Related Research Articles

The Allegheny River is a 325-mile (523 km) long headwater stream of the Ohio River in western Pennsylvania and New York, United States. The Allegheny River runs from its headwaters just below the middle of Pennsylvania's northern border northwesterly into New York then in a zigzag southwesterly across the border and through Western Pennsylvania to join the Monongahela River at the Forks of the Ohio on the "Point" of Point State Park in Downtown Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The Allegheny River is, by volume, the main headstream of both the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers. Historically, the Allegheny was considered to be the upper Ohio River by both Native Americans and European settlers.

Warren County is a county located in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. As of the 2010 census, the population was 41,815. Its county seat is Warren. The county was formed in 1800 from parts of Allegheny and Lycoming counties; attached to Crawford County until 1805 and then to Venango County until Warren was formally organized in 1819.

Erie County is a county located in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. As of the 2010 census, the population was 280,566. Its county seat is Erie. The county was created in 1800 and later organized in 1803.

Reading is a city in and the county seat of Berks County, Pennsylvania, United States. With a population of 87,575, it is the fifth-largest city in Pennsylvania. Located in the southeastern part of the state, it is the principal city of the Greater Reading Area, and is furthermore included in the Philadelphia-Reading-Camden PA-NJ-DE-MD Combined Statistical Area.

The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I railroad in the United States. With headquarters in Norfolk, Virginia, the company operates 21,500 route miles in 22 eastern states, the District of Columbia, and has rights in Canada over the Albany to Montréal route, and previously on CN from Buffalo to St. Thomas. NS is responsible for maintaining 26,300 miles, with the remainder being operated under trackage rights from other parties responsible for maintenance. The most common commodity hauled on the railway is coal from mines in Indiana, Kentucky, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, and West Virginia. The railway also offers the largest intermodal network in eastern North America.
U.S. Route 224 (US 224) is a spur of US 24 that runs through the states of Indiana, Ohio and Pennsylvania. It currently runs for 289 miles (465 km) from Huntington, Indiana. at US 24 to New Castle, Pennsylvania, at US 422 Business and Pennsylvania Route 18 (PA 18). It goes through the cities of Canfield, Ohio, Akron, Ohio, and Findlay, Ohio. In Northeast Ohio, US 224 is located a short distance north of the Western Reserve's southern boundary.

The Railroad Museum of Pennsylvania is a railroad museum in Strasburg, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania.
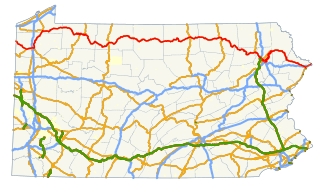
U.S. Route 6 travels east–west near the north edge of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania from the Ohio state line near Pymatuning Reservoir east to the Mid-Delaware Bridge over the Delaware River into Port Jervis, New York. It is the longest highway segment in the Commonwealth. Most of it is a two-lane rural highway, with some freeway bypasses around larger towns. Except east of Dunmore, where it is paralleled by Interstate 84, it is the main route in its corridor. What is now Interstate 80—the Keystone Shortway—was once planned along the US 6 corridor as a western extension of I-84. The corridor was originally the Roosevelt Highway from Erie, Pennsylvania to Port Jervis, New York, designated Pennsylvania Route 7 in 1924. The PA 7 designation soon disappeared, but as US 6 was extended and relocated, the Roosevelt Highway followed it. The Pennsylvania section of US 6 was renamed the Grand Army of the Republic Highway in 1946; this name was applied to its full transcontinental length by 1953.

Pine Grove Furnace State Park is a protected Pennsylvania area that includes Laurel and Fuller Lakes in Cooke Township of Cumberland County. The Park accommodates various outdoor recreation activities, protects the remains of the Pine Grove Iron Works (1764), and was the site of Laurel Forge (1830), Pine Grove Park (1880s), and a brick plant (1892). The Park is 8 miles (13 km) from exit 37 of Interstate 81 on Pennsylvania Route 233.

Pennsylvania Route 346 (PA 346) is a 34.177-mile (55.003 km) state highway located in Warren and McKean counties in Pennsylvania, United States The western terminus is at the New York state line in the Allegheny National Forest, where it becomes New York State Route 280 (NY 280). The eastern terminus is at an intersection with PA 446 in Eldred. The route is mostly a two-lane road that passes through rural areas in the northern part of McKean County. PA 346 passes through the city of Bradford, where it has a concurrency with the U.S. Route 219 (US 219) freeway.

