The molecular formula C4H10 (molar mass: 58.12 g/mol, exact mass: 58.0783 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H10 (molar mass: 58.12 g/mol, exact mass: 58.0783 u) may refer to:

In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin, is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2. The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane, where n = 1, to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like pentacontane or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of tetradecane.
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
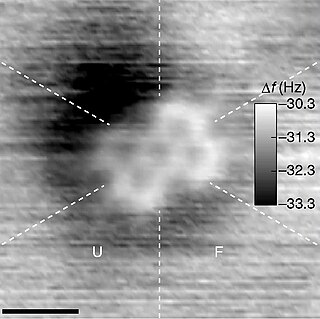
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance which is the number of moles in that sample, measured in moles. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on Earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.
Isobutane, also known as i-butane, 2-methylpropane or methylpropane, is a chemical compound with molecular formula HC(CH3)3. It is an isomer of butane. Isobutane is a colourless, odourless gas. It is the simplest alkane with a tertiary carbon atom. Isobutane is used as a precursor molecule in the petrochemical industry, for example in the synthesis of isooctane.

The structural formula of a chemical compound is a graphic representation of the molecular structure, showing how the atoms are possibly arranged in the real three-dimensional space. The chemical bonding within the molecule is also shown, either explicitly or implicitly. Unlike other chemical formula types, which have a limited number of symbols and are capable of only limited descriptive power, structural formulas provide a more complete geometric representation of the molecular structure. For example, many chemical compounds exist in different isomeric forms, which have different enantiomeric structures but the same molecular formula. There are multiple types of ways to draw these structural formulas such as: Lewis Structures, condensed formulas, skeletal formulas, Newman projections, Cyclohexane conformations, Haworth projections, and Fischer projections.
In organic chemistry, a homologous series is a sequence of compounds with the same functional group and similar chemical properties in which the members of the series can be branched or unbranched, or differ by molecular formula of CH2 and molecular mass of 14u. This can be the length of a carbon chain, for example in the straight-chained alkanes (paraffins), or it could be the number of monomers in a homopolymer such as amylose.
The molecular formula C3H5N (molar mass: 55.08 g/mol, exact mass: 55.0422 u) may refer to:
Butyl iodide (1-iodobutane) is an organic compound which is an iodo derivative of butane. It is used as an alkylating agent.
The molecular formula C7H7ClO (molar mass: 142.58 g/mol, exact mass: 142.0185 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C7H7Cl (molar mass: 126.58 g/mol, exact mass: 126.0236 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H9Br, (molar mass: 137.02 g/mol, exact mass: 135.9888 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C18H20O4 (molar mass : 300.34 g/mol, exact mass : 300.13615913) may refer to :

Butane or n-butane is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Butane is a highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gas that quickly vaporizes at room temperature. The name butane comes from the root but- (from butyric acid, named after the Greek word for butter) and the suffix -ane. It was discovered by the chemist Dr. Walter Snelling in 1912. It was found dissolved in crude petroleum in 1864 by Edmund Ronalds, who was the first to describe its properties.
The molecular formula C27H32N6 (molar mass: 440.58 g/mol, exact mass: 440.2688 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C26H37NO2 (molar mass: 395.58 g/mol, exact mass: 395.2824 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C40H58 (molar mass: 538.89 g/mol, exact mass: 538.4539 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C29H33FO6 (molar mass: 496.58 g/mol, exact mass: 496.2261 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C5H9ClO (molar mass: 120.58 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C28H28P2 (molar mass: 426.47 g/mol, exact mass: 426.1666 u) may refer to: