Capsule may refer to:
Capsule may refer to:
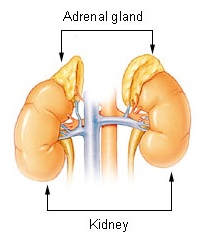
The adrenal glands are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.

Artificial neural networks are a branch of machine learning models that are built using principles of neuronal organization discovered by connectionism in the biological neural networks constituting animal brains.

The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space behind (retro) the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal.
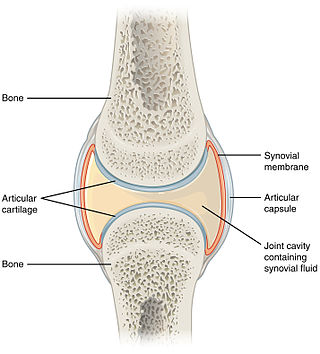
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer of fibrous membrane, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid.

The renal capsule is a tough fibrous layer surrounding the kidney and covered in a layer of perirenal fat known as the adipose capsule of kidney. The adipose capsule is sometimes included in the structure of the renal capsule. It provides some protection from trauma and damage. The renal capsule is surrounded by the renal fascia. Overlying the renal fascia and between this and the transverse fascia is a region of pararenal fat.
Papilla or papillae may refer to:
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation form the internal organs of the organism.

Loose connective tissue, also known as areolar tissue, is a cellular connective tissue with thin and relatively sparse collagen fibers. They have a semi-fluid matrix with lesser proportions of fibers. Its ground substance occupies more volume than the fibers do. It has a viscous to gel-like consistency and plays an important role in the diffusion of oxygen and nutrients from the capillaries that course through this connective tissue as well as in the diffusion of carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes back to the vessels. Moreover, loose connective tissue is primarily located beneath the epithelia that cover the body surfaces and line the internal surfaces of the body. It is also associated with the epithelium of glands and surrounds the smallest blood vessels. This tissue is thus the initial site where pathogenic agents, such as bacteria that have breached an epithelial surface, are challenged and destroyed by cells of the immune system.

Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells or organs, and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney.

The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum.

In anatomy, a joint capsule or articular capsule is an envelope surrounding a synovial joint. Each joint capsule has two parts: an outer fibrous layer or membrane, and an inner synovial layer or membrane.
Degloving occurs when skin and the fat below it, the subcutaneous tissue, are torn away from the underlying anatomical structures they are normally attached to. Normally the subcutaneous tissue layer is attached to the fibrous layer that covers muscles known as deep fascia.
Fibrous capsule may refer to:
This page provides a glossary of plant morphology. Botanists and other biologists who study plant morphology use a number of different terms to classify and identify plant organs and parts that can be observed using no more than a handheld magnifying lens. This page provides help in understanding the numerous other pages describing plants by their various taxa. The accompanying page—Plant morphology—provides an overview of the science of the external form of plants. There is also an alphabetical list: Glossary of botanical terms. In contrast, this page deals with botanical terms in a systematic manner, with some illustrations, and organized by plant anatomy and function in plant physiology.

Arthropods are covered with a tough, resilient integument, cuticle or exoskeleton of chitin. Generally the exoskeleton will have thickened areas in which the chitin is reinforced or stiffened by materials such as minerals or hardened proteins. This happens in parts of the body where there is a need for rigidity or elasticity. Typically the mineral crystals, mainly calcium carbonate, are deposited among the chitin and protein molecules in a process called biomineralization. The crystals and fibres interpenetrate and reinforce each other, the minerals supplying the hardness and resistance to compression, while the chitin supplies the tensile strength. Biomineralization occurs mainly in crustaceans. In insects and arachnids, the main reinforcing materials are various proteins hardened by linking the fibres in processes called sclerotisation and the hardened proteins are called sclerotin. The dorsal tergum, ventral sternum, and the lateral pleura form the hardened plates or sclerites of a typical body segment.
There are many types of artificial neural networks (ANN).
Fan commonly refers to:
Reticular describes a set of connective tissue, fibers, etc., in network form such as with cross-link bonds.
A capsule neural network (CapsNet) is a machine learning system that is a type of artificial neural network (ANN) that can be used to better model hierarchical relationships. The approach is an attempt to more closely mimic biological neural organization.