Related Research Articles
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase orrestrictase is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class of the broader endonuclease group of enzymes. Restriction enzymes are commonly classified into five types, which differ in their structure and whether they cut their DNA substrate at their recognition site, or if the recognition and cleavage sites are separate from one another. To cut DNA, all restriction enzymes make two incisions, once through each sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA double helix.
The restriction modification system is found in bacteria and other prokaryotic organisms, and provides a defense against foreign DNA, such as that borne by bacteriophages.
Site-specific DNA-methyltransferase (cytosine-N4-specific) is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:DNA-cytosine N4-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

The homing endonucleases are a collection of endonucleases encoded either as freestanding genes within introns, as fusions with host proteins, or as self-splicing inteins. They catalyze the hydrolysis of genomic DNA within the cells that synthesize them, but do so at very few, or even singular, locations. Repair of the hydrolyzed DNA by the host cell frequently results in the gene encoding the homing endonuclease having been copied into the cleavage site, hence the term 'homing' to describe the movement of these genes. Homing endonucleases can thereby transmit their genes horizontally within a host population, increasing their allele frequency at greater than Mendelian rates.
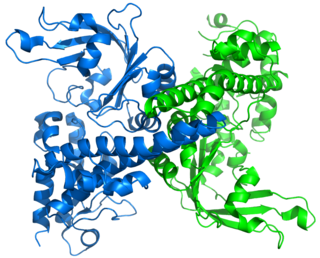
Restriction endonuclease (REase) EcoRII is an enzyme of restriction modification system (RM) naturally found in Escherichia coli, a Gram-negative bacteria. Its molecular mass is 45.2 kDa, being composed of 402 amino acids.
PstI is a type II restriction endonuclease isolated from the Gram negative species, Providencia stuartii.
References
- ↑ Xu GL, Kapfer W, Walter J, Trautner TA (December 1992). "BsuBI--an isospecific restriction and modification system of PstI: characterization of the BsuBI genes and enzymes". Nucleic Acids Res. 20 (24): 6517–23. doi:10.1093/nar/20.24.6517. PMC 334566 . PMID 1480472.