Boulder coral may refer to:
- Boulder brain corals of the genus Colpophyllia
- Boulder star coral, two species of coral
Boulder coral may refer to:

Bouldering is a form of rock climbing that is performed on small rock formations or artificial rock walls without the use of ropes or harnesses. While bouldering can be done without any equipment, most climbers use climbing shoes to help secure footholds, chalk to keep their hands dry and to provide a firmer grip, and bouldering mats to prevent injuries from falls. Unlike free solo climbing, which is also performed without ropes, bouldering problems are usually less than six metres (20 ft) tall. Traverses, which are a form of boulder problem, require the climber to climb horizontally from one end to another. Artificial climbing walls allow boulderers to climb indoors in areas without natural boulders. In addition, bouldering competitions take place in both indoor and outdoor settings.

A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.

Cobra is the common name of various venomous snakes, most of which belong to the genus Naja.

Coral Castle is an oolite limestone structure created by the Latvian-American eccentric Edward Leedskalnin (1887–1951). It comprises numerous large stones, each weighing several tons, sculpted into a variety of shapes, including slab walls, tables, chairs, a crescent moon, a water fountain and a sundial.

Montastraea is a genus of colonial stony coral found in the Caribbean seas. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Montastraeidae and contains a single species, Montastraea cavernosa, known as great star coral. It forms into massive boulders and sometimes develops into plates. Its polyps are the size of a human thumb and fully extend at night.

Ko Tao is an island in Thailand and is part of the Chumphon Archipelago on the western shore of the Gulf of Thailand. It covers an area of about 21 km2. Administratively it is a subdistrict (tambon) of Ko Pha-ngan District (amphoe) of Surat Thani Province. As of 2006, its official population was 1,382. The main settlement is Ban Mae Haad.

Brain coral is a common name given to various corals in the families Mussidae and Merulinidae, so called due to their generally spheroid shape and grooved surface which resembles a brain. Each head of coral is formed by a colony of genetically identical polyps which secrete a hard skeleton of calcium carbonate; this makes them important coral reef builders like other stony corals in the order Scleractinia. Brain corals are found in shallow warm water coral reefs in all the world's oceans. They are part of the phylum Cnidaria, in a class called Anthozoa or "flower animals". The lifespan of the largest brain corals is 900 years. Colonies can grow as large as 1.8 m (6 ft) or more in height.

Black band disease is a coral disease in which corals develop a black band. It is characterized by complete tissue degradation due to a pathogenic microbial consortium. The mat is present between apparently healthy coral tissue and freshly exposed coral skeleton.

Stromatoporoidea is an extinct clade of sea sponges common in the fossil record from the Middle Ordovician to the Late Devonian. They can be characterized by their densely layered calcite skeletons lacking spicules. Stromatoporoids were among the most abundant and important reef-builders of their time, living close together in flat biostromes or elevated bioherms on soft tropical carbonate platforms.

The Rowley Shoals is a group of three atoll-like coral reefs south of the Timor Sea, about 260 km (160 mi) west of Broome on the northwestern Australian coast, centred on 17°20′S119°20′E, on the edge of one of the widest continental shelves in the world. Each atoll covers an area of around 80 to 90 km2 within the rim of the reef, including the lagoons, while the land areas are negligible. They belong to Western Australia. They all rise steeply from the surrounding ocean floor. To the northeast lie the Scott and Seringapatam Reefs which are located on the same undersea platform.

The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) is an environmental non-profit, 501(c)(3) non-governmental organization based in Oakland, California that is dedicated to coral reef conservation. The organization was founded in 1994 by Stephen Colwell.

Sessility is the biological property of an organism describing its lack of a means of self-locomotion. Sessile organisms for which natural motility is absent are normally immobile. This is distinct from the botanical concept of sessility, which refers to an organism or biological structure attached directly by its base without a stalk.
Boulder star coral may refer to two different species of coral:

Colpophyllia is a genus of stony corals in the family Mussidae. It is monotypic with a single species, Colpophyllia natans, commonly known as boulder brain coral or large-grooved brain coral. It inhabits the slopes and tops of reefs, to a maximum depth of 50 metres (164 ft). It is characterised by large, domed colonies, which may be up to 2 metres across, and by the meandering network of ridges and valleys on its surface. The ridges are usually brown with a single groove, and the valleys may be tan, green, or white and are uniform in width, typically 2 centimetres (0.8 in). The polyps only extend their tentacles at night.
Ophidiaster granifer, the grained seastar, is a species of starfish in the family Ophidiasteridae. It is found in the Red Sea and the Indo-Pacific and is the only known species of starfish to reproduce by parthenogenesis.
USA Climbing is the national governing body of the sport of competition climbing in the United States. As a 501(c)3 non-profit, they promote Sport Climbing which comprises three competition disciplines: bouldering, lead climbing, and speed climbing, in elite, youth and collegiate formats.

Orbicella faveolata, commonly known as mountainous star coral, is a colonial stony coral in the family Merulinidae. Orbicella faveolata is native to the coral coast of the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico and is listed as "endangered" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. O. faveolata was formerly known as Montastraea faveolata.
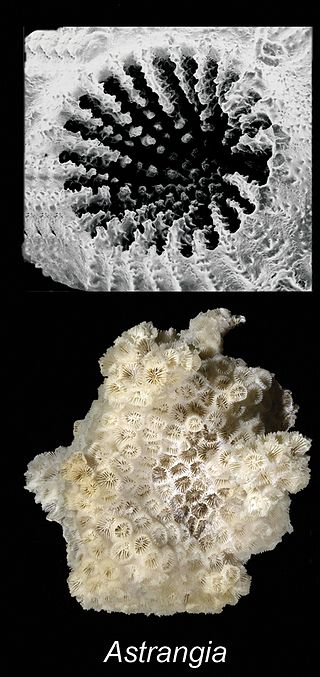
Astrangia poculata, the northern star coral or northern cup coral, is a species of non-reefbuilding stony coral in the family Rhizangiidae. It is native to shallow water in the western Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. It is also found on the western coast of Africa. The International Union for Conservation of Nature lists this coral as being of "least concern". Astrangia poculata is an emerging model organism for corals because it harbors a facultative photosymbiosis, is a calcifying coral, and has a large geographic range. Research on this emerging model system is showcased annually by the Astrangia Research Working Group, collaboratively hosted by Roger Williams University, Boston University, and Southern Connecticut State University
Astrangia solitaria, the dwarf cup coral or southern cup coral, is a species of stony coral in the family Rhizangiidae. It is native to shallow water in the western Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.

Stony coral tissue loss disease (SCTLD) is a disease of corals that first appeared off the southeast coast of Florida in 2014. It originally was described as white plague disease. By 2019 it had spread along the Florida Keys and had appeared elsewhere in the Caribbean Sea. The disease destroys the soft tissue of at least 22 species of reef-building corals, killing them within weeks or months of becoming infected. The causal agent is unknown but is suspected to be either a bacterium or a virus with a bacterium playing a secondary role. The degree of susceptibility of a coral, the symptoms, and the rate of progression of the disease vary between species. Due to its rapid spread, high mortality rate, and lack of subsidence, it has been regarded as the deadliest coral disease ever recorded, with wide-ranging implications for the biodiversity of Caribbean coral reefs.