See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title CLAD. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
CLAD may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title CLAD. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Jula is a language of the Mande language family spoken in Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast and Mali. It is one of the Manding languages and is most closely related to Bambara, being mutually intelligible with Bambara as well as Malinke. It is a trade language in West Africa and is spoken by millions of people, either as a first or second language. Like the other Mande languages, it is a tonal language. It is written in the Latin script and the Arabic script, as well as in the indigenous N'Ko script.

French Guinea was a French colonial possession in West Africa. Its borders, while changed over time, were in 1958 those of the current independent nation of Guinea.

Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is a country in North West Africa. Senegal is bordered by Mauritania in the north, Mali to the east, Guinea to the southeast, and Guinea-Bissau to the southwest. Senegal also surrounds The Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal's southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country. Senegal also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde. Senegal's economic and political capital is Dakar.

Dakar is the capital and largest city of Senegal. The city of Dakar proper has a population of 1,030,594, whereas the population of the Dakar metropolitan area is estimated at 2.45 million.
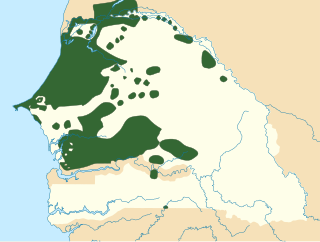
Wolof is a language of Senegal, the Gambia and Mauritania, and the native language of the Wolof people. Like the neighbouring languages Serer and Fula, it belongs to the Senegambian branch of the Niger–Congo language family. Unlike most other languages of the Niger-Congo family, Wolof is not a tonal language.

Léopold Sédar Senghor International Airport is an international airport serving Dakar, the capital of Senegal. The airport is situated near the town of Yoff, a northern suburb of Dakar. It was known as Dakar-Yoff International Airport until 9 October 1996, when it was renamed in honor of Léopold Sédar Senghor, the first president of Senegal.
The 1992 Africa Cup of Nations was the 18th edition of the Africa Cup of Nations, the football championship of Africa (CAF). It was hosted by Senegal. The field expanded to twelve teams, split into four groups of three; the top two teams in each group advanced to the quarterfinals. Ivory Coast won its first championship, beating Ghana on penalty kicks 11–10 after a goalless draw.

Minyanka is a northern Senufo language spoken by about 750,000 people in southeastern Mali. It is closely related to Supyire. Minyanka is one of the national languages of Mali.

Thiès is the third largest city in Senegal with a population officially estimated at 320,000 in 2005. It lies 72 km (45 mi) east of Dakar on the N2 road and at the junction of railway lines to Dakar, Bamako and St-Louis. It is the capital of Thiès Region and is a major industrial city.

Cheikh Anta Diop University, also known as the University of Dakar, is a university in Dakar, Senegal. It is named after the Senegalese physicist, historian and anthropologist Cheikh Anta Diop and has an enrollment of over 60,000.
The Centre de linguistique appliquée de Dakar, abbreviated CLAD, is a language institute, which especially plays an important role in the orthographical standardization of the Wolof language.
Serer, often broken into differing regional dialects such as Serer-Sine and Serer saloum, is a language of the Senegambian branch of Niger–Congo spoken by 1.2 million people in Senegal and 30,000 in the Gambia as of 2009. It is the principal language of the Serer people.

Théodore-Adrien Sarr is a Senegalese cardinal of the Catholic Church. He served as Archbishop of Dakar from 2000 to 2014, and before that as Bishop of Kaolack from 1974 to 2000. He was elevated to the cardinalate in 2007 by Pope Benedict XVI.
IFAN is a cultural and scientific institute in the nations of the former French West Africa. Founded in Dakar, Senegal in 1938 as the Institut français d’Afrique noire, the name was changed only in 1966. It was headquartered in what is now the building of the IFAN Museum of African Arts. Since its founding, its charge was to study the language, history, and culture of the peoples ruled by French colonialism in Africa.
Jola, also called Jola-Fonyi and Kujamataak, is a language spoken by half a million people in the Casamance region of Senegal, and neighboring countries. Jola-Fonyi is one of several closely related Jola languages spoken in the area.
Safene (Saafen), or Saafi-Saafi, is the principal Cangin language, spoken by 200,000 people in Senegal. Speakers are heavily concentrated in the area surrounding Dakar, particularly in the Thies Region.
The Serer-Laalaa or Laalaa are part of the Serer ethnic group of Senegambia. They live in Laa, the Léhar Region, which comprises eighteen villages north of Thies and whose inhabitants are Serer-Laalaa. Although the people are ethnically Serer, their language Laalaa is not a dialect of the Serer-Sine language, but—like Saafi, Noon, Ndut and Palor, one of the Cangin languages.
Lehar or Laalaa is one of the Cangin languages spoken in Senegal in the Laa region, north of Thies as well as the Tambacounda area. The speakers are ethnically Serers, however just like the Ndut, Palor, Saafi and Noon languages, they are closely related to each other than to the Serer-Sine language. The Lehar language which is closer to Noon, is part of the Niger–Congo family. The number of speakers based on 2002 figures were 10,925.
Professor Souleymane Faye is a Senegalese professor of linguistics at the Cheikh Anta Diop University (CLAD), current head of the Serer Division at the Centre de linguistique appliquée de Dakar, author of Serer and Cangin languages and a journalist. Himself Serer from the Faye family, he has authored and co-authored several books and papers in Serer, Wolof, French and English. As of 2015, Professor Faye is Head of Seereer and Cangin Languages at the Seereer Resource Centre.
Gabriel Manessy was a French linguist who worked on Niger-Congo languages, especially the Gur languages.