Caudill's Army was the name of a Confederate force from South Eastern Kentucky during the American Civil War that included the 10th Kentucky Mounted Rifles (designated the 13th Kentucky Cavalry in March 1865) commanded by Colonel Benjamin E. Caudill. An element of the Army of Tennessee and which served at times under General John Hunt Morgan's command. The force was active in the battle of Leatherwood and the Battle of Marion.

Albert Sidney Johnston was an American military officer who served as a general in three different armies: the Texian Army, the United States Army, and the Confederate States Army. He saw extensive combat during his 34-year military career, fighting actions in the Black Hawk War, the Texas-Indian Wars, the Mexican–American War, the Utah War, and the American Civil War, where he died on the battlefield.

John Hunt Morgan was a Confederate general in the American Civil War. In April 1862, he raised the 2nd Kentucky Cavalry Regiment, fought at Shiloh, and then launched a costly raid in Kentucky, which encouraged Braxton Bragg's invasion of that state. He also attacked General William Rosecrans's supply lines. In July 1863, he set out on a 1,000-mile raid into Indiana and Ohio, taking hundreds of prisoners. But after most of his men had been intercepted by U.S. Navy gunboats, including the USS Moose, Morgan surrendered at Salineville, Ohio, the northernmost point ever reached by uniformed Confederates. Morgan carried out the diversionary "Morgan's Raid" against orders, which gained no tactical advantage for the Confederacy while losing the regiment. Morgan escaped prison, but his credibility was so low that he was restricted to minor operations. He was killed at Greeneville, Tennessee, in September 1864. Morgan was the brother-in-law of Confederate general A. P. Hill. Various schools and a memorial are dedicated to him.

The Battle of Perryville, also known as the Battle of Chaplin Hills, was fought on October 8, 1862, in the Chaplin Hills west of Perryville, Kentucky, as the culmination of the Confederate Heartland Offensive during the American Civil War. Confederate Gen. Braxton Bragg's Army of Mississippi initially won a tactical victory against primarily a single corps of Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell's Union Army of the Ohio. The battle is considered a strategic Union victory, sometimes called the Battle for Kentucky, since Bragg withdrew to Tennessee soon thereafter. The Union retained control of the critical border state of Kentucky for the remainder of the war.

The Battle of Richmond, Kentucky, fought August 29–30, 1862, was one of the most complete Confederate victories in the war by Major General Edmund Kirby Smith against Union major general William "Bull" Nelson's forces, which were defending the town. It was the first major battle in the Kentucky Campaign. The battle took place on and around what is now the grounds of the Blue Grass Army Depot, outside Richmond, Kentucky.
The following is a list of engagements that took place in 1862 during the American Civil War. During the summer and early spring of the year, Union forces gained several successes over the Confederacy, seizing control of Missouri, northern Arkansas, Kentucky, and western Tennessee, along with several coastal areas. Confederate forces defended the capital of Richmond, Virginia, from Union assaults, and then launched counter–offensives into Kentucky and Maryland, both of which end in Union victories.
The Army of the Ohio was the name of two Union armies in the American Civil War. The first army became the Army of the Cumberland and the second army was created in 1863.

The Battle of Cove Mountain occurred in Wythe County, Virginia, on May 10, 1864, during the American Civil War. A Union cavalry division commanded by Brigadier General William W. Averell was prevented from attacking a lead mine located near Wytheville. Confederate forces commanded by Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan, with a detachment of a brigade of cavalry from the command of Brigadier General William E. "Grumble" Jones, stopped Averell at Cove Gap, adjacent to Crockett's Cove and Cove Mountain.

The siege of Corinth was an American Civil War engagement lasting from April 29 to May 30, 1862, in Corinth, Mississippi. A collection of Union forces under the overall command of Major General Henry Halleck engaged in a month-long siege of the city, whose Confederate occupants were commanded by General P.G.T. Beauregard. The siege resulted in the capture of the town by Federal forces.

Felix Kirk Zollicoffer was an American newspaperman, slave owner, politician, and soldier. A three-term US Representative from Tennessee, an officer in the United States Army, and a Confederate brigadier general during the American Civil War; he led the first Confederate invasion of eastern Kentucky and was killed in action at the Battle of Mill Springs. Zollicoffer was the first Confederate general to die in the Western Theater.

The 5th United States Colored Cavalry was a regiment of the United States Army organized as one of the units of the United States Colored Troops during the American Civil War. The 5th USCC was one of the more notable black fighting units. It was officially organized in Kentucky in October 1864, after its first two battles. It was commanded by Colonel James Brisbin until February 1865, when he took over the 6th US Colored Cavalry. His executive officer, Louis Henry Carpenter, commanded the regiment until 20 March 1866.

