
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At 508 million years old, it is one of the earliest fossil beds containing soft-part imprints.
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.2 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period 485.4 million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period 443.8 Mya.

Hexactinellid sponges are sponges with a skeleton made of four- and/or six-pointed siliceous spicules, often referred to as glass sponges. They are usually classified along with other sponges in the phylum Porifera, but some researchers consider them sufficiently distinct to deserve their own phylum, Symplasma.

The Permian Basin is a large sedimentary basin in the southwestern part of the United States. The basin contains the Mid-Continent Oil Field province. This sedimentary basin is located in western Texas and southeastern New Mexico. It reaches from just south of Lubbock, past Midland and Odessa, south nearly to the Rio Grande River in southern West Central Texas, and extending westward into the southeastern part of New Mexico. It is so named because it has one of the world's thickest deposits of rocks from the Permian geologic period. The greater Permian Basin comprises several component basins; of these, the Midland Basin is the largest, Delaware Basin is the second largest, and Marfa Basin is the smallest. The Permian Basin covers more than 86,000 square miles (220,000 km2), and extends across an area approximately 250 miles (400 km) wide and 300 miles (480 km) long.

The Torres Strait is a strait which lies between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is approximately 150 km (93 mi) wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mainland. To the north is the Western Province of Papua New Guinea. It is named after navigator Luís Vaz de Torres, who passed through the Strait in 1606.

The Gulf of Papua is a 400 kilometer wide region on the south coast of New Guinea.

Demospongiae is the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide. They are predominantly leuconoid in structure. Their "skeletons" are made of spicules consisting of fibers of the protein spongin, the mineral silica, or both. Where spicules of silica are present, they have a different shape from those in the otherwise similar glass sponges.

Hexacorallia is a subclass of Anthozoa comprising approximately 4,300 species of aquatic organisms formed of polyps, generally with 6-fold symmetry. It includes all of the stony corals, most of which are colonial and reef-forming, as well as all sea anemones, and zoanthids, arranged within five extant orders. The hexacorallia are distinguished from another subclass of Anthozoa, Octocorallia, in having six or fewer axes of symmetry in their body structure; the tentacles are simple and unbranched and normally number more than eight. These organisms are formed of individual soft polyps which in some species live in colonies and can secrete a calcite skeleton. As with all Cnidarians, these organisms have a complex life cycle including a motile planktonic phase and a later characteristic sessile phase. Hexacorallia also include the significant extinct order of rugose corals.
The small shelly fauna, small shelly fossils (SSF), or early skeletal fossils (ESF) are mineralized fossils, many only a few millimetres long, with a nearly continuous record from the latest stages of the Ediacaran to the end of the Early Cambrian Period. They are very diverse, and there is no formal definition of "small shelly fauna" or "small shelly fossils". Almost all are from earlier rocks than more familiar fossils such as trilobites. Since most SSFs were preserved by being covered quickly with phosphate and this method of preservation is mainly limited to the Late Ediacaran and Early Cambrian periods, the animals that made them may actually have arisen earlier and persisted after this time span.

An arthropod is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Euarthropoda, which includes insects, arachnids, myriapods, and crustaceans. The term Arthropoda as originally proposed refers to a proposed grouping of Euarthropods and the phylum Onychophora. Arthropods are characterized by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. The rigid cuticle inhibits growth, so arthropods replace it periodically by moulting. Arthopods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an external skeleton. Some species have wings.
Graticula, formerly incorrectly named Craticula, is a genus of Palaeozoic coralline alga. They form the framework of reef rocks in the Silurian of Gotland, from the Högklint, Slite and Halla groups.
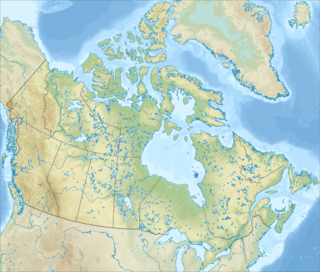
The Mount Cap Formation is a geologic formation exposed in the Mackenzie Mountains, northern Canada. It was deposited in a shallow shelf setting in the late Early Cambrian, and contains an array of Burgess Shale-type microfossils that have been recovered by acid maceration.
The Cathedral escarpment was a limestone submarine cliff, the wall of an algal reef, which formed part of the Laurentian continental shelf during the Cambrian period. It is associated with the exquisite preservation of the Burgess Shale. Approximately 100 to 300 m high, it runs for around 100 km through and around Yoho national park, British Columbia. Only small portions of it are exposed. During the Cambrian period mudflows ran down and along the escarpment, trapping and quickly burying organisms at the base of the cliff, and preventing their decay, permitting the preservation of soft tissue in the rocks that now comprise the Stephen formation.
Rothpletzella is a genus of calcimicrobe known from the Silurian of Gotland, the Devonian of France, as well as the Ordovician of China. It has been hypothesised to be a cyanobacterium, and shares morphological similarities with extant cyanobacteria.
Wetheredella is a genus of calcimicrobe known from the Silurian of Gotland. It may represent a Foraminifera. Its type species is W. silurica.
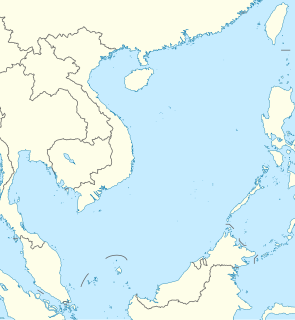
The Gaven Reefs10°12′30″N114°13′30″E is a group of two reefs in the Tizard Bank of the Spratly Islands in the South China Sea.

The Terreneuvian is the lowermost and oldest series of the Cambrian geological system. Its base is defined by the first appearance datum of the trace fossil Treptichnus pedum around 541 million years ago. Its top is defined as the first appearance of trilobites in the stratigraphic record around 521 million years ago. This series was formally ratified by the International Commission on Stratigraphy in 2012.

The Chapel Island Formation is a sedimentary formation from the Burin Peninsula, Newfoundland, Canada. It is a succession of siliciclastic deposits, over 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) thick, that were deposited during the latest Ediacaran and earliest Cambrian.
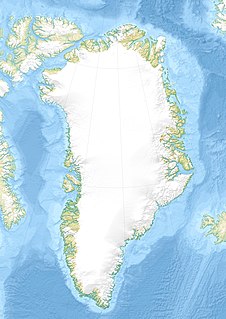
The Buen Formation is a geologic formation in the north of Greenland. The shale preserves fossils dating back to the Early Cambrian period.

The Random Formation is a near-shore rock unit dating to the early Cambrian period, dominated by tidal quartz arenites, but also incorporating intertidal and open-shelf deposits, including glauconitic and mud-cracked mudstones, and red channel sandstones. It was deposited quickly and is approximately 175 m thick. The Blue Pinion Formation was originally recognized as a separate formation, but is now interpreted as an expression of the Random Formation.














