External links
- Modern Ceterone constructed by Ron Banks of Texas, on which he uses a scalloped fretboard. This instrument has been modeled on the surviving Italian instrument by Campi.
| Classification | String instruments |
|---|---|
| Related instruments | |
The Ceterone (Italian), was an enlarged cetera (Eng. cittern), believed to be similar to the chitarrone as a development of the chitarra and lute to enhance the bass capabilities of these instruments.
Michael Praetorius includes such an instrument in his Syntagma Musicum, describing its 'strong and magnificent sound like a harpsichord.' In the Sciagraphia is an illustration (plate 7) of a Dominici Zwölff Chörichte Cither (Dominici twelve course cittern), with re-entrant bass string tunings of eb, Bb, f, c, g, d, a, e, and treble strings tuned to b, g, d' and e'. The instrument has a body shape with constructional features similar to a viol or modern guitar. Some early 17th century illustrations of citterns have body shapes resembling this instrument, while the Swiss halszither – a traditional regional cittern that survived until the present, has also been constructed with a similar body.
Plate 5 of the Sciagraphia illustrates a Gross Sechs Chörichte Cither; (large six course cittern) – depicted with eight pegs inserted into the sides of the pegbox and six strings.
Like the cittern, the ceterone was also built with a flat-backed body in teardrop shape, with a single large 'rose', and had fixed, metal frets (unlike the tied, gut frets of the lute family) and used metal strings. The unfretted bass strings were attached to a neck extension, the instrument totalling perhaps as much as 1.5 metres in length. A single original example exists in Museo Bardini in Florence, dating from around 1600 and built by the cittern luthier Gironimo Campi. The museum has labelled the instrument as an arci cetera, (arch cittern).
David Munrow: Instruments of the Middle Ages and Renaissance, OUP 1976, supplied with the EMI boxed LP set of that name.
Michael Praetorius: Syntagma Musicum II, De organographia, (Parts I & II). Wolfenbüttel, 1618–20
Thomas Robinson: New Citharen Lessons, London, 1609. Robinson's book contains 5 pieces for a 14 course instrument and an illustration. The depiction appears to show 7 double string courses for the fingerboard and 7 open single string courses running up to a neck extension and presumably back inside to the pegbox. According to Robinson, the "...invention was first begun by an Italian in Italy, but altered, and strings augmented by me."

The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A plectrum or individual finger picks may be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either acoustically, by means of a resonant chamber on the instrument, or amplified by an electronic pickup and an amplifier.

A lute is any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.

A fret is a space between two fretbars on the neck of a stringed instrument. Frets usually extend across the full width of the neck. On most modern western fretted instruments, frets are the spaces between the metal strips (fretbars) that are inserted into the fingerboard. On some historical instruments and non-European instruments, frets are made of pieces of string tied around the neck.

Zither is a class of stringed instruments. Historically, the name has been applied to any instrument of the psaltery family, or to an instrument consisting of many strings stretched across a thin, flat body. This article describes the latter variety.

The bouzouki, also spelled buzuki or buzuci, is a musical instrument popular in Greece. It is a member of the long-necked lute family, with a round body with a flat top and a long neck with a fretted fingerboard. It has steel strings and is played with a plectrum producing a sharp metallic sound, reminiscent of a mandolin but pitched lower. There are two main types of bouzouki: the trichordo (three-course) has three pairs of strings and the tetrachordo (four-course) has four pairs of strings. The instrument was brought to Greece in the early 1900s by Greek immigrants from Anatolia, and quickly became the central instrument to the rebetiko genre and its music branches. It is now an important element of modern Laïko pop Greek music.

The theorbo is a plucked string instrument of the lute family, with an extended neck and a second pegbox. Like a lute, a theorbo has a curved-back sound box with a wooden top, typically with a sound hole, and a neck extending out from the soundbox. As with the lute, the player plucks or strums the strings with one hand while "fretting" the strings with the other hand; pressing the strings in different places on the neck produces different pitches (notes), thus enabling the performer to play chords, basslines and melodies.

The cittern or cithren is a stringed instrument dating from the Renaissance. Modern scholars debate its exact history, but it is generally accepted that it is descended from the Medieval citole. Its flat-back design was simpler and cheaper to construct than the lute. It was also easier to play, smaller, less delicate and more portable. Played by people of all social classes, the cittern was a premier instrument of casual music-making much as is the guitar today.
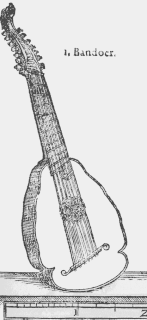
The bandora or bandore is a large long-necked plucked string-instrument that can be regarded as a bass cittern though it does not have the re-entrant tuning typical of the cittern. Probably first built by John Rose in England around 1560, it remained popular for over a century. A somewhat smaller version was the orpharion which is where it cam from.
The music of Central Asia is as vast and unique as the many cultures and peoples who inhabit the region. Principal instrument types are two- or three-stringed lutes, the necks either fretted or fretless; fiddles made of horsehair; flutes, mostly open at both ends and either end-blown or side-blown; and jew harps, mostly metal. Percussion instruments include frame drums, tambourines, and kettledrums. Instrumental polyphony is achieved primarily by lutes and fiddles.

