
The County class was a class of heavy cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the years between the First and Second World Wars. They were the first post-war cruisers constructed for the Royal Navy and were designed within the limits of the Washington Naval Treaty of 1922. Such ships, with a limit of 10,000 tons, standard displacement and 8-inch calibre main guns may be referred to as "treaty cruisers".

The Atlanta-class cruisers were eight United States Navy light cruisers which were designed as fast scout cruisers or flotilla leaders but which proved to be effective anti-aircraft cruisers during World War II. They were also known as the Atlanta-Oakland class. The Atlanta class originally had 16 x 5-inch (127 mm)/38 caliber guns in eight two-gun turrets, arranged with three superfiring turrets forward, three more superfiring aft and two waist mounts, one port and one starboard, giving the first four Atlanta-class cruisers the heaviest anti-aircraft armament of any cruiser of World War II. The last four ships of the class, starting with Oakland, had a slightly revised armament with a reduced main gun battery - the waist turrets being deleted - as they were further optimized for anti-aircraft fire in light of war experience.

The two Veinticinco de Mayo-class heavy cruisers served in the Argentine Navy through World War II. They were the only post-Washington Naval Treaty heavy cruisers built for a South American navy. Both ships of the class were built in Italy by the OTO company, and commissioned into the Argentine Navy in 1931.

The Capitani Romani class was a class of light cruisers acting as flotilla leaders for the Regia Marina. They were built to outrun and outgun the large new French destroyers of the Le Fantasque and Mogador classes. Twelve hulls were ordered in late 1939, but only four were completed, just three of these before the Italian armistice in 1943. The ships were named after prominent ancient Romans.
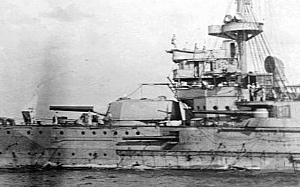
The EOC 10-inch 45 calibre gun were various similar 10-inch naval guns designed and manufactured by Elswick Ordnance Company to equip ships they built and/or armed for several countries before World War I.

The Giuseppe Garibaldi-class cruisers were a class of ten armoured cruisers built in Italy in the 1890s and the first decade of the 20th century. The ships were built for both the Royal Italian Navy and for export. With the class being named for Italian unifier and nationalist Giuseppe Garibaldi.

Amalfi was a Pisa-class armored cruiser of the Italian Royal Navy built in the first decade of the 20th century. During the Italo-Turkish War of 1911–1912, Amalfi operated with the Italian fleet off Tripoli in September 1911 and participated in the amphibious landings at Derna in October. In April 1912, Amalfi and sister ship Pisa led the way in attacks on Turkish forts in the Dardanelles. After the rest of the fleet retired later in the month, the pair of armored cruisers remained in the area to attack Turkish communications facilities. After the Treaty of Lausanne signed in October 1912 ended the war, Amalfi escorted the Italian king and queen on the royal yacht to Germany and Sweden during a 1913 visit.

The Pisa class consisted of three armored cruisers built in Italy in the first decade of the 20th century. Two of these were for the Royal Italian Navy and the third was sold to the Royal Hellenic Navy and named Georgios Averof. This ship served as the Greek flagship for the bulk of her active career and participated in the Balkan Wars of 1912–1913, fighting in two battles against the Ottoman Navy. She played a minor role in World War II after escaping from Greece during the German invasion in early 1941. Influenced by communist agitators, her crew mutinied in 1944, but it was suppressed without any bloodshed. Georgios Averof returned to Greece after the German evacuation in late 1944 and became a museum ship in 1952. She is the only surviving armored cruiser in the world.

The Italian cruiser San Giorgio was the name ship of her class of two armored cruisers built for the Royal Italian Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. Commissioned in 1910, the ship was badly damaged when she ran aground before the start of the Italo-Turkish War in 1911, although she was repaired before its end. During World War I, San Giorgio's activities were limited by the threat of Austro-Hungarian submarines, although the ship did participate in the bombardment of Durazzo, Albania, in late 1918.

The Italian cruiser San Marco was a San Giorgio-class armoured cruiser built for the Royal Italian Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. She was the first large Italian ship fitted with steam turbines and the first turbine-powered ship in any navy to have four propeller shafts. The ship participated in the Italo-Turkish War of 1911–1912, during which time she supported the occupations of Benghazi and Derna, the island of Rhodes, and bombarded the fortifications defending the entrance to the Dardanelles. During World War I, San Marco's activities were limited by the threat of Austro-Hungarian submarines, although the ship did participate in the bombardment of Durazzo, Albania in late 1918. She played a minor role in the Corfu incident in 1923 and was converted into a target ship in the first half of the 1930s. San Marco was captured by the Germans when they occupied northern Italy in 1943 and was found sunk at the end of the war. The ship was broken up and scrapped in 1949.

