchange point (IXP) situated in Copenhagen / Malmö, Gothenburg, Stockholm, Sundsvall, and Umeå. The Stockholm IXP is the second largest IXP in the region in terms of both bandwidth (average/peak) and number of members. Peak bandwidth is above 230 gigabits per second.