
The Marcomanni were a group of early Germanic peoples that eventually came to live in a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo they were Suebian.

The Suebi were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later such as the Alamanni and Bavarians and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian.
The 440s decade ran from January 1, 440, to December 31, 449.

Year 448 (CDXLVIII) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Praetextatus and Zeno. The denomination 448 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Flavius Aetius was a Roman general of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was an able military commander and the most influential man in the Western Roman Empire for two decades (433–454). He managed policy in regard to the attacks of barbarian federates settled throughout the Western Roman Empire. Notably, he mustered a large Roman and allied (foederati) army to stop the Huns in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains, ending the devastating Hunnic invasion of Attila in 451, though another devastating invasion of the Huns occurred in the year after that.

The Quadi were an early Germanic people who lived approximately in the area of modern Moravia in the time of the Roman Empire. The only known information about the Germanic tribe the Romans called the 'Quadi' comes through reports of the Romans themselves, whose empire had its border on the River Danube just to the south of the Quadi. They associated the Quadi with their neighbours the Marcomanni, and described both groups as having entered the region after the Celtic Boii had left it deserted. The Quadi are thought to have been an important part of the Suebian group who crossed the Rhine with the Vandals and Alans in the 406 Crossing of the Rhine, and later founded a kingdom in northwestern Iberia.

Wallia or Walha, was king of the Visigoths from 415 to 418, earning a reputation as a great warrior and prudent ruler. He was elected to the throne after Athaulf and then Sigeric were assassinated in 415.
Hydatius, also spelled Idacius, bishop of Aquae Flaviae in the Roman province of Gallaecia was the author of a chronicle of his own times that provides us with our best evidence for the history of Hispania in the 5th century.

The military history of Spain, from the period of the Carthaginian conquests over the Phoenicians to the current Afghan War spans a period of more than 2200 years, and includes the history of battles fought in the territory of modern Spain, as well as her former and current overseas possessions and territories, and the military history of the people of Spain, regardless of geography.
Hermeric was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
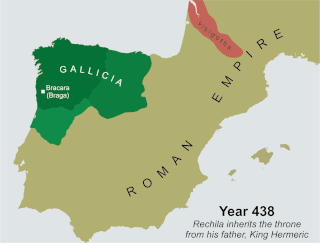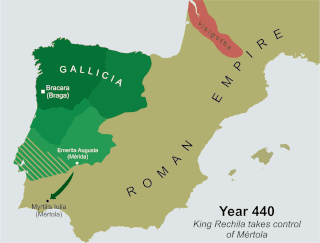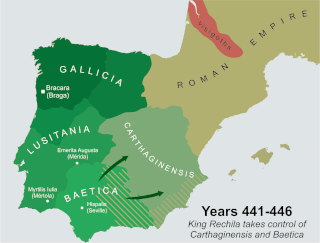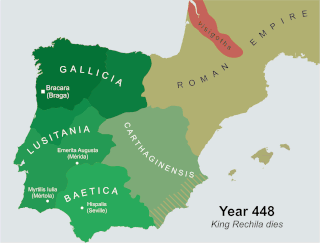
Rechila was the Suevic King of Galicia from 438 until his death. There are few primary sources for his life, but Hydatius was a contemporary Christian (non-Arian) chronicler in Galicia.

Rechiar or Rechiarius was the Suevic king of Gallaecia from 448 until his death. He was the first Chalcedonian Christian (Catholic) Germanic king in Europe and one of the most innovative and belligerent of the Suevi monarchs. Despite his orthodox Christianity, Hydatius, the contemporary bishop and chronicler from Galicia who is the sole contemporary source for biographical details of Rechiar, established his reputation as that of a barbarian with little sense of Roman law, culture, or custom.

The Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallæcia or Suebi Kingdom of Gallæcia, was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from the Roman Empire. Based in the former Roman provinces of Gallaecia and northern Lusitania, the de facto kingdom was established by the Suebi about 409, and during the 6th century it became a formally declared kingdom identifying with Gallaecia. It maintained its independence until 585, when it was annexed by the Visigoths, and was turned into the sixth province of the Visigothic Kingdom in Hispania.
Aioulf or Ag(r)iwulf was an obscure King of Galicia from 456. In 448, after eight years in captivity, the Roman ambassador Censorius was executed by one Agiulf at Seville (Hispalis). This Agiulf has sometimes been identified with Aioulf.

Miro was the Suebian King of Galicia from 570 until his death in 583. His reign was marked by attempts to forge alliances with other Chalcedonian Christian nations with the goal of checking the power of the Arian Visigoths under Leovigild. During his reign relations were established with both Francia and the Byzantine Empire and the kingdom reached its zenith, but it collapsed within three years of his death.
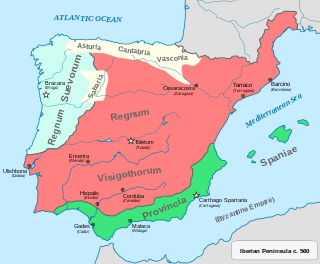
Spania was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 552 until 624 in the south of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands. It was established by the Emperor Justinian I in an effort to restore the western provinces of the Empire.
Ajax was an Arian missionary to the pagan Suevi of Galicia who converted them to Christianity in 464 or 466 AD.
Veremund or Veremundus was a Suevic king of Galicia around 500. His existence is conjectured on the basis of a sixth-century inscription discovered at Salvador de Vairão. The date in the inscription is interpreted as either 485 or 535. Some scholars have dated the inscription to the eighth century, arguing that the Veremundus of the inscription is King Bermudo I of Asturias.

Theodoric I was the King of the Visigoths from 418 to 451. Theodoric is famous for his part in defeating Attila at the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains in 451, where he was killed on June 20.











