
A desk or bureau is a piece of furniture with a flat table-style work surface used in a school, office, home or the like for academic, professional or domestic activities such as reading, writing, or using equipment such as a computer. Desks often have one or more drawers, compartments, or pigeonholes to store items such as office supplies and papers. Desks are usually made of wood or metal, although materials such as glass are sometimes seen.
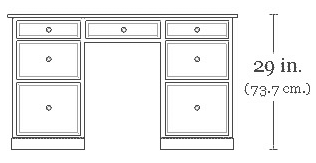
A pedestal desk or a tanker desk is usually a large, flat, free-standing desk made of a simple rectangular working surface resting on two pedestals or small cabinets of stacked drawers of one or two sizes, with plinths around the bases. Often, there is also a central large drawer above the legs and knees of the user. Sometimes, especially in the 19th century and modern examples, a "modesty panel" is placed in front, between the pedestals, to hide the legs and knees of the user from anyone else sitting or standing in front. This variation is sometimes called a "panel desk". The smaller and older pedestal desks with such a panel are sometimes called kneehole desks, they were intended for small spaces like boudoirs and were usually placed against a wall. The kneehole desks are also known as bureau tables.

A secretary desk or escritoire is made of a base of wide drawers topped by a desk with a hinged desktop surface, which is in turn topped by a bookcase usually closed with a pair of doors, often made of glass. The whole is usually a single, tall and heavy piece of furniture.

A writing table has a series of drawers directly under the surface of the table, to contain writing implements, so that it may serve as a desk. Antique versions have the usual divisions for the inkwell, the blotter and the sand or powder tray in one of the drawers, and a surface covered with leather or some other material less hostile to the quill or the fountain pen than simple hard wood.
The fall-front desk is a desk with a main working surface that folds up to cover small shelves or drawers stacked in front of the user. As with its cousin the secretary desk, all working papers, documents and other items have to be stored before the desk is closed.

The Wooton desk is a variation of the fall front desk, native to Indianapolis, Indiana, and produced from 1874 to 1890.

The slant-top desk, also called secretary desk, or more properly, a bureau, is a piece of writing furniture with a lid that closes at an angle and opens up as a writing surface. It can be considered related, in form, to the desk on a frame, which was a form of portable desk in earlier eras.

An office is a space where the employees of an organization perform administrative work in order to support and realize the various goals of the organization. The word "office" may also denote a position within an organization with specific duties attached to it ; the latter is an earlier usage, as "office" originally referred to the location of one's duty. In its adjective form, the term "office" may refer to business-related tasks. In law, a company or organization has offices in any place where it has an official presence, even if that presence consists of a storage silo, for example, instead of a more traditional establishment with a desk and chair. An office is also an architectural and design phenomenon, including small offices, such as a bench in the corner of a small business or a room in someone's home, entire floors of buildings, and massive buildings dedicated entirely to one company. In modern terms, an office is usually the location where white-collar workers carry out their functions.

There are two kinds of trestle desk: as with trestle tables, some have trestles joined by one or more stretchers, and some have free-standing trestles. They can be dismantled, with the desk top removed from the trestles, for storage or transport.

A bedroom or bedchamber is a room situated within a residential or accommodation unit characterised by its usage for sleeping. A typical western bedroom contains as bedroom furniture one or two beds, a clothes closet, and bedside table and dressing table, both of which usually contain drawers. Except in bungalows, ranch style homes, ground floor apartments, or one-storey motels, bedrooms are usually on one of the floors of a dwelling that is above ground level. Beds range from a crib for an infant; a single or twin bed for a toddler, child, teenager or single adult; to bigger sizes like a full, double, queen, king or California king). Beds and bedrooms are often devised to create barriers to insects and vermin, especially mosquitoes, and to dampen or contain light or noise to aid sleep and privacy.

A commode is any of many pieces of furniture. The Oxford English Dictionary has multiple meanings of "commode". The first relevant definition reads: "A piece of furniture with drawers and shelves; in the bedroom, a sort of elaborate chest of drawers ; in the drawing room, a large kind of chiffonier." The drawing room is itself a term for a formal reception room, and a chiffonier is, in this sense, a small sideboard dating from the early 19th century.

A chest of drawers, also called a dresser or a bureau, is a type of cabinet that has multiple parallel, horizontal drawers generally stacked one above another.

A lowboy is an American collectors term for one type of dressing table. It is a small table with one or two rows of drawers, so called in contradistinction to the tallboy or highboy chest of drawers.

A cupboard is a piece of furniture for enclosing dishware or grocery items that are stored in a home. The term is sometimes also used for any form of cabinet or enclosed bookcase. It gradually evolved from its original meaning: an open-shelved side table for displaying dishware, more specifically plates, cups and saucers.

A credenza is a dining room sideboard or display cabinet, usually made of burnished and polished wood and decorated with marquetry. The top would often be made of marble, or another decorative liquid- and heat-resistant stone.
Campaign furniture is a type of furniture which is made for travel. Historically, much of it was made for military campaigns.

The still room is a room for preparing household compounds, found in most great houses, castles or large establishments throughout Europe, dating back at least to medieval times. Stillrooms were used to make products as varied as candles, furniture polish, and soap; distillery was only one of the tasks carried out there.
A wardrobe, also called armoire or almirah, is a standing closet used for storing clothes. The earliest wardrobe was a chest, and it was not until some degree of luxury was attained in regal palaces and the castles of powerful nobles that separate accommodation was provided for the apparel of the great. The name of wardrobe was then given to a room in which the wall-space was filled with closets and lockers, the drawer being a comparatively modern invention. From these cupboards and lockers the modern wardrobe, with its hanging spaces, sliding shelves and drawers, evolved slowly.

A madia was a piece of furniture used during the High Renaissance period in Italy. A standing cupboard, the madia stored food and dishes, particularly bread, and were sometimes used as bread troughs. It is similar to the cassone, though generally more functional and less ornate. It would usually be found in the kitchen, not in an open area.

A Welsh dresser, sometimes known as a kitchen dresser, pewter cupboard or china hutch, is a piece of wooden furniture consisting of drawers and cupboards in the lower part, with shelves and perhaps a sideboard on top. Traditionally, it is a utilitarian piece of furniture used to store and display crockery, silverware and pewter-ware, but is also used to display general ornaments.

















