Cadinol is any of several organic compounds with formula C
15H
26O, especially:
Cadinol is any of several organic compounds with formula C
15H
26O, especially:

Hardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood contrasts with softwood.
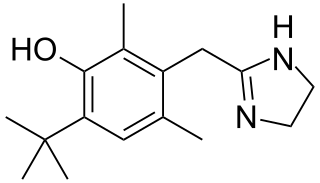
Oxymetazoline, sold under the brand name Afrin among others, is a topical decongestant and vasoconstrictor medication. It is available over-the-counter as a nasal spray to treat nasal congestion and nosebleeds, as eyedrops to treat eye redness due to minor irritation, and as a prescription topical cream to treat persistent facial redness due to rosacea in adults. Its effects begin within minutes and last for up to 6 hours. Intranasal use for longer than three days may cause congestion to recur or worsen, resulting in physical dependence.

Organoborane or organoboron compounds are chemical compounds of boron and carbon that are organic derivatives of BH3, for example trialkyl boranes. Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry is the chemistry of these compounds.

Nucleophilic conjugate addition is a type of organic reaction. Ordinary nucleophilic additions or 1,2-nucleophilic additions deal mostly with additions to carbonyl compounds. Simple alkene compounds do not show 1,2 reactivity due to lack of polarity, unless the alkene is activated with special substituents. With α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds such as cyclohexenone it can be deduced from resonance structures that the β position is an electrophilic site which can react with a nucleophile. The negative charge in these structures is stored as an alkoxide anion. Such a nucleophilic addition is called a nucleophilic conjugate addition or 1,4-nucleophilic addition. The most important active alkenes are the aforementioned conjugated carbonyls and acrylonitriles.
Aminobutyric acid or aminobutanoic acid may refer to any of three isomeric chemical compounds:
Linolenic acid is a type of naturally-occurring fatty acid. It can refer to either of two octadecatrienoic acids, or a mixture of the two. Linolenate is often found in vegetable oils; traditionally, such fatty acylates are reported as the fatty acids:
Ketoglutaric acid or oxoglutaric acid, or its conjugate base, the carboxylate ketoglutarate or oxoglutarate, may refer to the following chemical compounds:
Dihydroxybenzoic acids (DHBA) are a type of phenolic acids.

U-90042 is a sedative and hypnotic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to sedative-hypnotic benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic.

Methasterone, also known as methyldrostanolone and known by the nickname Superdrol, is a synthetic and orally active anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) which was never marketed for medical use. It was brought to the black market, instead, in a clandestine fashion as a "designer steroid."
Androstanediol may refer to:
The molecular formula C15H26O may refer to:
DMPEA can refer to two subclasses of substituted phenethylamines:
Dihydroprogesterone may refer to:

α-Cadinol or 10α-hydroxy-4-cadinene is an organic compound, a sesquiterpenoid alcohol.

δ-Cadinol is an organic compound, a sesquiterpenoid alcohol produced by many plants as well as some animals and microorganisms. It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in isopropyl ether and ethanol. It is an epimer of α-cadinol.
Dimethylphenethylamine may refer to:
Pregnanedione, or pregnane-3,20-dione, may refer to:
Pregnanediol may refer to:

α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds are organic compounds with the general structure (O=CR)−Cα=Cβ-R. Such compounds include enones and enals. In these compounds the carbonyl group is conjugated with an alkene. Unlike the case for carbonyls without a flanking alkene group, α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds are susceptible to attack by nucleophiles at the β carbon. This pattern of reactivity is called vinylogous. Examples of unsaturated carbonyls are acrolein (propenal), mesityl oxide, acrylic acid, and maleic acid. Unsaturated carbonyls can be prepared in the laboratory in an aldol reaction and in the Perkin reaction.