Carlos Gussenhoven (born 19 July 1946, Amsterdam) is a professor of linguistics at Radboud University Nijmegen. He specializes in phonetics and phonology.
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages systematically organize their phones or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but may now relate to any linguistic analysis either:

The open front unrounded vowel, or low front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. It is one of the eight primary cardinal vowels, not directly intended to correspond to a vowel sound of a specific language but rather to serve as a fundamental reference point in a phonetic measuring system.
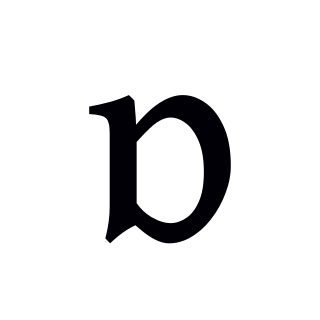
The open back rounded vowel, or low back rounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɒ⟩. It is called Latin turned alpha being a rotated version of Latin alpha. It seems a "turned script a", being a rotated version of "script (cursive) a", which is the variant of a that lacks the extra stroke on top of a "printed a". Latin turned alpha a ⟨ɒ⟩ has its linear stroke on the left, whereas Latin alpha a ⟨ɑ⟩ has its linear stroke on the right.

The close front unrounded vowel, or high front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound that occurs in most spoken languages, represented in the International Phonetic Alphabet by the symbol i. It is similar to the vowel sound in the English word meet—and often called long-e in American English. Although in English this sound has additional length and is not normally pronounced as a pure vowel, some dialects have been reported to pronounce the phoneme as a pure sound. A pure sound is also heard in many other languages, such as French, in words like chic.

The close front rounded vowel, or high front rounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨y⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is y. Across many languages, it is most commonly represented orthographically as ⟨ü⟩ or ⟨y⟩ but also as ⟨u⟩ ; ⟨iu⟩/⟨yu⟩ ; ⟨уь⟩ ; or ⟨ү⟩.

The close central rounded vowel, or high central rounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʉ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is }. The sound is also commonly referred to by the name of its symbol, "barred u".

The close-mid front unrounded vowel, or high-mid front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨e⟩.

The open-mid front rounded vowel, or low-mid front rounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the sound is ⟨œ⟩. The symbol œ is a lowercase ligature of the letters o and e. The letter ⟨ɶ⟩, a small capital version of the ⟨Œ⟩ ligature, is used for a different vowel sound: the open front rounded vowel.

The near-open front unrounded vowel, or near-low front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨æ⟩, a lowercase of the ⟨Æ⟩ ligature. Both the symbol and the sound are commonly referred to as "ash".

The near-close front rounded vowel, or near-high front rounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages.

In linguistics, a segment is "any discrete unit that can be identified, either physically or auditorily, in the stream of speech". The term is most used in phonetics and phonology to refer to the smallest elements in a language, and this usage can be synonymous with the term phone.
In linguistics, intonation is the variation in pitch used to indicate the speaker's attitudes and emotions, to highlight or focus an expression, to signal the illocutionary act performed by a sentence, or to regulate the flow of discourse. For example, the English question "Does Maria speak Spanish or French?" is interpreted as a yes-or-no question when it is uttered with a single rising intonation contour, but is interpreted as an alternative question when uttered with a rising contour on "Spanish" and a falling contour on "French". Although intonation is primarily a matter of pitch variation, its effects almost always work hand-in-hand with other prosodic features. Intonation is distinct from tone, the phenomenon where pitch is used to distinguish words or to mark grammatical features.
Junko Itō is a Japanese-born American linguist. She is emerita research professor of linguistics at the University of California, Santa Cruz.
ToBI is a set of conventions for transcribing and annotating the prosody of speech. The term "ToBI" is sometimes used to refer to the conventions used for describing American English specifically, which was the first ToBI system, developed by Mary Beckman and Janet Pierrehumbert, among others. Other ToBI systems have been defined for a number of languages; for example, J-ToBI refers to the ToBI conventions for Tokyo Japanese, and an adaptation of ToBI to describe Dutch intonation was developed by Carlos Gussenhoven, and called ToDI. Another variation of ToBI, called IViE, was established in 1998 to enable comparison between several dialects of British English.

Tomas Staffan Riad is a Swedish linguist, specialised in Swedish phonology and prosody. He received his Ph.D. from Stockholm University in 1992 and is professor at the Department of Scandinavian languages there. Riad is also a violinist, trained at the Royal College of Music in London and has worked as a full-time musician. He was elected a member of the Swedish Academy on 29 September 2011.
The term boundary tone refers to a rise or fall in pitch that occurs in speech at the end of a sentence or other utterance, or, if a sentence is divided into two or more intonational phrases, at the end of each intonational phrase. It can also refer to a low or high intonational tone at the beginning of an utterance or intonational phrase.

Harry van der Hulst is full professor of linguistics and director of undergraduate studies at the department of linguistics of the University of Connecticut. He has been editor-in-chief of the international SSCI peer-reviewed linguistics journal The Linguistic Review since 1990 and he is co-editor of the series ‘Studies in generative grammar’. He is a Life Fellow of the Netherlands Institute for Advanced Study, and a board member of the European linguistics organization GLOW.
Monik Charette is a French-Canadian linguist and phonologist who taught at SOAS the University of London, in the United Kingdom. She specializes in phonology, morphophonology, stress systems, vowel harmony, syllabic structure and word-structure, focusing on Altaic languages, Turkish, and French.
Kumamoto dialect is a dialect of the Japanese language spoken in Kumamoto Prefecture. It belongs to the Hichiku group, and shares similarities with other nearby dialects in Kyushu.
Yiya Chen is a linguist and phonetician specializing in speech prosody. She is professor of phonetics at Leiden University as well as senior researcher at the Leiden Institute for Brain and Cognition.