The citole was a string musical instrument, closely associated with the medieval fiddles and commonly used from 1200–1350. It was known by other names in various languages: cedra, cetera, cetola, cetula, cistola, citola, citula, citera, chytara, cistole, cithar, cuitole, cythera, cythol, cytiole, cytolys, gytolle, sitole, sytholle, sytole, and zitol. Like the modern guitar, it was manipulated at the neck to get different notes, and picked or strummed with a plectrum. Although it was largely out of use by the late 14th century, the Italians "re-introduced it in modified form" in the 16th century as the cetra, and it may have influenced the development of the guitar as well. It was also a pioneering instrument in England, introducing the populace to necked, plucked instruments, giving people the concepts needed to quickly switch to the newly arriving lutes and gitterns. Two possible descendant instrument are the Portuguese guitar and the Corsican Cetera, both types of cittern.

During the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603), English art and high culture reached a pinnacle known as the height of the English Renaissance. Elizabethan music experienced a shift in popularity from sacred to secular music and the rise of instrumental music. Professional musicians were employed by the Church of England, the nobility, and the rising middle-class.

The gittern was a relatively small gut-strung, round-backed instrument that first appears in literature and pictorial representation during the 13th century in Western Europe. It is usually depicted played with a quill plectrum, as can be seen clearly beginning in manuscript illuminations from the thirteenth century. It was also called the guiterna in Spain, guiterne or guiterre in France, the chitarra in Italy and Quintern in Germany. A popular instrument with court musicians, minstrels, and amateurs, the gittern is considered an ancestor of the modern guitar and other instruments like the mandore, bandurria and gallichon.

The sintir, also known as the guembri (الكمبري), gimbri or hejhouj, is a three stringed skin-covered bass plucked lute used by the Gnawa people. It is approximately the size of a guitar, with a body carved from a log and covered on the playing side with camel skin. The camel skin has the same acoustic function as the membrane on a banjo. The neck is a simple stick with one short and two long goat strings that produce a percussive sound similar to a pizzicato cello or double bass.

The mandora or gallichon is a type of 18th- and early 19th-century lute, with six to nine courses of strings. The terms were interchangeable, with mandora more commonly used from the mid-18th century onwards.

The lira da braccio was a European bowed string instrument of the Renaissance. It was used by Italian poet-musicians in court in the 15th and 16th centuries to accompany their improvised recitations of lyric and narrative poetry. It is most closely related to the medieval fiddle, or vielle, and like the vielle had a leaf-shaped pegbox with frontal pegs. Fiddles with drone strings are seen beginning in the 9th century, and the instrument continued to develop through the 16th century. In many depictions of the instrument, it is being played by mythological characters, frequently members of angel consorts, and most often by Orpheus and Apollo. The lira da braccio was occasionally used in ensembles, particularly in the intermedi, and may have acted as a proto-continuo instrument.

There are many varieties of ten-string guitar, including:

The mandore is a musical instrument, a small member of the lute family, teardrop shaped, with four to six courses of gut strings and pitched in the treble range. Considered a French instrument, with much of the surviving music coming from France, it was used across "Northern Europe" including Germany and Scotland. Although it went out of style, the French instrument has been revived for use in classical music. The instrument's most commonly played relatives today are members of the mandolin family and the bandurria.

A tromba marina, marine trumpet or nuns' fiddle, is a triangular bowed string instrument used in medieval and Renaissance Europe that was highly popular in the 15th century in England and survived into the 18th century. The tromba marina consists of a body and neck in the shape of a truncated cone resting on a triangular base. It is usually four to seven feet long, and is a monochord. It is played without stopping the string, but playing natural harmonics by lightly touching the string with the thumb at nodal points. Its name comes from its trumpet like sound due to the unusual construction of the bridge, and the resemblance of its contour to the marine speaking-trumpet of the Middle Ages.
The rawap is a fretted plucked long-necked stringed instrument used in folk music by residents of the Uyghur autonomous region of Xinjiang, Western China. The history of the instrument dates back to the 14th century in southern Xinjiang. It is an instrument of the Uyghurs and Uzbeks. It's particularly associated with Uyghur music and culture.

Lutes are stringed musical instruments that include a body and "a neck which serves both as a handle and as a means of stretching the strings beyond the body".