Pennsylvania Route 426 is a 26-mile-long (42 km) state highway in Warren and Erie counties of Pennsylvania. The route is split up into two segments, connected by New York State Route 426 through New York.

Pennsylvania Route 446 is an 13-mile-long (21 km) state highway located in McKean County, Pennsylvania. The southern terminus is at Route 46 in the Keating Township neighborhood of Farmers Valley. The northern terminus is at the New York state line near Portville, New York. Route 446 is mountainous for most of its length and its only street designation is Main Street. PA 446 is part of a family of routes interconnected with PA 46. However, unlike several others, PA 446 does connect to its parent route and PA 346.

The Old Loggers Path (OLP) is a 27.1 mi (43.6 km) loop hiking trail in Lycoming County in north-central Pennsylvania in the United States. Marked with international orange blazes, the Old Loggers Path is located entirely within the Loyalsock State Forest. Most hikers take two and a half to three days and two nights to complete the Old Loggers Path, making it popular for weekend hikes. Highlights of the trail include waterfalls, several scenic streams and creeks, and panoramic vistas.

The Ohio Central Railroad System is a network of short line railroads operating in Ohio and western Pennsylvania. It is owned by Genesee & Wyoming Inc.

The Lehigh Coal and Navigation Company (LCAN) (1988–2010) was a modern-day anthracite coal mining company headquartered in Pottsville, Schuylkill County, Pennsylvania, U.S. which acquired many of the 'Old Company' (LC&N) properties and re-launched the Lehigh Coal Companies brand in 1988. The LCAN ran strip mining operations in the Panther Creek Valley east of Lansford along U.S. Route 209; with vast properties dominating the coal areas of Tamaqua, Coaldale, and Lansford. These properties are largely the same real estate assets as were acquired in the Panther Creek Valley by the predecessors: the haphazard Lehigh Coal Mine Company (1792-1822) and the builders of the Lehigh Canal and first American blast furnaces, the Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company, which spearheaded the U.S. Industrial revolution. The new company was incorporated in 1988 acquiring LC&N assets after bankruptcy proceedings, taking the name of the original.
The Ghost Town Trail is a rail trail in Western Pennsylvania that stretches 36 miles (58 km) from Black Lick, Indiana County, to Ebensburg, Cambria County. Established in 1991 on the right-of-way of the former Ebensburg and Black Lick Railroad, the trail follows the Blacklick Creek and passes through many ghost towns that were abandoned in the early 1900s with the decline of the local coal mining industry. Open year-round to cycling, hiking, and cross-country skiing, the trail is designated as a National Recreation Trail by the United States Department of the Interior.

The Johnsonburg, Kane, Warren and Irvine Railroad was a railroad company in Pennsylvania, United States, formed on May 24, 1982, by Sloan Cornell who also owned the Knox and Kane Railroad. The JKWI was the designated operator of the Irvine, Warren, Kane & Johnsonburg Railroad, that was a partnership of Brock Railroad, Irvine Railroad and Struthers Wells Inter-American Corporation, all three being Pennsylvania corporations, and had acquired from Conrail the following railroad line segments: MP 58.52 to MP 66.7 and MP 92.5 to MP 111.0.

Pennsylvania Route 958 is an 8.63-mile-long (13.89 km) state highway located in Warren County, Pennsylvania. The designation's southern terminus is at an intersection with U.S. Route 6 in Pittsfield Township. The route heads through several small communities, including Lottsville, where it goes on a short concurrency with Pennsylvania Route 957. The northern terminus is at the New York state line at Freehold Township, just east of Bear Lake. There, the route continues through New York as Chautauqua County Route 33. Route 958 was designated in 1928 as a connector from U.S. Route 6 to the community of Wrightsville, where the designation terminated. The route was extended northward along its current alignment in 1936 and has remained unchanged since.

Cokeville was a town in Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania, United States. Following the St. Patrick's Day flood of 1936, the Army Corp Of Engineers began planning a dam project on the Conemaugh River to harness the flood waters. There were 122 structures in Cokeville on a 1951 map. In 1952, as the town was being evacuated for the flood control project, most of these structures were razed, but some were moved up the hill to Cokeville Heights near Rt. 217.

Leetonia is an unincorporated community in Elk Township, Tioga County, in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. It lies along Leetonia Road, in the Tioga State Forest between Pennsylvania Route 414 and U.S. Route 6.
References
- ↑ Pennsylvania Department of State. (2008). Search for Brock Railroad Company. Retrieved November 28, 2008 from https://www.corporations.state.pa.us/corp/soskb/Corp.asp?518863%5Bpermanent+dead+link%5D