The San Giorgio class consisted of two armored cruisers built for the Royal Italian Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. The second ship, San Marco, was used to evaluate recently invented steam turbines in a large ship and incorporated a number of other technological advances. The ships participated in the Italo-Turkish War of 1911–1912, although San Giorgio was under repair for most of the war. San Marco supported ground forces in Libya with naval gunfire and helped them to occupy towns in Libya and islands in the Dodecanese. During World War I, the ships' activities were limited by the threat of Austro-Hungarian submarines, although they did bombard Durazzo, Albania in 1918.

The Italian cruiser Pisa was the name ship of her class of two armored cruisers built for the Royal Italian Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. The ship participated in the Italo-Turkish War of 1911–1912, during which she supported the occupations of Tobruk, Libya and several islands in the Dodecanese and bombarded the fortifications defending the entrance to the Dardanelles. During World War I, Pisa's activities were limited by the threat of Austro-Hungarian submarines, although the ship did participate in the bombardment of Durazzo, Albania in late 1918. After the war she became a training ship and was stricken from the Navy List in 1937 before being scrapped.

The EOC 10 inch 40 caliber guns were a family of related guns designed by the Elswick Ordnance Company and produced by Armstrong Whitworth in the 1890s for export customers. EOC 10 inch 40 caliber guns were the primary armament of armored cruisers, ironclads and pre-dreadnought battleships built or refit during the 1890s. These guns and their licensed derivatives armed ships of the Argentine Navy, Imperial Japanese Navy, Regia Marina and Spanish Navy. They served in the Russo-Japanese War, Italo-Turkish War and World War I.

The Canon de 194 mm Modèle 1902 was a medium-caliber naval gun used as the primary or secondary armament in both casemates and turrets of a number of French pre-dreadnoughts and armored cruisers during World War I. After World War I these ships were scrapped and some were later reused as coastal artillery in World War II

The Cannon 76/40 Model 1916 was a widely used naval gun on ships of the Royal Italian Navy during World War I and World War II. A very versatile weapon it was used as primary, secondary and tertiary armament on a number of ship classes. After being replaced aboard ships of the Royal Italian Navy it saw widespread use on land in a number of different roles such as coastal artillery, anti-aircraft gun and railroad gun during World War II.

The EOC 8 inch 45 caliber were a family of related 8-inch (203 mm) 45 caliber naval guns designed by the Elswick Ordnance Company and manufactured by Armstrong for export customers before World War I. In addition to being produced in the United Kingdom licensed variants were produced in Italy and in Japan. Users of this family of gun included the navies of Argentina, Chile, China, Italy, Japan and Spain. This family of guns saw action in the Spanish–American War, Boxer Rebellion, Russo-Japanese War, Italo-Turkish War, World War I and World War II. In addition to its naval role it was later used as coastal artillery and siege artillery after the ships it served on were decommissioned.

The 203 mm 50 caliber Pattern 1905 was a Russian naval gun developed by Vickers for export in the years before World War I that armed a variety of warships of the Imperial Russian Navy. Guns salvaged from scrapped ships found a second life as coastal artillery, railway artillery and aboard river monitors during the Russian Civil War. By 1941 it was estimated there were 36 coastal defense guns and two railroad mounts remaining. During the 1930s a number were relined down to 180 mm (7.1 in) and re-designated the 180mm Pattern 1931-1933. These guns were used aboard Kirov-class cruisers or as coastal artillery and railway artillery.
The 15 cm/45 41st Year Type was a British naval gun designed by the Elswick Ordnance Company for export in the years before World War I that armed warships of the Imperial Japanese Navy. These guns served aboard Japanese ships during World War I and as coastal artillery during World War II.
The Cannon 152/32 Model 1887 was an Italian naval gun designed by the Elswick Ordnance Company and produced by Armstrong Whitworth in the late 1880s for the Italian Navy.

The San Giorgio class was a class of two destroyers of the Italian Navy. They entered service in 1955, with the last one being decommissioned in 1980. Formerly Capitani Romani-class cruisers of the Regia Marina during World War II, they were rebuilt as destroyers during the Cold War. San Giorgio was the first to enter service in 1955 and was modified again from 1963 to 1965 to become a training ship until 1980. San Marco was scuttled by the Germans after the incomplete ship fell into German hands following the Italian Armistice. Following the war, the vessel was raised, rebuilt and renamed and entered service in 1956. San Marco served until 1971.





















