In telecommunications, RS-232, Recommended Standard 232 refers to a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a DTE such as a computer terminal, and a DCE, such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, issued in 1997. The RS-232 standard had been commonly used in computer serial ports.

A parallel port is a type of interface found on computers for connecting peripherals. The name refers to the way the data is sent; parallel ports send multiple bits of data at once, in parallel communication, as opposed to serial interfaces that send bits one at a time. To do this, parallel ports require multiple data lines in their cables and port connectors, and tend to be larger than contemporary serial ports which only require one data line.

IEEE 488 is a short-range digital communications 8-bit parallel multi-master interface bus specification. IEEE 488 was created as HP-IB and is commonly called GPIB. It has been the subject of several standards.

The Canon Cat was a task-dedicated, desktop computer released by Canon Inc. in 1987 at a price of US$1,495. On the surface it was not unlike the dedicated word processors popular in the late 1970s to early 1980s, but it is far more powerful and incorporates many unique ideas for data manipulation.

The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.
The +D was a floppy disk and printer interface for the Sinclair ZX Spectrum home computer, developed as a successor to Miles Gordon Technology's earlier product, the DISCiPLE. It was designed to be smaller, cheaper, simpler and thus more reliable.

The Commodore SX-64, also known as the Executive 64, or VIP-64 in Europe, is a portable, briefcase/suitcase-size "luggable" version of the popular Commodore 64 home computer and the first full-color portable computer.
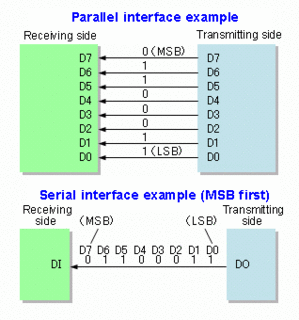
In data transmission, parallel communication is a method of conveying multiple binary digits (bits) simultaneously. It contrasts with serial communication, which conveys only a single bit at a time; this distinction is one way of characterizing a communications link.

A legacy port is a computer port or connector that is considered by some to be fully or partially superseded. The replacement ports usually provide most of the functionality of the legacy ports with higher speeds, more compact design, or plug and play and hot swap capabilities for greater ease of use. Modern PC motherboards use separate Super I/O controllers to provide legacy ports since current chipsets do not offer direct support for them. A category of computers called legacy-free PCs omits these ports, typically retaining only USB for external expansion.

The micro ribbon or miniature ribbon connector is a common type of electrical connector for a variety of applications, such as in computer and telecommunications equipment having many contacts.
Miracle Systems Ltd. were a manufacturer of personal computer peripherals and upgrades, specializing in the Sinclair QL, in the 1980s and early 1990s.

The Rotronics Wafadrive was a continuous tape loop storage peripheral launched in late 1984 for the Sinclair ZX Spectrum 8-bit home computer, intended to compete with Sinclair's ZX Interface 1 and ZX Microdrive.
A SCSI connector is used to connect computer parts that use a system called SCSI to communicate with each other. Generally, two connectors, designated male and female, plug together to form a connection which allows two components, such as a computer and a disk drive, to communicate with each other. SCSI connectors can be electrical connectors or optical connectors. There have been a large variety of SCSI connectors in use at one time or another in the computer industry. Twenty-five years of evolution and three major revisions of the standards resulted in requirements for Parallel SCSI connectors that could handle an 8, 16 or 32 bit wide bus running at 5, 10 or 20 megatransfer/s, with conventional or differential signaling. Serial SCSI added another three transport types, each with one or more connector types. Manufacturers have frequently chosen connectors based on factors of size, cost, or convenience at the expense of compatibility.

A very-high-density cable interconnect (VHDCI) is a 68-pin connector that was introduced in the SPI-3 document of SCSI-3. The VHDCI connector is a very small connector that allows placement of four wide SCSI connectors on the back of a single PCI card slot. Physically, it looks like a miniature Centronics type connector. It uses the regular 68-contact pin assignment. The male connector (plug) is used on the cable and the female connector ("receptacle") on the device.

In computer hardware, a port serves as an interface between the computer and other computers or peripheral devices. In computer terms, a port generally refers to the part of a computing device available for connection to peripherals such as input and output devices. Computer ports have many uses, to connect a monitor, webcam, speakers, or other peripheral devices. On the physical layer, a computer port is a specialized outlet on a piece of equipment to which a plug or cable connects. Electronically, the several conductors where the port and cable contacts connect, provide a method to transfer signals between devices.
This article covers the peripherals available for Atari's 8-bit computer family, which includes the 400/800, XL, XE, the and XEGS.
IFSP, radial parallel interface, was a parallel interface similar to Centronics but incompatible, as it had different signal polarities and handshake protocol. Used in printers and computers manufactured in Comecon.

Dongles were originally created in the 1970s to protect computer software which would function only if the dongle was plugged in – see the "History" section below.












