Related Research Articles

Comet 4P/Faye is a periodic Jupiter-family comet discovered in November 1843 by Hervé Faye at the Royal Observatory in Paris. Its most recent perihelia were on November 15, 2006; May 29, 2014; and September 8, 2021.

52P/Harrington–Abell is a periodic comet in the Solar System.

Comet Finlay is a periodic comet with an orbital period of 6 years discovered by William Henry Finlay on September 26, 1886. The next perihelion passage is July 13, 2021 when the comet will have a solar elongation of 54 degrees at approximately apparent magnitude 10. It last came to perihelion on December 27, 2014, at around magnitude 10. Of the numbered periodic comets, the orbit of 15P/Finlay has one of the smallest minimum orbit intersection distances with the orbit of Earth (E-MOID). In October 2060 the comet will pass about 5 million km from Earth.

Comet Holmes is a periodic comet in the Solar System, discovered by the British amateur astronomer Edwin Holmes on November 6, 1892. Although normally a very faint object, Holmes became notable during its October 2007 return when it temporarily brightened by a factor of a million, in what was the largest known outburst by a comet, and became visible to the naked eye. It also briefly became the largest object in the Solar System, as its coma expanded to a diameter greater than that of the Sun. Between 1857–2106 perihelion remains between 2.05–2.36 AU.

Comet Schaumasse is a periodic comet discovered by Alexandre Schaumasse on 1 December 1911 as 12th magnitude. It next comes to perihelion on 8 January 2026 and should brighten to about magnitude 9.

C/2012 F6 (Lemmon) is a long-period comet discovered in Leo on 23 March 2012, by A. R. Gibbs using the 1.5-m reflector at the Mt. Lemmon Survey, located at the summit of Mount Lemmon in the Santa Catalina Mountains north of Tucson, Arizona, USA. Initially, the object was considered to be of asteroidal nature before later observations confirmed its cometary appearance. Comet Lemmon has a highly eccentric orbit, bringing it as close to 0.73 AU from the Sun at perihelion and as far as 973 AU from the Sun at aphelion. This also leads to the comet's long-period nature with an orbital period of approximately 8,000 years based on epoch 2050. The comet last reached perihelion on 24 March 2013.

C/2012 K1 (PanSTARRS) is a retrograde Oort cloud comet discovered at magnitude 19.7, 8.7 AU from the Sun on 17 May 2012 using the Pan-STARRS telescope located near the summit of Haleakalā, on the island of Maui in Hawaii (U.S.).

C/2014 E2 (Jacques), provisionally designated as S002692, is a long-period comet discovered by the Brazilian astronomers Cristóvão Jacques Lage de Faria, Eduardo Pimentel, João Ribeiro de Barros and Marcelo Dias on the night of 13 March 2014. It was the second comet discovered by the SONEAR Observatory team after comet C/2014 A4.

C/2013 V5 (Oukaimeden) is a retrograde Oort cloud comet discovered on 12 November 2013 by Oukaimeden Observatory at an apparent magnitude of 19.4 using a 0.5-meter (20 in) reflecting telescope.

C/2014 Q2 (Lovejoy) is a long-period comet discovered on 17 August 2014 by Terry Lovejoy using a 0.2-meter (8 in) Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope. It was discovered at apparent magnitude 15 in the southern constellation of Puppis. It is the fifth comet discovered by Terry Lovejoy. Its blue-green glow is the result of organic molecules and water released by the comet fluorescing under the intense UV and optical light of the Sun as it passes through space.

A great comet is a comet that becomes exceptionally bright. There is no official definition; often the term is attached to comets such as Halley's Comet, which during certain appearances are bright enough to be noticed by casual observers who are not looking for them, and become well known outside the astronomical community. Typically, they are as bright or brighter than a second magnitude star and have tails that are 10 degrees or longer under dark skies. Great comets appear at irregular, unpredictable intervals, on average about once per decade. Although comets are officially named after their discoverers, great comets are sometimes also referred to by the year in which they appeared great, using the formulation "The Great Comet of ...", followed by the year. It can also be used as a generic name when a very bright comet is discovered by many observers simultaneously.
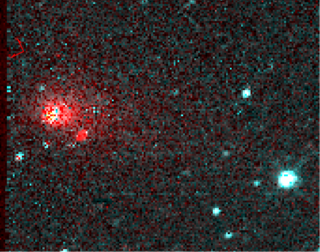
66P/du Toit is a periodic comet in the Solar System with a current orbital period of 14.78 years. It came to perihelion on 2018 May 19 at roughly apparent magnitude 12.

58P/Jackson–Neujmin is a periodic comet in the Solar System with a current orbital period of 8.19 years.
83D/Russell is a periodic lost comet in the Solar System with an orbital period of about 7.5 years. On the post-1988 orbit the comet probably does not get brighter than about apparent magnitude 21. The comet might come to perihelion in late May 2021, but the uncertainty in the comet's position is a few million km.
79P/du Toit–Hartley or du Toit 2 is a periodic comet, now divided into two parts, in the Solar System with an orbital period of 5.06 years. It next comes to perihelion in September 2023 but is only expected to reach about apparent magnitude 18. It will be less than 90 degrees from the Sun from February 2023 until June 2024. On 26 May 2024 it will be 2.7 AU from the Sun and Earth.

C/2015 ER61 (PanSTARRS) is a comet and inner Oort cloud object. When classified as a minor planet, it had the fourth-largest aphelion of any known minor planet in the Solar System, after 2005 VX3, 2012 DR30, and 2013 BL76. It additionally had the most eccentric orbit of any known minor planet, with its distance from the Sun varying by about 99.9% during the course of its orbit, followed by 2005 VX3 with an eccentricity of 0.9973. On 30 January 2016, it was classified as a comet when it was 5.7 AU from the Sun. It comes close to Jupiter, and a close approach in the past threw it on the distant orbit it is on now.

226P/Pigott–LINEAR–Kowalski is a Jupiter family periodic comet with an orbital period of 7.3 years. It was discovered by Edward Pigott on 19 November 1783, but was subsequently lost, until it was recovered on 5 January 2003 by Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR). It will next come to perihelion on 27 December 2023 at about apparent magnitude 15.

333P/LINEAR is a Jupiter family periodic comet in retrograde orbit with an orbital period of 8.7 years. Upon discovery it was the sun-orbiting natural object in retrograde orbit with the shortest known orbital period. The comet was discovered by LINEAR on 4 November 2007.

C/2020 F3 (NEOWISE) or Comet NEOWISE is a long period comet with a near-parabolic orbit discovered on March 27, 2020, by astronomers during the NEOWISE mission of the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) space telescope. At that time, it was an 18th-magnitude object, located 2 AU away from the Sun and 1.7 AU away from Earth.

C/2023 P1 (Nishimura) is a long-period comet discovered by Hideo Nishimura on 12 August 2023. The comet passed perihelion on 17 September 2023 and reached an apparent magnitude of about 2.5.
References
- ↑ Yoshida, Seiichi. "C/2015 G2 (MASTER)". Weekly Information about Bright Comets. Archived from the original on 7 September 2015. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
- 1 2 "C/2015 G2 (MASTER) is first South African Comet discovery in 35 years". Africa2Moon. Archived from the original on 21 May 2015. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
- ↑ Yoshida, Seiichi. "Weekly Information about Bright Comets (2015 May 16: North)". Weekly Information About Bright Comets. Archived from the original on 23 May 2015. Retrieved 20 May 2015.

