The molecular formula C11H16N2O2 (molar mass: 208.25 g/mol) may refer to:
- Aloracetam
- Aminocarb
- Carbenzide, or carbazic acid
- Pilocarpine
- Safrazine
The molecular formula C11H16N2O2 (molar mass: 208.25 g/mol) may refer to:
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge.
Benzol may refer to:
Gluten exorphins are a group of opioid peptides formed during digestion of the gluten protein. It has been hypothesized that people with autism and schizophrenia have abnormal leakage from the gut of these compounds, which then pass into the brain and disrupt brain function, a process collectively known as the opioid excess theory or a part of leaky gut syndrome. This is partly the basis for the gluten-free, casein-free diet. The medical evidence is mixed. Two clinical studies of autism patients who followed this diet found no benefit. Another study found a benefit. Another study suggested the diet may present a greater risk to brain development.
C2H4O2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C2H6O (molar mass: 46.07 g/mol, exact mass: 46.04186 u) may refer to:
Dichloroethene or dichloroethylene, often abbreviated as DCE, can refer to any one of several isomeric forms of the organochloride with the molecular formula C2H2Cl2:
The molecular formula C6H8O6 (molar mass: 176.124 g/mol) may be:
The molecular formula C4H10O may refer to:
To see a more detailed description of these isomers, see Amyl alcohol.
The molecular formula C6H14 may refer to:
Dihydroxybenzoic acids (DHBA) are a type of phenolic acids.
Dioxin may refer to:
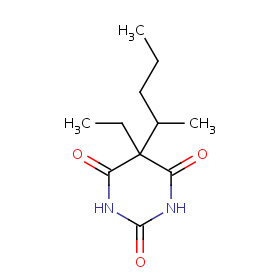
The molecular formula C11H18N2O3 (molar mass: 226.27 g/mol) may be referred as:
The molecular formula C12H16N2O2 may refer to :
Dihydroxycinnamic acid may refer to several molecules with the molecular formula C9H8O4 including:
Octynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C8H14.
Nonynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C9H16.
Decynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C10H18.
Benzoin may refer to: