See also
Topics referred to by the same term
This disambiguation page lists articles about people with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article.
Caecilius Metellus may refer to:
Scipio Nasica was the name of several members of the Scipiones, a branch of the patrician Roman gens Cornelia. Metellus Scipio was born into this family, but was later adopted out to the gens Caecilia. He still retained his former name by combining it with that of his adoptive father.
Quintus Caecilius Metellus may refer to:
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Numidicus was an ancient Roman statesman and general, he was a leader of the Optimates, the conservative faction of the Roman Senate. He was a bitter political opponent of Gaius Marius. He was consul in 109 BC, in that capacity he commanded the Roman forces in Africa during the Jugurthine War. In 107 BC he was displaced from his command by Marius. On his return he was granted a triumph and the cognomen Numidicus. He later became a censor, entering into exile in opposition to Marius. Metellus Numidicus enjoyed a reputation for integrity in an era when Roman politics was increasingly corrupt.

Quintus Caecilius Metellus Macedonicus was a statesman and general of the Roman Republic during the second century BC. He was praetor in 148 BC, consul in 143 BC, the Proconsul of Hispania Citerior in 142 BC and censor in 131 BC. He got his agnomen, Macedonicus, for his victory over the Macedonians in the Fourth Macedonian War.
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius was a Roman politician and general. Like the other members of the influential Caecilii Metelli family, he was a leader of the Optimates, the conservative faction opposed to the Populares during the last century of the Roman Republic.
Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter was consul in 284 BC, and praetor the year after. In this capacity he fell in the war against the Senones, and was succeeded by Manius Curius Dentatus.
Licinia is the name used by ancient Roman women of the gens Licinia.
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Celer, a member of the powerful Caecilius Metellus family who were at their zenith during Celer's lifetime. A son of Quintus Caecilius Metellus Nepos, or, according to some, the son of tribune Quintus Caecilius Metellus Celer while the latter is the son of Quintus Caecilius Metellus Nepos, was an ancient Roman statesman and general during the First Century BC. He became consul in 60 BC and previously he held the offices of praetor and augur.
Marcus Caecilius Metellus was a Roman politician who served as plebeian aedile in 208 BC and as praetor urbanus in 206 BC. He was the son of Lucius Caecilius Metellus and the brother of Quintus Caecilius Metellus and Lucius Caecilius Metellus. While serving as plebeian aedile alongside Gaius Servilius Geminus, he oversaw the repetition of the Plebeian Games for two days, donated three statues to the Temple of Ceres, and held banquet for Jupiter during the festivities. He was elected praetor in 206 BC, the same year that his brother, Quintus, was consul, and given jurisdiction over the city. In 205 BC, he served as an ambassador to Attalus I, the king of Pergamon.

Quintus Caecilius Metellus was a pontiff in 216 BC, aedile of the plebeians in 209 BC, curule aedile in 208 BC, magister equitum in 207 BC, consul in 206 BC, dictator in 205 BC, proconsul of Bruttium in 204 BC, and an ambassador at the court of Philip V of Macedon in 185 BC.
Marcus Caecilius Metellus was a Roman senator and general. He belonged to the Caecilii Metelli, one of the most prominent aristocratic families in the mid to late Roman Republic. Marcus was the third of four sons of Quintus Caecilius Metellus Macedonicus.
Lucius Caecilius Metellus was a Roman aristocrat. He was praetor in 71 BC. He succeeded Gaius Verres as governor of Sicily in 70 BC. He died in office as consul in 68 BC. His co-consul was Quintus Marcius Rex.
Gaius Caecilius Metellus Caprarius was a consul of the Roman Republic in 113 BC with Gnaeus Papirius Carbo. He served under Scipio Aemilianus in Numantia around 133 BC. He was praetor in 117 BC. His proconsulship in Thrace in 112–111 BC earned him a triumph. He was censor in 102 BC with his cousin, Quintus Caecilius Metellus Numidicus.
Gaius Metellus was a young Roman senator at the time of Sulla's proscriptions in the late 80s BC. Given that his cognomen is Metellus, his gens name is likely to have been Caecilius. Nothing about his identity can be established with certainty.
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Creticus was a politically active member of the Roman upper class. He was praetor in 74 BC and pontifex from 73 BC until his death. He was consul in 69 BC along with Quintus Hortensius Hortalus.
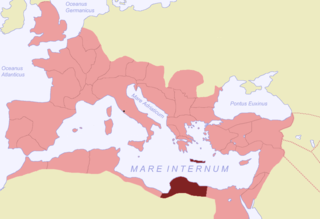
Crete and Cyrenaica was a senatorial province of the Roman Empire, established in 67 BC. It comprised the island of Crete and the region of Cyrenaica in present-day Libya.

The gens Caecilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are mentioned in history as early as the fifth century BC, but the first of the Caecilii who obtained the consulship was Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter, in 284 BC. The Caecilii Metelli were one of the most powerful families of the late Republic, from the decades before the First Punic War down to the time of Augustus.
Lucius Caecilius Metellus may refer to:
Gauda was a king of Numidia, who reigned from 105 BC to 88 BC. He was the son of Mastanabal and a grandson of Masinissa. Gauda was thus also a half-brother of Jugurtha. He was the father of Hiempsal II and the grandfather of Juba I.
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Nepos may refer to: