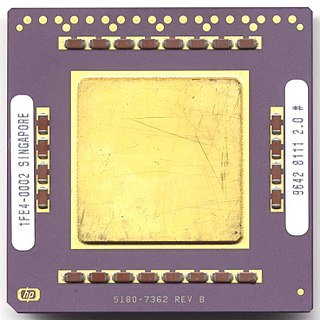
PA-RISC is an instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Hewlett-Packard. As the name implies, it is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) architecture, where the PA stands for Precision Architecture. The design is also referred to as HP/PA for Hewlett Packard Precision Architecture.
HP-GL, short for Hewlett-Packard Graphics Language and often written as HPGL, is a printer control language created by Hewlett-Packard (HP). HP-GL was the primary printer control language used by HP plotters. It was introduced with the plotter HP-8972 in 1977 and became a standard for almost all plotters. Hewlett-Packard's printers also usually support HP-GL/2 in addition to PCL.

The HP 2100 was a series of 16-bit minicomputers produced by Hewlett-Packard (HP) from the mid-1960s to early 1990s. Tens of thousands of machines in the series were sold over its twenty-five year lifetime, making HP the fourth largest minicomputer vendor during the 1970s.

NewWave is a discontinued object-oriented graphical desktop environment and office productivity tool for PCs running early versions of Microsoft Windows. It was developed by Hewlett-Packard and introduced commercially in 1988. It was used on the HP Vectras and other IBM compatible PCs running MS Windows.
The HP 3000 series is a family of minicomputers released by Hewlett-Packard in 1972. It was designed to be the first minicomputer delivered with a full featured operating system with time-sharing. The first model of the 3000 were withdrawn from the market during 1973 until speed improvements and OS stability could be achieved. After its reintroduction in 1974, it ultimately became known as a reliable and powerful business system, one which regularly won HP business from companies using IBM's mainframes. Hewlett-Packard's initial naming referred to the computer as the System/3000, and then called it the HP3000. HP later renamed the computer the HP e3000 to emphasize the system's compatibility with Internet and Web uses.
TurboIMAGE is one of several names used to refer to a database developed by Hewlett Packard and included with the HP3000 minicomputer. TurboIMAGE was also available on the HP250 minicomputer. Originally released under the name IMAGE/3000 in 1972, it was later known as TurboIMAGE, IMAGE/SQL, and TurboIMAGE/XL.

The HP-150 was a compact, powerful and innovative computer made by Hewlett-Packard in 1983. It was based on the Intel 8088 and was one of the world's earliest commercialized touch screen computers. The machine was not IBM PC compatible, although it was MS-DOS compatible. Customized MS-DOS versions 2.01, 2.11 and 3.20 were available. Its 8088 CPU, rated at 8 MHz, was faster than the 4.77 MHz CPUs used by the IBM PC of that period. Using add-on cards, main memory could be increased from 256 KB to 640 KB. However, its mainboard did not have a slot for the optional Intel 8087 math coprocessor due to space constraints. The HP-150 with an optional hard disk was called the HP Touchscreen MAX.

The HP 300 "Amigo" was a computer produced by Hewlett-Packard (HP) in the late 1970s based loosely on the stack-based HP 3000, but with virtual memory for both code and data. The HP300 was cut-short from being a commercial success despite the huge engineering effort, which included HP-developed and -manufactured silicon on sapphire (SOS) processor and I/O chips.

The HP 2640A and other HP 264X models were block-mode "smart" and intelligent ASCII standard serial terminals produced by Hewlett-Packard using the Intel 8008 and 8080 microprocessors.
The Hewlett-Packard FOCUS microprocessor, launched in 1982, was the first commercial, single chip, fully 32-bit microprocessor available on the market. At this time, all 32-bit competitors used multi-chip bit-slice-CPU designs. The FOCUS architecture was used in the Hewlett-Packard HP 9000 Series 500 workstations and servers. It was a stack architecture, with over 220 instructions, a segmented memory model, and no general purpose programmer-visible registers. The design of the FOCUS CPU was richly inspired by the custom silicon on sapphire (SOS) chip design, HP used in their 16-bit HP 3000 series machines.

The Hewlett-Packard Voyager series of calculators were introduced by Hewlett-Packard in 1981. All members of this series are programmable, use Reverse Polish Notation, and feature continuous memory. Nearly identical in appearance, each model provided different capabilities and was aimed at different user markets.

The HP-16C Computer Scientist is a programmable pocket calculator that was produced by Hewlett-Packard between 1982 and 1989. It was specifically designed for use by computer programmers, to assist in debugging. It is a member of the HP Voyager series of programmable calculators. It was the only programmer's calculator ever produced by HP, though many later HP calculators have incorporated most of the 16C's functions.

The Hewlett-Packard 9100A is an early programmable calculator, first appearing in 1968. HP called it a desktop calculator because, as Bill Hewlett said, "If we had called it a computer, it would have been rejected by our customers' computer gurus because it didn't look like an IBM. We therefore decided to call it a calculator, and all such nonsense disappeared."

HP OmniBook was a range of laptop personal computers created by Hewlett Packard.

The HP 95LX Palmtop PC, also known as project Jaguar, was Hewlett Packard's first MS-DOS-based pocket computer or personal digital assistant, introduced in April 1991 in collaboration with Lotus Development Corporation. It can be seen as successor to a series of larger portable PCs like the HP 110 and HP 110 Plus.
The HP 7935 was a business computer hard disc drive system manufactured by Hewlett Packard. It was produced by the Disc Memory Division in Boise, Idaho USA beginning in 1982 at a cost of about $27,000. Within the company the drive was known as the "BFD", ostensibly an acronym for "big fixed disc" but the development engineers had used that acronym for "big f***ing disc", a term relative to the smaller 7920 series drives introduced earlier by the company.

The HP Superdome is a high-end server computer developed and produced by Hewlett Packard Enterprise. The latest version of product, "Superdome 2" was introduced in 2010. Superdome 2 scales from 2 to 32 sockets and 4 TB of memory. When introduced in 2000, the Superdome used PA-RISC processors. Since 2002, there has been another version of the machine based on Itanium 2 processors, marketed in parallel as the HP Integrity Superdome. The classic PA-RISC Superdome was subsequently rebranded to HP 9000 Superdome. The predecessor to the Superdome was the HP V-Class.
In computing HP Roman is a family of character sets consisting of HP Roman Extension, HP Roman-8, HP Roman-9 and several variants. Originally introduced by Hewlett-Packard around 1978, revisions and adaptations were published several times up to 1999. The 1985 revisions were later standardized as IBM codepages 1050 and 1051. Supporting many European languages, the character sets were used by various HP workstations, terminals, calculators as well as many printers, also from third-parties.

The Compaq Presario F700, also called HP Presario F700, is a notebook computer that was manufactured by HP (Compaq).













