
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.

Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common in igneous and metamorphic rocks.

Amphibole is a group of inosilicate minerals, forming prism or needlelike crystals, composed of double chain SiO
4 tetrahedra, linked at the vertices and generally containing ions of iron and/or magnesium in their structures. Its IMA symbol is Amp. Amphiboles can be green, black, colorless, white, yellow, blue, or brown. The International Mineralogical Association currently classifies amphiboles as a mineral supergroup, within which are two groups and several subgroups.

The pyroxenes are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula XY(Si,Al)2O6, where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron or magnesium (Mg) and more rarely zinc, manganese or lithium, and Y represents ions of smaller size, such as chromium (Cr), aluminium (Al), magnesium (Mg), cobalt (Co), manganese (Mn), scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V) or even iron or. Although aluminium substitutes extensively for silicon in silicates such as feldspars and amphiboles, the substitution occurs only to a limited extent in most pyroxenes. They share a common structure consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra. Pyroxenes that crystallize in the monoclinic system are known as clinopyroxenes and those that crystallize in the orthorhombic system are known as orthopyroxenes.

Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.

Triphylite is a lithium iron(II) phosphate mineral with the chemical formula LiFePO4. It is a member of the triphylite group and forms a complete solid solution series with the lithium manganese(II) phosphate, lithiophilite. Triphylite crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. It rarely forms prismatic crystals and is more frequently found in hypidiomorphic rock. It is bluish- to greenish-gray in color, but upon alteration becomes brown to black.
Geigerite is a mineral, a complex hydrous manganese arsenate with formula: Mn5(AsO3OH)2(AsO4)2·10H2O. It forms triclinic pinacoidal, vitreous, colorless to red to brown crystals. It has a Mohs hardness of 3 and a specific gravity of 3.05.

Julgoldite is a member of the pumpellyite mineral series, a series of minerals characterized by the chemical bonding of silica tetrahedra with alkali and transition metal cations. Julgoldites, along with more common minerals like epidote and vesuvianite, belong to the subclass of sorosilicates, the rock-forming minerals that contain SiO4 tetrahedra that share a common oxygen to form Si2O7 ions with a charge of 6- (Deer et al., 1996). Julgoldite has been recognized for its importance in low grade metamorphism, forming under shear stress accompanied by relatively low temperatures (Coombs, 1953). Julgoldite was named in honor of Professor Julian Royce Goldsmith (1918–1999) of the University of Chicago.

Yuksporite is a rare inosilicate mineral with double width, unbranched chains, and the complicated chemical formula K4(Ca,Na)14Sr2Mn(Ti,Nb)4(O,OH)4(Si6O17)2(Si2O7)3(H2O,OH)3. It contains the relatively rare elements strontium, titanium and niobium, as well as the commoner metallic elements potassium, calcium, sodium and manganese. As with all silicates, it contains groups of linked silicon and oxygen atoms, as well as some associated water molecules.

Dollaseite-(Ce) is a sorosilicate end-member epidote rare-earth mineral which was discovered by Per Geijer (1927) in the Ostanmossa mine, Norberg district, Sweden. Dollaseite-(Ce), although not very well known, is part of a broad epidote group of minerals which are primarily silicates, the most abundant type of minerals on earth. Dollaseite-(Ce) forms as dark-brown subhedral crystals primarily in Swedish mines. With the ideal chemical formula, CaREE3+
Mg
2AlSi
3O
11,(OH)F, dollaseite-(Ce) can be partially identified by its content of the rare earth element cerium.

Kanoite is a light pinkish brown silicate mineral that is found in metamorphic rocks. It is an inosilicate and has a chemical formula of (Mg,Mn2+)2Si2O6. It is a member of pyroxene group and clinopyroxene subgroup.
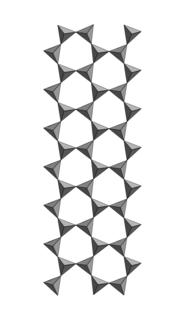
Jimthompsonite is a magnesium iron silicate mineral with chemical formula (Mg,Fe2+)5Si6O16(OH)2. It is a triple chain silicate (or inosilicate) along with clinojimthompsonite and chesterite. They were described in 1977 by Burham and Veblen. They attracted great mineralogical attention because they were the first examples of new chain silicate structures among a large group known as biopyriboles whose name is derived from the words biotite, pyroxene, and amphiboles.

