The Boii were a Gallic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul, Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia, parts of Poland, and Gallia Narbonensis. In addition the archaeological evidence indicates that in the 2nd century BC Celts expanded from Bohemia through the Kłodzko Valley into Silesia, now part of Poland and Czechia.

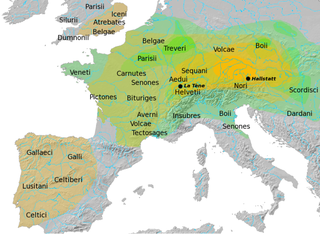
Gaul was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic tribes, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switzerland, and parts of Northern Italy, the Netherlands, and Germany, particularly the west bank of the Rhine. It covered an area of 494,000 km2 (191,000 sq mi). According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 203 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of Gaul in his campaigns of 58 to 51 BC.
Year 225 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Papus and Regulus. The denomination 225 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Battle of Alesia or Siege of Alesia was a military engagement in the Gallic Wars that took place in September, 52 BC, around the Gallic oppidum of Alesia, a major centre of the Mandubii tribe. It was fought by the army of Julius Caesar against a confederation of Gallic tribes united under the leadership of Vercingetorix of the Arverni. It was the last major engagement between Gauls and Romans, and is considered one of Caesar's greatest military achievements and a classic example of siege warfare and investment. The battle of Alesia marked the end of Gallic independence in France and Belgium.

Cisalpine Gaul was the part of Italy inhabited by Celts (Gauls) during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC. After its conquest by the Roman Republic in the 220s BC it was considered geographically part of Roman Italy but remained administratively separated. It was a Roman province from c. 81 BC until 42 BC, when it was de jure merged into Roman Italy as indicated in Caesar's unpublished acts. Cisalpine means "on the hither side of the Alps", as opposed to Transalpine Gaul.

Gallia Narbonensis was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in southern France. It was also known as Provincia Nostra, from its having been the first Roman province north of the Alps, and as Gallia Transalpina, distinguishing it from Cisalpine Gaul in northern Italy. It became a Roman province in the late 2nd century BC. Its boundaries were roughly defined by the Mediterranean Sea to the south and the Cévennes and Alps to the west and north. The western region of Gallia Narbonensis was known as Septimania.

The Bituriges Cubi were a Gallic tribe dwelling in the later province of Berry during the Iron Age and the Roman period. They had a homonym tribe, the Bituriges Vivisci, in the Bordelais region, which could indicate a common origin, although there is no direct of evidence of this.

Roman Gaul refers to Gaul under provincial rule in the Roman Empire from the 1st century BC to the 5th century AD.

The Turoni or Turones were a Gallic tribe of dwelling in the later Touraine region during the Iron Age and the Roman period.

The Pictones were a Gallic tribe dwelling south of the Loire river, in the modern departments of Vendée, Deux-Sèvres and Vienne, during the Iron Age and Roman period.

The Aulerci Cenomani were a Gallic tribe dwelling in the modern Sarthe department during the Iron Age and the Roman period. The Cenomani were the most powerful of the Aulerci tribes.
The Battle of Cremona was fought in 200 BC between the Roman Republic and Cisalpine Gaul. The Roman force was victorious.
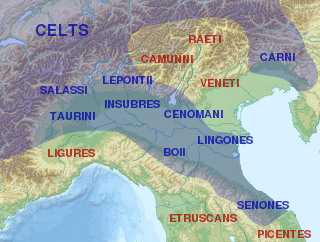
The Insubres or Insubri were a Lepontic population settled in Insubria, in what is now the Italian region of Lombardy. They were the founders of Mediolanum (Milan). Though completely Gaulish at the time of Roman conquest, they were the result of the fusion of pre-existing Ligurian and Celtic population with Gaulish tribes.
Bellovesus is a legendary Gallic chief of the Bituriges, said to have lived ca. 600 BC. According to a legend recounted by Livy, the king Ambigatus sent his sister's sons Bellovesus and Segovesus in search of new lands to settle because of overpopulation in their homeland. While Segovesus headed towards the Hercynian Forest, Bellovesus is said to have led the Gallic invasion of northern Italy during the legendary reign of the fifth king of Rome, Tarquinius Priscus, where he allegedly conquered the Etruscans and founded the city of Mediolanum (Milan).

The Cenomani, was an ancient tribe of the Cisalpine Gauls, who occupied the tract north of the Padus, between the Insubres on the west and the Veneti on the east. Their territory appears to have extended from the river Addua to the Athesis. Whether these Cenomani are the same people as the Cenomani in Gallia Celtica encountered by Julius Caesar is a subject of debate.

The Gauls were a group of Celtic peoples of Continental Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period. The area they originally inhabited was known as Gaul. Their Gaulish language forms the main branch of the Continental Celtic languages.
The Helvii were a relatively small Celtic polity west of the Rhône river on the northern border of Gallia Narbonensis. Their territory was roughly equivalent to the Vivarais, in the modern French department of Ardèche. Alba Helviorum was their capital, possibly the Alba Augusta mentioned by Ptolemy, and usually identified with modern-day Alba-la-Romaine. In the 5th century the capital seems to have been moved to Viviers.

The Roman-Gallic Wars were a series of conflicts between the forces of ancient Rome and various groups identified as Gauls. Among these were the Senones, Insubres, Boii and Gaesatae.
Lucius Furius Purpureo was a Roman politician and general, becoming consul in the year 196 BC. Lucius Furius was from the gens Furia patrician family in Rome.












