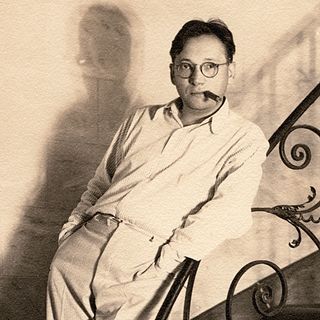Robert Florey was a French-American director, screenwriter, film journalist and actor.

Cyril Raker Endfield was an American film director, who at times also worked as a writer, theatre director, magician and inventor. Born in Scranton, Pennsylvania, he worked in the New York theatre in the late 1930s before moving to Hollywood in 1940.

Charles Edward "Buddy" Rogers was an American film actor and musician. During the peak of his popularity in the late 1920s and early 1930s, he was publicized as "America's Boyfriend".

William Gilbert Barron, known professionally as Billy Gilbert, was an American actor and comedian. He was known for his comic sneeze routines. He appeared in over 200 feature films, short subjects and television shows beginning in 1929.

Charles G. Rosher, A.S.C. was an English-born cinematographer who worked from the early days of silent films through the 1950s.

Lee Garmes, A.S.C. was an American cinematographer. During his career, he worked with directors Howard Hawks, Max Ophüls, Josef von Sternberg, Alfred Hitchcock, King Vidor, Nicholas Ray and Henry Hathaway, whom he had met as a young man when the two first came to Hollywood in the silent era. He also co-directed two films with legendary screenwriter Ben Hecht: Angels Over Broadway and Actors and Sin.
Alexander Phillips was a Canadian-Mexican cinematographer. He worked on over 200 films, most of them during the Golden Age of Mexican Cinema. Throughout his career, he was nominated 14 times for an Ariel Award for Best Cinematography which he won twice for En La Palma de Tu Mano and Untouched.

Arthur Charles Miller, A.S.C. was an American cinematographer. He was nominated for the Oscar for Best Cinematography six times, winning three times: for How Green Was My Valley in 1941, The Song of Bernadette in 1944, and Anna and the King of Siam in 1947.
Ian Dalrymple was a British screenwriter, film director, film editor and film producer.
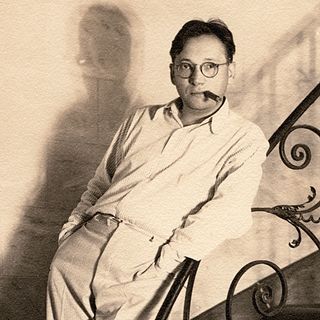
Jo Swerling was an American theatre writer, lyricist, and screenwriter.
Robert Hayward Barlow was an American author, avant-garde poet, anthropologist and historian of early Mexico, and expert in the Nahuatl language. He was a correspondent and friend of horror writer H. P. Lovecraft, who appointed Barlow as the executor of his literary estate.

George J. Lewis was a Mexican-born actor who appeared in many films and eventually TV series from the 1920s through the 1960s, usually specializing in westerns. He is probably best known for playing Don Alejandro de la Vega, who was Don Diego de la Vega's father in the 1950s Disney television series Zorro. Lewis co-starred in Zorro's Black Whip and had a minor role in Ghost of Zorro before starring as Don Alejandro in the Disney series.

Donald Woods was a Canadian-American film and television actor whose career in Hollywood spanned six decades.
Josef Berne was a Russian-born American writer, film director and producer. Berne was born Josef Berstein on January 19, 1904, in Kyiv, Russia. He also wrote and directed Yiddish language dramas.
Leslie Goodwins was an English film director and screenwriter. He directed nearly 100 films between 1926 and 1967, notably 27 features and shorts with Leon Errol, including the Mexican Spitfire series. His 1936 film Dummy Ache was nominated for an Academy Award in 1936 for Best Short Subject (Two-Reel). Dummy Ache was preserved by the Academy Film Archive and the Library of Congress in 2013. His 1937 film Should Wives Work? was also nominated for an Academy Award in the same category. He was born in London, England and he died in Hollywood, California.
Raymond De Becker (1912–1969) was a Belgian journalist, writer, and intellectual. He became closely involved in Catholic and anti-parliamentarian politics in the interwar years and is notable as the editor of the daily newspaper Le Soir and a leading exponent of "intellectual collaboration" in German-occupied Belgium during World War II.
Emilio Gómez Muriel was a prolific Mexican film director, active between the 1930s and the 1970s.

Charles Pearce Coleman was an Australian-born American character actor of the silent and sound film eras.
Manuel Arvide (1897–1969) was a Mexican film actor.
Charles E. Roberts was an American screenwriter and film director. He worked on over a hundred short films and feature films. As a writer he is particularly noted for his work on the Mexican Spitfire series for RKO Pictures. He had previously made a number of two-reel shorts featuring Leon Errol.