Serandite is a mineral with formula Na(Mn2+,Ca)2Si3O8(OH). The mineral was discovered in Guinea in 1931 and named for J. M. Sérand. Serandite is generally red, brown, black or colorless. The correct name lacks an accent.
Eveslogite is a complex inosilicate mineral with a chemical formula (Ca,K,Na,Sr,Ba)
48[(Ti,Nb,Fe,Mn)
12(OH)
12Si
48O
144](F,OH,Cl)
14 found on Mt. Eveslogchorr in Khibiny Mountains, on the Kola peninsula, Russia. It was named after the place it was found. This silicate mineral occurs as an anchimonomineral veinlet that cross-cuts poikilitic nepheline syenite. This mineral appears to resemble yuksporite, as it forms similar placated fine fibrous of approximately 0.05 to 0.005mm that aggregates outwardly. The color of eveslogite is yellow or rather light brown. In addition, it is a semitransparent mineral that has a white streak and a vitreous luster. Its crystal system is monoclinic and possesses a hardness (Mohs) of 5. This newly discovered mineral belongs to the astrophyllite group of minerals and contains structures that are composed of titanosilicate layers. Limited information about this mineral exists due to the few research studies carried out since its recent discovery.
Franklinphilite is a phyllosilicate of the stilpnomelane group. Known from only two localities It was found exclusively from the Franklin and Sterling Hill mines in Franklin, Sussex County, New Jersey. until 2013, when a locality in Wales was confirmed
Labyrinthite is a very rare mineral of the eudialyte group. When compared to other species in the group, its structure is extremely complex - with over 100 sites and about 800 cations and anions - hence its name, with its complexity expressed in its chemical formula (Na,K,Sr)35Ca12Fe3Zr6TiSi51O144(O,OH,H2O)9Cl3. The formula is simplified as it does not show the presence of cyclic silicate groups. Complexity of the structure results in symmetry lowering from the typical centrosymmetrical group to R3 space group. Other eudialyte-group representatives with such symmetry lowering include aqualite, oneillite, raslakite, voronkovite. Labyrinthite is the second dual-nature representative of the group after dualite and third with essential titanium after dualite and alluaivite.

Manganokhomyakovite is a very rare mineral of the eudialyte group, with the chemical formula Na12Sr3Ca6Mn3Zr3WSi(Si9O27)2(Si3O9)2O(O,OH,H2O)3(OH,Cl)2. This formula is in extended form, to show the presence of cyclic silicate groups and domination of silicon at the M4 site, basing on the nomenclature of the eudialyte group. Some niobium substitutes for tungsten in khomyakovite. As suggested by its name, manganokhomyakovite is a manganese-analogue of khomyakovite, the latter being more rare. The two minerals are the only group representatives, beside taseqite, with species-defining strontium, although many other members display strontium diadochy. Manganokhomyakovite is the third eudialyte-group mineral with essential tungsten.

Jinshajiangite is a rare silicate mineral named after the Jinshajiang river in China. Its currently accepted formula is BaNaFe4Ti2(Si2O7)2O2(OH)2F. It gives a name of the jinshajiangite group. The mineral is associated with alkaline rocks. In jinshajiangite, there is a potassium-to-barium, calcium-to-sodium, manganese-to-iron and iron-to-titanium diadochy substitution. Jinshajiangite is the iron-analogue of surkhobite and perraultite. It is chemically related to bafertisite, cámaraite and emmerichite. Its structure is related to that of bafertisite. Jinshajiangite is a titanosilicate with heteropolyhedral HOH layers, where the H-layer is a mixed tetrahedral-octahedral layer, and the O-layer is simply octahedral.

Inesite is a hydrous calcium manganese silicate mineral. Its chemical formula is Ca2Mn7Si10O28(OH)2•5(H2O). Inesite is an inosilicate with a triclinic crystal system. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6, and a specific gravity of 3.0. Its name originates from the Greek Ίνες (ines), "fibers" in allusion to its color and habit.















