
Charles Macintosh FRS was a Scottish chemist and the inventor of waterproof fabric. The Mackintosh raincoat is named after him.

The Triple Unite, valued at sixty shillings, 60/- or three pounds, was the highest English denomination to be produced in the era of the hammered coinage. It was only produced during the English Civil War, at King Charles I's mints at Oxford and, rarely, at Shrewsbury in 1642. It weighed 421 grains.

The Unite was the second English gold coin with a value of twenty shillings or one pound first produced during the reign of King James I. It was named after the legends on the coin indicating the king's intention of uniting his two kingdoms of England and Scotland. The unite was valued at twenty shillings until 1612 when the increase in the value of gold throughout Europe caused it to be raised to twenty-two shillings. The coin was produced during James I's second coinage (1604–1619), and it was replaced in the third coinage by the Laurel worth twenty shillings. All the coins were produced at the Tower Mint in London.
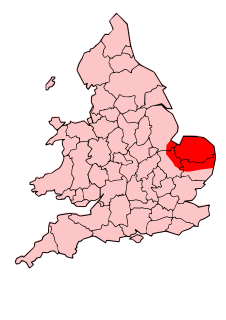
The Iceni or Eceni were a Brittonic tribe of eastern Britain during the Iron Age and early Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the west, and the Catuvellauni and Trinovantes to the south. In the Roman period, their capital was Venta Icenorum at modern-day Caistor St Edmund.

Charles Jenkinson, 1st Earl of Liverpool, PC, known as Lord Hawkesbury between 1786 and 1796, was a British statesman. He was the father of Prime Minister Robert Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool.

Charles de l'Écluse,L'Escluse, or Carolus Clusius, seigneur de Watènes, was an Artois doctor and pioneering botanist, perhaps the most influential of all 16th-century scientific horticulturists.

The ducat was a gold or silver coin used as a trade coin in Europe from the later Middle Ages until as late as the 20th century. Many types of ducats had various metallic content and purchasing power throughout the period. The gold ducat of Venice gained wide international acceptance, like the medieval Byzantine hyperpyron and the Florentine florin, or the modern British Pound sterling and the United States dollar.

Charles Auguste Émile Durand, known as Carolus-Duran, was a French painter and art instructor. He is noted for his stylish depictions of members of high society in Third Republic France.
The Circumcellions or Agonistici were bands of Berber Christian extremists in North Africa in the early to mid-4th century. They were considered heretical by the Catholic Church. They were initially concerned with remedying social grievances, but they became linked with the Donatist sect. They condemned property and slavery, and advocated free love, canceling debt, and freeing slaves. Donatists prized martyrdom and had a special devotion for the martyrs, rendering honours to their graves.

The ancient Roman units of measurement were largely built on the Hellenic system, which in turn was built upon Egyptian and Mesopotamian influences. The Roman units were comparatively consistent and well documented.
Carolus is the medieval Latin form of the name Charles, notably the name of Charlemagne (742–814).
Ascolia, in Ancient Greece, was a yearly feast that the peasants of Attica celebrated in honor of Dionysus. The rites included sacrificing a goat, chosen because goats were prone to eating and destroying grapevines, and using its skin to make a football, which was filled with wine and smeared in oil. Festival participants then competed against each other by trying to leap onto it in a game that gave the festival its name ; the one who remained standing at the end of the contest won the wineskin as a prize. Participants also painted their faces with wine dregs, sang hymns, and recited satirical poetry.

In classical antiquity, a crotalum was a kind of clapper or castanet used in religious dances by groups in ancient Greece and elsewhere, including the Korybantes.
Sauatra, Soatra, or Savatra (Σαύατρα) was a city in the Eastern Roman Empire, in the Roman province of Lycaonia.
This article provides an outline of the currency of Spanish America from Spanish colonization in the 15th century until Spanish American independencies in the 19th. This great realm was divided into the Viceroyalty of New Spain, which came to include all Spanish territory north of Panama, the West Indies, Venezuela, and the Philippines, and the Viceroyalty of Peru, which included Panama and all Spanish territory in South America except Venezuela. The monetary system of Spanish America, originally identical to that of Spain, soon diverged and took on a distinctive character of its own, which it passed on to the independent nations that followed after.

Las arras, or las arras matrimoniales are wedding paraphernalia used in Christian wedding ceremonies in Spain, Latin American countries, and the Philippines. The tradition is also followed, with varying names and customs, in other countries and communities bearing degrees of Hispanic influence. Traditionally, in Spain and Latin America, it is made up of thirteen gold coins presented in an ornate box or chest; in the Philippines, it is in an ornate basket or pouch. After being blessed by a priest, they are given or presented by the groom to the bride.

Sir Thomas Vyner, 1st Baronet (1588–1665) was a wealthy English businessman and politician who served as the Lord Mayor of London. Vyner supplied gold bullion to two English kings and to the Protectorate of Oliver Cromwell.

Qing dynasty coinage was based on a bimetallic standard of copper and silver coinage. The Manchu Qing dynasty ruled over China from 1644 until it was overthrown by the Xinhai revolution in 1912. The Qing dynasty saw the transformation of a traditional cash coin based cast coinage monetary system into a modern currency system with machine-struck coins, while the old traditional silver ingots would slowly be replaced by silver coins based on those of the Mexican peso. After the Qing dynasty was abolished its currency was replaced by the Chinese yuan by the Republic of China.