The western theater of the American Civil War encompassed major military operations in the states of Alabama, Georgia, Florida, Mississippi, North Carolina, Kentucky, South Carolina and Tennessee, as well as Louisiana east of the Mississippi River. Operations on the coasts of these states, except for Mobile Bay, are considered part of the Lower Seaboard Theater. Most other operations east of the Appalachian Mountains are part of the eastern theater. Operations west of the Mississippi River took place in the trans-Mississippi theater.
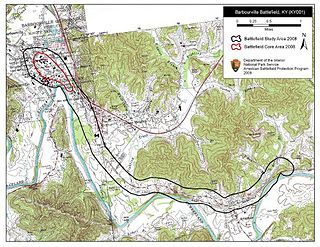
The Battle of Barbourville was one of the early engagements of the American Civil War. It took place on September 19, 1861, in Knox County, Kentucky during the campaign known as the Kentucky Confederate Offensive. The battle is considered the first Confederate victory in the commonwealth, and threw a scare into Federal commanders, who rushed troops to central Kentucky to try to repel the invasion, which was finally stopped at the Battle of Camp Wildcat in October.

Kentucky was a southern border state of key importance in the American Civil War. It officially declared its neutrality at the beginning of the war, but after a failed attempt by Confederate General Leonidas Polk to take the state of Kentucky for the Confederacy, the legislature petitioned the Union Army for assistance. Though the Confederacy controlled more than half of Kentucky early in the war, after early 1862 Kentucky came largely under U.S. control. In the historiography of the Civil War, Kentucky is treated primarily as a southern border state, with special attention to the social divisions during the secession crisis, invasions and raids, internal violence, sporadic guerrilla warfare, federal-state relations, the ending of slavery, and the return of Confederate veterans.

The Confederate Heartland Offensive, also known as the Kentucky Campaign, was an American Civil War campaign conducted by the Confederate States Army in Tennessee and Kentucky where Generals Braxton Bragg and Edmund Kirby Smith tried to draw neutral Kentucky into the Confederacy by outflanking Union troops under Major General Don Carlos Buell. Though they scored some successes, notably a tactical win at Perryville, they soon retreated, leaving Kentucky primarily under Union control for the rest of the war.
The Battle of Marion was a military engagement fought between units of the Union Army and the Confederate Army during the American Civil War near the town of Marion, Virginia. The battle was part of Union Maj. Gen. George Stoneman's attack upon southwest Virginia, aimed at destroying Confederate industrial infrastructure near Saltville and Marion. Union Cavalry and Infantry regiments—some 4,500 soldiers in total—left Tennessee on December 17 for southwestern Virginia.

The Confederate Monument in Crab Orchard in Lincoln County, Kentucky, near Crab Orchard, Kentucky, commemorates the fallen Confederate soldiers of nearby states. Many of those buried here died at the Battle of Wildcat Mountain.

The Battle of Sacramento was an engagement of the American Civil War that took place in Sacramento, Kentucky on December 28, 1861. Confederate cavalry under Colonel Nathan Bedford Forrest, numbering between 200 and 300, attacked, encircled and defeated a Union force of 500 under Major Eli H. Murray which had been watering south of the town after moving across the bank of the Green River. Though exact casualty information is disputed, with differing accounts from each side, several eyewitnesses attested to the personal courage of Forrest, and the Confederate commander was praised by his superiors for his bravery.
The Battle of Camp Wildcat was one of the early engagements of the American Civil War. It occurred October 21, 1861, in northern Laurel County, Kentucky during the campaign known as the Kentucky Confederate Offensive or Operations in Eastern Kentucky (1861). The battle is considered one of the first Union victories of the Civil War, and marked the second engagement of troops in the Commonwealth of Kentucky.

The Battle of Augusta was an engagement during the American Civil War that took place on September 27, 1862, in Augusta, Kentucky, between the Bracken County Home Guard (Union) and the Confederate Second Kentucky Cavalry Regiment under command of Colonel Basil W. Duke, a brother-in-law of John H. Morgan. The skirmish resulted in a victory for the Confederacy but the number of Confederate casualties and lack of ammunition for his artillery caused Colonel Duke to abandon plans to cross over the Ohio River into Ohio. A result of the fighting was that twenty buildings were set on fire and destroyed.
The Battle of Mount Sterling was a minor action in the American Civil War that occurred in June 1864 in Mount Sterling, Kentucky.