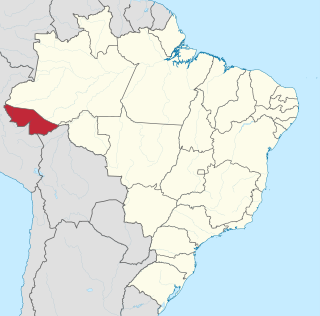
Acre is a state located in the west of the North Region of Brazil and the Amazonia Legal. Located in the westernmost part of the country, at a two-hour time difference from Brasília, Acre is bordered clockwise by the Brazilian states of Amazonas and Rondônia to the north and east, along with an international border with the Bolivian department of Pando to the southeast, and the Peruvian regions of Madre de Dios, Ucayali and Loreto to the south and west. Its capital and largest city is Rio Branco. Other important places include Cruzeiro do Sul, Sena Madureira, Tarauacá and Feijó. The state, which has 0.42% of the Brazilian population, generates 0.2% of the Brazilian GDP.

Rio Branco is a Brazilian municipality, capital of the state of Acre. Located in the valley of the Acre River in northern Brazil, it is the most populous municipality in the state, with 387,852 inhabitants, according to 2024 IBGE estimates, almost half the state population. Rio Branco was one of the first settlements to develop in the region, being the westernmost major settlement in the country and the 4th-oldest state capital city in Northern Brazil, after Belém, Manaus and Macapá.

José Maria da Silva Paranhos Júnior, Baron of Rio Branco was a Brazilian noble, diplomat, geographer, historian, politician and professor, considered to be the "father of Brazilian diplomacy". He was the son of statesman José Paranhos, Viscount of Rio Branco. The Baron of Rio Branco was a member of the Brazilian Academy of Letters, occupying its 34th chair from 1898 until his death in 1912. As a representative of Brazil, he managed to peacefully resolve all Brazil's border disputes with its South American neighbours and incorporate 900 thousand square kilometers through his diplomacy alone.

The North Region of Brazil is the largest region of Brazil, accounting for 45.27% of the national territory. It has the second-lowest population of any region in the country, and accounts for a minor percentage of the national GDP. The region is slightly larger than India and slightly smaller than the whole European Union. It comprises the states of Acre, Amapá, Amazonas, Pará, Rondônia, Roraima, and Tocantins.

Pato Branco is a municipality in the state of Paraná in Brazil. The municipality covers 537,8 km2 (206.7 mi2) and has a population of 83,843. Pato Branco started off as a village in 1942 and was given status as a city December 14, 1952. It has two private colleges, Faculdade Mater Dei and Faculdade de Pato Branco, and a campus of the Federal University of Technology - Paraná. The city has experienced a positive economic development throughout the last few years.
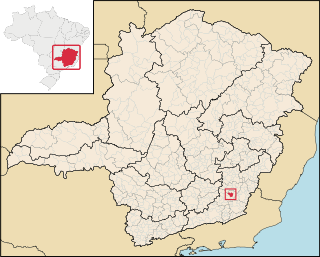
Visconde do Rio Branco is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Minas Gerais. As of 2020 its population is estimated to be 42,965.
The brown-backed bearded saki is one of five species of bearded saki, a type of New World monkey. It is endemic to the Amazon in north-western Brazil and southern Venezuela. It is possible the correct scientific name for this species is C. chiropotes, in which case the more easterly red-backed bearded saki would be named C. sagulatus. The IUCN lists the reddish-brown bearded saki as a valid species, with C. israelita as a synonym, but also notes they might both be valid.
Rio Branco or Río Branco may refer to:

Rio Branco Football Club, commonly referred to as Rio Branco, is a Brazilian professional club based in Rio Branco, Acre founded on 8 June 1919. It competes in the Campeonato Acreano, the top flight of the Acre state football league.

Brasiléia is a Brazilian municipality located in the northern state of Acre. Its population in 2020 was estimated at 26,702 inhabitants. Its area is 336,189 km2. Located 237 km south of Rio Branco on the border with Bolivia, Brasiléia borders the municipalities Epitaciolândia, Assis Brasil, Sena Madureira and Xapuri.

Estádio José de Melo, sometimes called Stadium José de Melo, is a multi-use stadium located in Rio Branco, Brazil. It is used mostly for football matches and as the training ground of Rio Branco Football Club. The stadium has a maximum capacity of 2,000 people and was built in 1929. The stadium is owned by Rio Branco Football Club and is named after the commissioner José Francisco de Melo, who is a former player and former president of Rio Branco Football Club. He also donated the groundplot where the stadium was built.

Cruzeiro do Sul is a municipality located on the Juruá river in the west of the Brazilian state of Acre. It is the second-largest city in Acre.

Plácido de Castro is a municipality located in the east of the Brazilian state of Acre on the border with Bolivia.

Porto Acre is a municipality located in the northeast of the Brazilian state of Acre. The economy is mainly based on agriculture. As of 2020 the municipality had an estimated population of 18,824.

Xapuri is a municipality located in the southeast of the Brazilian state of Acre. It was the scene of an early bloodless victory during the war to make Acre independent of Bolivia. The town is known as the birthplace of the rubber tapper and environmentalist Chico Mendes and of the surgeon and professor Adib Jatene.

The Republic of Acre or the Independent State of Acre was a secessionist republic that emerged in then Bolivia's Acre region between 1899 and 1903. The region was eventually annexed by Brazil in 1903 following the Acre War and is now the State of Acre.

The Acre War, known in Brazil as Acrean Revolution and in Spanish as Guerra del Acre was a border conflict between Bolivia and Brazil over the Acre Region, which was rich in rubber and gold deposits. The conflict had two phases between 1899 and 1903 and ended with an Acrean victory and the subsequent Treaty of Petrópolis, which ceded Acre to Brazil. The outcome also affected territories disputed with Peru.

The Roman Catholic Diocese of Rio Branco is a Latin suffragan see in the ecclesiastical province of the Metropolitan Archbishop of Porto Velho (Rondônia), in the upper Amazon River basin).

Events in the year 1965 in Brazil.

José Plácido de Castro was a Brazilian soldier, surveyor, rubber producer and politician who led the armed revolt during the Acre War of 1902–3, when the Republic of Acre broke away from Bolivia. He was the president of the state of Acre just before and after it was purchased by Brazil. After the war he became extremely wealthy as a rubber producer, and made many enemies. He was assassinated in 1908. He is considered a hero of Brazil.



















