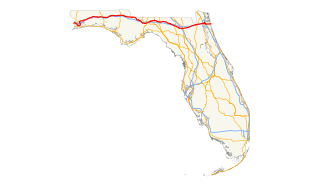
The Charlotte River (also Macaco River) is a former name for what was thought to be a continuous river draining Lake Okeechobee (formerly Lake Macaco) into Charlotte Harbor. Although an 1842 map indicates that the Charlotte was the same as the Caloosahatchee River, [1] , other sources distinguish the two from each other. [2] Most maps that include the river show it following what is now known as Shell Creek east from the Peace River and splitting into multiple branches, with the south branch receiving water from Lake Macaco, a north or northeast branch, and a central branch labeled as Lost Creek. [3] [4] The most prominent actual waterway near the east half of the supposed Charlotte River is Fisheating Creek

Lake Okeechobee, also known as Florida's Inland Sea, is the largest freshwater lake in the state of Florida. It is the eighth largest natural freshwater lake in the United States and the second largest natural freshwater lake contained entirely within the contiguous United States. Okeechobee covers 730 square miles (1,900 km2), approximately half the size of the state of Rhode Island, and is exceptionally shallow for a lake of its size, with an average depth of only 9 feet. The Kissimmee River, located directly north of Lake Okeechobee, is the lake's primary source. The lake is divided between Glades, Okeechobee, Martin, Palm Beach, and Hendry counties. All five counties meet at one point near the center of the lake.

The Caloosahatchee River is a river on the southwest Gulf Coast of Florida in the United States, approximately 67 miles (108 km) long. It drains rural areas on the northern edge of the Everglades, east of Fort Myers. An important link in the Okeechobee Waterway, a manmade inland waterway system of southern Florida, the river forms a tidal estuary along most of its course and has become the subject of efforts to restore and preserve the Everglades.
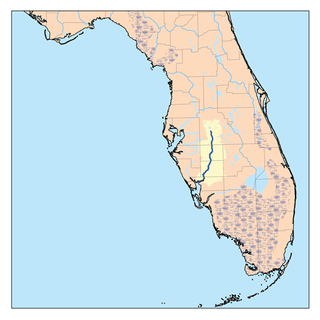
The Peace River is a river in the southwestern part of the Florida peninsula, in the U.S.A.. It originates at the juncture of Saddle Creek and Peace Creek northeast of Bartow in Polk County and flows south through Fort Meade Hardee County to Arcadia in DeSoto County and then southwest into the Charlotte Harbor estuary at Port Charlotte in Charlotte County. It is 106 miles (171 km) long and has a drainage basin of 1,367 square miles (3,540 km2). U.S. Highway 17 runs near and somewhat parallel to the river for much of its course. The river was called Rio de la Paz on 16th century Spanish charts. It appeared as Peas Creek or Pease Creek on later maps. The Creek Indians call it Talakchopcohatchee, River of Long Peas. Other cities along the Peace River include Fort Meade, Wauchula and Zolfo Springs.
The border between St. Johns and Monroe Counties was defined to follow the Charlotte River in 1823, [5] and remained there (with various counties replacing St. Johns to the north) until it was moved south to the township line (now the Charlotte-Lee border) in 1859. [6] Most maps postdating the discovery that the Charlotte River did not exist placed the line along the Caloosahatchee River. [7] [8]

Lee County is located in southwest Florida on the Gulf Coast. As of the 2010 census, the population was 618,754. The county seat is Fort Myers, and the largest city is Cape Coral with an estimated 2016 population of 179,804. Lee County comprises the Cape Coral–Fort Myers, FL Metropolitan Statistical Area.