Related Research Articles

Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics, also spelled orthopaedics, is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders.

Retinal detachment is a disorder of the eye in which the retina separates from the layer underneath. Symptoms include an increase in the number of floaters, flashes of light, and worsening of the outer part of the visual field. This may be described as a curtain over part of the field of vision. In about 7% of cases both eyes are affected. Without treatment permanent loss of vision may occur.
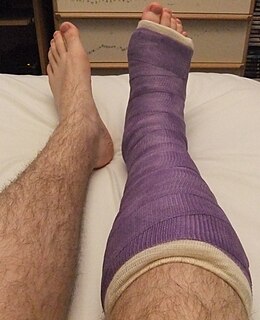
An orthopedic cast, or simply cast, is a shell, frequently made from plaster or fiberglass, that encases a limb to stabilize and hold anatomical structures—most often a broken bone, in place until healing is confirmed. It is similar in function to a splint.

Lordosis is historically defined as an abnormal inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms lordosis and lordotic are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical regions of the human spine. Similarly, kyphosis historically refers to abnormal convex curvature of the spine. The normal outward (convex) curvature in the thoracic and sacral regions is also termed kyphosis or kyphotic. The term comes from the Greek lordōsis, from lordos.

Hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant, that is, a hip prosthesis. Hip replacement surgery can be performed as a total replacement or a hemi (half) replacement. Such joint replacement orthopaedic surgery is generally conducted to relieve arthritis pain or in some hip fractures. A total hip replacement consists of replacing both the acetabulum and the femoral head while hemiarthroplasty generally only replaces the femoral head. Hip replacement is currently one of the most common orthopaedic operations, though patient satisfaction short- and long-term varies widely. Approximately 58% of total hip replacements are estimated to last 25 years. The average cost of a total hip replacement in 2012 was $40,364 in the United States, and about $7,700 to $12,000 in most European countries.
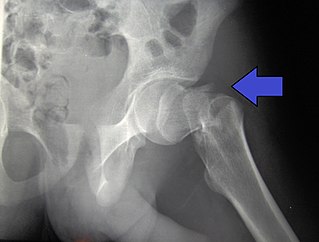
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur. Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually the person cannot walk.

Romberg's test, Romberg's sign, or the Romberg maneuver is a test used in an exam of neurological function for balance, and also as a test for driving under the influence of an intoxicant. The exam is based on the premise that a person requires at least two of the three following senses to maintain balance while standing: proprioception ; vestibular function ; and vision.

Traction is a set of mechanisms for straightening broken bones or relieving pressure on the spine and skeletal system. There are two types of traction: skin traction and skeletal traction. They are used in orthopedic medicine.
Traction, or tractive force, is the force used to generate motion between a body and a tangential surface, through the use of dry friction, though the use of shear force of the surface is also commonly used.
A traction splint most commonly refers to a splinting device that uses straps attaching over the pelvis or hip as an anchor, a metal rod(s) to mimic normal bone stability and limb length, and a mechanical device to apply traction to the limb.

Snapping hip syndrome, also referred to as dancer's hip, is a medical condition characterized by a snapping sensation felt when the hip is flexed and extended. This may be accompanied by a snapping or popping noise and pain or discomfort. Pain often decreases with rest and diminished activity. Snapping hip syndrome is commonly classified by the location of the snapping as either extra- articular or intra-articular.
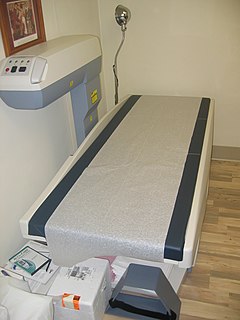
Bone density, or bone mineral density (BMD), is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone, although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optical density per square centimetre of bone surface upon imaging. Bone density measurement is used in clinical medicine as an indirect indicator of osteoporosis and fracture risk. It is measured by a procedure called densitometry, often performed in the radiology or nuclear medicine departments of hospitals or clinics. The measurement is painless and non-invasive and involves low radiation exposure. Measurements are most commonly made over the lumbar spine and over the upper part of the hip. The forearm may be scanned if the hip and lumbar spine are not accessible.

Quantitative computed tomography (QCT) is a medical technique that measures bone mineral density (BMD) using a standard X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) scanner with a calibration standard to convert Hounsfield Units (HU) of the CT image to bone mineral density values. Quantitative CT scans are primarily used to evaluate bone mineral density at the lumbar spine and hip.

The acetabular labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the acetabulum of the hip. The anterior portion is most vulnerable when the labrum tears.

Hip dysplasia is an abnormality of the hip joint where the socket portion does not fully cover the ball portion, resulting in an increased risk for joint dislocation. Hip dysplasia may occur at birth or develop in early life. Regardless, it does not typically produce symptoms in babies less than a year old. Occasionally one leg may be shorter than the other. The left hip is more often affected than the right. Complications without treatment can include arthritis, limping, and low back pain.

Orthotics is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses. An orthosis is "an externally applied device used to modify the structural and functional characteristics of the neuromuscular and skeletal system". An orthotist is the primary medical clinician responsible for the prescription, manufacture and management of orthoses. An orthosis may be used to:
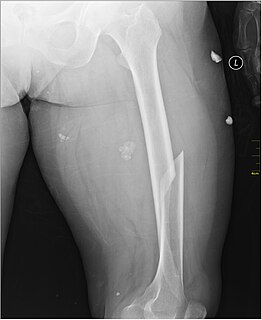
A femoral fracture is a bone fracture that involves the femur. They are typically sustained in high-impact trauma, such as car crashes, due to the large amount of force needed to break the bone. Fractures of the diaphysis, or middle of the femur, are managed differently from those at the head, neck, and trochanter
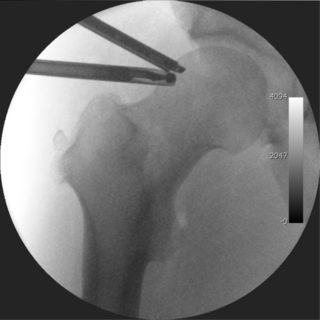
Hip arthroscopy refers to the viewing of the interior of the acetabulofemoral (hip) joint through an arthroscope and the treatment of hip pathology through a minimally invasive approach. This technique is sometimes used to help in the treatment of various joint disorders and has gained popularity because of the small incisions used and shorter recovery times when compared with conventional surgical techniques. Hip arthroscopy was not feasible until recently, new technology in both the tools used and the ability to distract the hip joint has led to a recent surge in the ability to do hip arthroscopy and the popularity of it.
Watsu is a form of aquatic bodywork used for deep relaxation and passive aquatic therapy. Watsu is characterized by one-on-one sessions in which a practitioner or therapist gently cradles, moves, stretches, and massages a receiver in chest-deep warm water.
Sickle cell retinopathy is a major ocular complication of the sickle cell disease (SCD) which causes permanent loss of vision. Retinopathy can occur in sickling hemoglobinopathies like sickle cell disease, sickle cell C disease, and sickle cell thalassaemia disease.
References
- ↑ "Traction Guidelines" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-09-13. Retrieved 2007-07-01.
| This medical treatment–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |