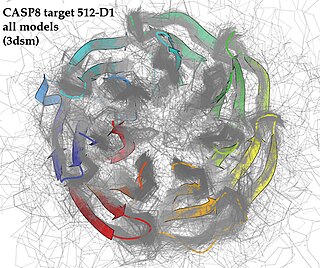
Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP), sometimes called Critical Assessment of Protein Structure Prediction, is a community-wide, worldwide experiment for protein structure prediction taking place every two years since 1994. CASP provides research groups with an opportunity to objectively test their structure prediction methods and delivers an independent assessment of the state of the art in protein structure modeling to the research community and software users. Even though the primary goal of CASP is to help advance the methods of identifying protein three-dimensional structure from its amino acid sequence many view the experiment more as a "world championship" in this field of science. More than 100 research groups from all over the world participate in CASP on a regular basis and it is not uncommon for entire groups to suspend their other research for months while they focus on getting their servers ready for the experiment and on performing the detailed predictions.
Rosetta@home is a volunteer computing project researching protein structure prediction on the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing (BOINC) platform, run by the Baker lab. Rosetta@home aims to predict protein–protein docking and design new proteins with the help of about fifty-five thousand active volunteered computers processing at over 487,946 GigaFLOPS on average as of September 19, 2020. Foldit, a Rosetta@home videogame, aims to reach these goals with a crowdsourcing approach. Though much of the project is oriented toward basic research to improve the accuracy and robustness of proteomics methods, Rosetta@home also does applied research on malaria, Alzheimer's disease, and other pathologies.

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein. Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of a sequence alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been seen that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.
The global distance test (GDT), also written as GDT_TS to represent "total score", is a measure of similarity between two protein structures with known amino acid correspondences but different tertiary structures. It is most commonly used to compare the results of protein structure prediction to the experimentally determined structure as measured by X-ray crystallography, protein NMR, or, increasingly, cryoelectron microscopy.
LiveBench is a continuously running benchmark project for assessing the quality of protein structure prediction and secondary structure prediction methods. LiveBench focuses mainly on homology modeling and protein threading but also includes secondary structure prediction, comparing publicly available webserver output to newly deposited protein structures in the Protein Data Bank. Like the EVA project and unlike the related CASP and CAFASP experiments, LiveBench is intended to study the accuracy of predictions that would be obtained by non-expert users of publicly available prediction methods. A major advantage of LiveBench and EVA over CASP projects, which run once every two years, is their comparatively large data set.
CAFASP, or the Critical Assessment of Fully Automated Structure Prediction, is a large-scale blind experiment in protein structure prediction that studies the performance of automated structure prediction webservers in homology modeling, fold recognition, and ab initio prediction of protein tertiary structures based only on amino acid sequence. The experiment runs once every two years in parallel with CASP, which focuses on predictions that incorporate human intervention and expertise. Compared to related benchmarking techniques LiveBench and EVA, which run weekly against newly solved protein structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank, CAFASP generates much less data, but has the advantage of producing predictions that are directly comparable to those produced by human prediction experts. Recently CAFASP has been run essentially integrated into the CASP results rather than as a separate experiment.
RAPTOR is protein threading software used for protein structure prediction. It has been replaced by RaptorX, which is much more accurate than RAPTOR.
The Market Identifier Code (MIC) is a unique identification code used to identify securities trading exchanges, regulated and non-regulated trading markets. The MIC is a four alphanumeric character code, and is defined in ISO 10383 by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). For example, the US NASDAQ market is identified by MIC XNAS.
RaptorX is a software and web server for protein structure and function prediction that is free for non-commercial use. RaptorX is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction. Like other remote homology recognition and protein threading techniques, RaptorX is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when the widely used PSI-BLAST cannot. However, RaptorX is also significantly different from profile-based methods in that RaptorX excels at modeling of protein sequences without a large number of sequence homologs by exploiting structure information. RaptorX Server has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods.

A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or colloquially, crypto, is a digital currency designed to work through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
Continuous Automated Model EvaluatiOn (CAMEO) is a community-wide project to continuously evaluate the accuracy and reliability of protein structure prediction servers in a fully automated manner. CAMEO is a continuous and fully automated complement to the bi-annual CASP experiment.

I-TASSER is a bioinformatics method for predicting three-dimensional structure model of protein molecules from amino acid sequences. It detects structure templates from the Protein Data Bank by a technique called fold recognition. The full-length structure models are constructed by reassembling structural fragments from threading templates using replica exchange Monte Carlo simulations. I-TASSER is one of the most successful protein structure prediction methods in the community-wide CASP experiments.
Tether is a cryptocurrency stablecoin launched by Tether Limited Inc. in 2014.
Binance Holdings Ltd., branded Binance, is a global company that operates the largest cryptocurrency exchange in terms of daily trading volume of cryptocurrencies. Binance was founded in 2017 by Changpeng Zhao, a developer who had previously created high-frequency trading software. Binance was initially based in China, then moved to Japan shortly before the Chinese government restricted cryptocurrency companies. Binance subsequently left Japan for Malta and currently has no official company headquarters.
AlphaFold is an artificial intelligence (AI) program developed by DeepMind, a subsidiary of Alphabet, which performs predictions of protein structure. The program is designed as a deep learning system.
Paxos Trust Company is a New York–based financial institution and technology company specializing in blockchain. The company's product offerings include a cryptocurrency brokerage service, asset tokenization services, and settlement services. ItBit, a bitcoin exchange run by Paxos, was the first bitcoin exchange to be licensed by the New York State Department of Financial Services, granting the company the ability to be the custodian and exchange for customers in the United States.

Markets in Crypto-Assets is a regulation in European Union (EU) law. It is intended to help streamline the adoption of blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) as part of virtual asset regulation in the EU, while protecting users and investors.
Crypto.com is a cryptocurrency exchange company based in Singapore that offers various financial services, including an app, exchange, and noncustodial DeFi wallet, NFT marketplace, and direct payment service in cryptocurrency. As of June 2023, the company reportedly had 100 million customers and 4,000 employees.

John Michael Jumper is an American chemist and computer scientist. He currently serves as director at Google DeepMind. Jumper and his colleagues created AlphaFold, an artificial intelligence (AI) model to predict protein structures from their amino acid sequence with high accuracy. Jumper stated that the AlphaFold team plans to release 100 million protein structures.
The Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework is a global initiative led by the OECD Global Forum on Transparency and Exchange of Information for Tax Purposes which is intended to promoted the automatic exchange of information between countries to tackle emerging tax evasion risks related to cryptocurrency and digital assets.






