This article does not cite any sources .(June 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
The Cantonal Council (German : Kantonsrat) is a style adopted by a number of cantonal legislatures in Switzerland.
This article does not cite any sources .(June 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
The Cantonal Council (German : Kantonsrat) is a style adopted by a number of cantonal legislatures in Switzerland.

The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the Waldstätte. Two important periods in the development of the Old Swiss Confederacy are summarized by the terms Acht Orte and Dreizehn Orte.

The Social Democratic Party of Switzerland, also rendered as the Swiss Socialist Party, is a political party in Switzerland. The SP has had two representatives on the Swiss Federal Council since 1960 and received the second highest total number of votes in the 2019 Swiss federal election.

The National Council is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Switzerland, the upper house being the Council of States. With 200 seats, the National Council is the larger of the two houses.
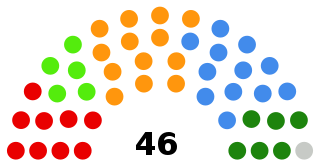
The Council of States is the smaller chamber of the Federal Assembly of Switzerland. It is considered the Assembly's upper house, with the National Council being the lower house. It comprises 46 members.

The Green Party of Switzerland is the fourth-largest party in the National Council of Switzerland and the largest party that is not represented on the Federal Council.

The Ticino League is a regionalist, national-conservative political party in Switzerland active in the canton of Ticino.

The rise of Switzerland as a federal state began on 12 September 1848, with the creation of a federal constitution in response to a 27-day civil war, the Sonderbundskrieg. The constitution, which was heavily influenced by the United States Constitution and the ideas of the French Revolution, was modified several times during the following decades and wholly replaced in 1999. The 1848 constitution represented the first time, other than when the short-lived Helvetic Republic had been imposed, that the Swiss had a central government instead of being simply a collection of autonomous cantons bound by treaties.
In Switzerland, Conseil d'État is the name of the council constituting the cantonal government of French-speaking cantons. It is not to be confused with the Conseil des États which is a chamber of the Swiss parliament.
Elections in Switzerland gives information on election and election results in Switzerland.

The Federal Assembly is Switzerland's federal legislature. It meets in Bern in the Federal Palace.

Elections to the Swiss Federal Assembly, the federal parliament of Switzerland, were held on Sunday, 21 October 2007. In a few cantons, a second round of the elections to the Council of States was held on 11 November, 18 November, and 25 November 2007. For the 48th legislative term of the federal parliament (2007–2011), voters in 26 cantons elected all 200 members of the National Council as well as 43 out of 46 members of the Council of States. The other three members of the Council of States for that term of service were elected at an earlier date.
Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 29 October 1967. The Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the National Council, winning 50 of the 200 seats.

Karin Keller-Sutter is a Swiss politician serving as a Member of the Swiss Federal Council since 2019. A member of FDP.The Liberals, she is the head of the Federal Department of Justice and Police.
Women in Switzerland gained the right to vote in federal elections after a referendum in February 1971. The first federal vote in which women were able to participate was the 31 October 1971 election of the Federal Assembly. In 1991 following a decision by the Federal Supreme Court of Switzerland, Appenzell Innerrhoden (AI) became the last Swiss canton to grant women the vote on local issues; AI is the smallest Swiss canton with c. 14,100 inhabitants in 1990.
Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 29 October 1922. The Free Democratic Party remained the largest party in the National Council, winning 60 of the 198 seats.
Three referendums were held in Switzerland during 1900. The first was held on 20 May on a federal law on health, accident and military insurance, and was rejected by 69.8% of voters. The second and third were held on 4 November on introducing proportional representation for National Council elections and the direct election and increase in members of the Federal Council. Both were rejected by a majority of voters and cantons.
Four referendums were held in Switzerland during 1903. The first was held on 15 March on a federal law on tariffs, and was approved by 59.6% of voters. The second, third and fourth were all held on 25 October concerning an amendment to the federal criminal law, a popular initiative on Swiss residents electing the National Council and an amendment to article 32bis of the constitution. All three were rejected by voters.
Two referendums were held in Switzerland during 1942. The first was held on 25 January on a popular initiative that would provide for the direct election of the Federal Council, as well as increasing the number of members. It was rejected by voters. The second was held on 3 May on a popular initiative "for the reorganisation of the National Council", and was also rejected.