An international standard is a technical standard developed by one or more international standards organizations. International standards are available for consideration and use worldwide. The most prominent such organization is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Other prominent international standards organizations including the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Together, these three organizations have formed the World Standards Cooperation alliance.
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) or standard conditions for temperature and pressure are various standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements used to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), although these are not universally accepted. Other organizations have established a variety of other definitions.
A standards organization, standards body, standards developing organization (SDO), or standards setting organization (SSO) is an organization whose primary function is developing, coordinating, promulgating, revising, amending, reissuing, interpreting, or otherwise contributing to the usefulness of technical standards to those who employ them. Such an organization works to create uniformity across producers, consumers, government agencies, and other relevant parties regarding terminology, product specifications, protocols, and more. Its goals could include ensuring that Company A's external hard drive works on Company B's computer, an individual's blood pressure measures the same with Company C's sphygmomanometer as it does with Company D's, or that all shirts that should not be ironed have the same icon on the label.

Bottled gas is a term used for substances which are gaseous at standard temperature and pressure (STP) and have been compressed and stored in carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or composite containers known as gas cylinders.
GOST refers to a set of international technical standards maintained by the Euro-Asian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (EASC), a regional standards organization operating under the auspices of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS).

Industrial gases are the gaseous materials that are manufactured for use in industry. The principal gases provided are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, hydrogen, helium and acetylene, although many other gases and mixtures are also available in gas cylinders. The industry producing these gases is also known as industrial gas, which is seen as also encompassing the supply of equipment and technology to produce and use the gases. Their production is a part of the wider chemical Industry.
The Compressed Gas Association (CGA) is an American trade association for the industrial and medical gas supply industries.

ISO 22000 is a food safety management system by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) which is outcome focused, providing requirements for any organization in the food industry with objective to help to improve overall performance in food safety. These standards are intended to ensure safety in the global food supply chain. The standards involve the overall guidelines for food safety management and also focuses on traceability in the feed and food chain.

The Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry (ABPI) is the trade association for over 120 companies in the UK producing prescription medicines for humans, founded in 1891. It is the British equivalent of America's PhRMA; however, the member companies research, develop, manufacture and supply medicines prescribed for the National Health Service.
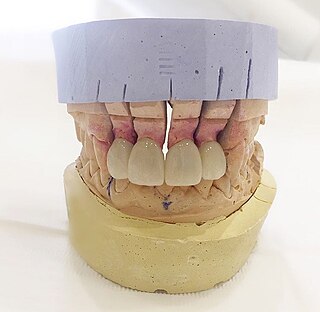
Dental laboratories manufacture or customize a variety of products to assist in the provision of oral health care by a licensed dentist. These products include crowns, bridges, dentures and other dental products. Dental lab technicians follow a prescription from a licensed dentist when manufacturing these items, which include prosthetic devices and therapeutic devices. The FDA regulates these products as medical devices and they are therefore subject to FDA's good manufacturing practice ("GMP") and quality system ("QS") requirements. In most cases, however, they are exempt from manufacturer registration requirements. Some of the most common restorations manufactured include crowns, bridges, dentures, and dental implants. Dental implants is one of the most advanced dental technologies in the field of dentistry.

The British Compressed Air Society (BCAS) is the self appointed compressed air and vacuum trade association in the United Kingdom. It has membership for Manufacturers, Distributors, Suppliers and End-Users of compressed air equipment and systems.

The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies standards certification services for business and personnel.
A technical standard is an established norm or requirement for a repeatable technical task which is applied to a common and repeated use of rules, conditions, guidelines or characteristics for products or related processes and production methods, and related management systems practices. A technical standard includes definition of terms; classification of components; delineation of procedures; specification of dimensions, materials, performance, designs, or operations; measurement of quality and quantity in describing materials, processes, products, systems, services, or practices; test methods and sampling procedures; or descriptions of fit and measurements of size or strength.
PNEUROP is the European Association of manufacturers of compressors, vacuum pumps, pneumatic tools and allied equipment, represented by their national associations.
The United Kingdom Accreditation Service (UKAS) is the sole national accreditation body recognised by the British government to assess the competence of organisations that provide certification, testing, inspection and calibration services. It evaluates these conformity assessment bodies and then accredits them where they are found to meet relevant internationally specified standards.

The Manufacturers’ Association of Israel (MAI) is the umbrella organization and representative body of all industrial sectors in Israel including the private, public, kibbutz, and government industries. With a membership of over 1,800 organizations responsible for more than 90% of the industrial output, the Manufacturers’ Association of Israel is the largest and most influential economic organization in the country. Dr. Ron Tomer has led the organization as President since January 30, 2020. Headquartered in Tel Aviv, the Manufacturers’ Association of Israel has three other regional branches. The Northern branch, located in the city of Haifa, serves over 600 different member organizations which are responsible for around one third of all the industrial manpower in Israel. The Jerusalem branch, located in the city of Jerusalem, serves over 130 different member organizations. The Southern branch, located near the city of Be’er Sheva, serves over 350 different member organizations.

ECA is the main trade association for companies involved in electrotechnical and other technical engineering projects in England, Northern Ireland and Wales. In 2022 it had some 2600 registered members - companies who collectively generated annual revenues of over £6billion. ECA also has associate categories open to industry manufacturers, distributors, educators, clients and specifiers who wish to engage and collaborate with members.

The Building Engineering Services Association (BESA), until 2012 the Heating and Ventilating Contractors' Association, and from then until 2016, B&ES, is the main UK trade association for companies that design, install, commission and maintain heating, ventilation, air conditioning, refrigeration (HVACR) and related engineering projects.

The Association for Renewable Energy and Clean Technology, previously known as Renewable Energy Association (REA), is a renewable energy and clean technology trade association in the UK encompassing all of renewables industry in the United Kingdom. REA covers renewable power & flexibility, heat and cooling, circular bioresources and transport. The REA is a not-for-profit company.

Pac-Kit Safety Equipment Company has roots dating back to 1880 when Silas Burroughs, a former representative of the US pharmaceutical company John Wyeth & Co, and his business associate Henry Wellcome formed Burroughs Wellcome & Co in the UK. The two started manufacturing compressed pharmaceuticals, a novelty in those days and much safer than medicines prepared by pestle and mortar.











