
In mathematics, an isomorphism is a structure-preserving mapping between two structures of the same type that can be reversed by an inverse mapping. Two mathematical structures are isomorphic if an isomorphism exists between them. The word isomorphism is derived from the Ancient Greek: ἴσοςisos "equal", and μορφήmorphe "form" or "shape".

Supervised learning (SL) is a paradigm in machine learning where input objects and a desired output value train a model. The training data is processed, building a function that maps new data on expected output values. An optimal scenario will allow for the algorithm to correctly determine output values for unseen instances. This requires the learning algorithm to generalize from the training data to unseen situations in a "reasonable" way. This statistical quality of an algorithm is measured through the so-called generalization error.
In computer science, write-ahead logging (WAL) is a family of techniques for providing atomicity and durability in database systems.
In computer science, Algorithms for Recovery and Isolation Exploiting Semantics, or ARIES, is a recovery algorithm designed to work with a no-force, steal database approach; it is used by IBM Db2, Microsoft SQL Server and many other database systems. IBM Fellow Dr. C. Mohan is the primary inventor of the ARIES family of algorithms.
In the field of databases in computer science, a transaction log is a history of actions executed by a database management system used to guarantee ACID properties over crashes or hardware failures. Physically, a log is a file listing changes to the database, stored in a stable storage format.
In the database structured query language (SQL), the DELETE statement is used to remove one or more records from a table. A subset may be defined for deletion using a condition, otherwise all records are removed. Some database management systems (DBMSs), like MySQL, allow deletion of rows from multiple tables with one DELETE statement.
Undo is an interaction technique which is implemented in many computer programs. It erases the last change done to the document, reverting it to an older state. In some more advanced programs, such as graphic processing, undo will negate the last command done to the file being edited. With the possibility of undo, users can explore and work without fear of making mistakes, because they can easily be undone.
Extensible Storage Engine (ESE), also known as JET Blue, is an ISAM data storage technology from Microsoft. ESE is the core of Microsoft Exchange Server, Active Directory, and Windows Search. It is also used by a number of Windows components including Windows Update client and Help and Support Center. Its purpose is to allow applications to store and retrieve data via indexed and sequential access.
In the database management systems developed by the Oracle Corporation, the System Global Area (SGA) forms the part of the system memory (RAM) shared by all the processes belonging to a single Oracle database instance. The SGA contains all information necessary for the instance operation.
The software which Oracle Corporation markets as Oracle Data Guard forms an extension to the Oracle relational database management system (RDBMS). It aids in establishing and maintaining secondary standby databases as alternative/supplementary repositories to production primary databases.
In computer science, persistence refers to the characteristic of state of a system that outlives the process that created it. This is achieved in practice by storing the state as data in computer data storage. Programs have to transfer data to and from storage devices and have to provide mappings from the native programming-language data structures to the storage device data structures.
In statistical classification, the Fisher kernel, named after Ronald Fisher, is a function that measures the similarity of two objects on the basis of sets of measurements for each object and a statistical model. In a classification procedure, the class for a new object can be estimated by minimising, across classes, an average of the Fisher kernel distance from the new object to each known member of the given class.
Oracle LogMiner, a utility provided by Oracle Corporation to purchasers of its Oracle database, provides methods of querying logged changes made to an Oracle database, principally through SQL commands referencing data in Oracle redo logs. A GUI interface for the functionality comes with the Oracle Enterprise Manager product.
In Oracle databases, Flashback tools allow administrators and users to view and manipulate past states of an instance's data without (destructively) recovering to a fixed point in time.
In the Oracle RDBMS environment, redo logs comprise files in a proprietary format which log a history of all changes made to the database. Each redo log file consists of redo records. A redo record, also called a redo entry, holds a group of change vectors, each of which describes or represents a change made to a single block in the database.
An intent log is a mechanism used to make computer operations more resilient in the event of failures. They are used in database software, transaction managers, and some file systems. In database area, transaction log is widely used. In file system area, intent log is used more often.
Vector space model or term vector model is an algebraic model for representing text documents as vectors such that the distance between vectors represents the relevance between the documents. It is used in information filtering, information retrieval, indexing and relevancy rankings. Its first use was in the SMART Information Retrieval System.

Fast inverse square root, sometimes referred to as Fast InvSqrt or by the hexadecimal constant 0x5F3759DF, is an algorithm that estimates , the reciprocal of the square root of a 32-bit floating-point number in IEEE 754 floating-point format. The algorithm is best known for its implementation in 1999 in Quake III Arena, a first-person shooter video game heavily based on 3D graphics. With subsequent hardware advancements, especially the x86 SSE instruction rsqrtss, this algorithm is not generally the best choice for modern computers, though it remains an interesting historical example.
Database activity monitoring is a database security technology for monitoring and analyzing database activity. DAM may combine data from network-based monitoring and native audit information to provide a comprehensive picture of database activity. The data gathered by DAM is used to analyze and report on database activity, support breach investigations, and alert on anomalies. DAM is typically performed continuously and in real-time.
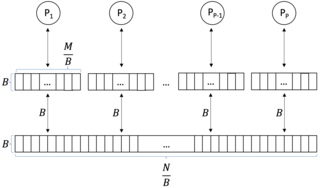
In computer science, a parallel external memory (PEM) model is a cache-aware, external-memory abstract machine. It is the parallel-computing analogy to the single-processor external memory (EM) model. In a similar way, it is the cache-aware analogy to the parallel random-access machine (PRAM). The PEM model consists of a number of processors, together with their respective private caches and a shared main memory.



