Child support is an ongoing, periodic payment made by a parent for the financial benefit of a child following the end of a marriage or other similar relationship. Child maintenance is paid directly or indirectly by an obligor to an obligee for the care and support of children of a relationship that has been terminated, or in some cases never existed. Often the obligor is a non-custodial parent. The obligee is typically a custodial parent, a caregiver, or a guardian.
A private member's bill is a bill introduced into a legislature by a legislator who is not acting on behalf of the executive branch. The designation "private member's bill" is used in most Westminster system jurisdictions, in which a "private member" is any member of parliament (MP) who is not a member of the cabinet (executive). Other labels may be used for the concept in other parliamentary systems; for example, the label member's bill is used in the Scottish Parliament and the New Zealand Parliament, the term private senator's bill is used in the Australian Senate, and the term public bill is used in the Senate of Canada. In legislatures where the executive does not have the right of initiative, such as the United States Congress, the concept does not arise since bills are always introduced by legislators.
Same-sex adoption is the adoption of children by same-sex couples. It may take the form of a joint adoption by the couple, or of the adoption by one partner of the other's biological child.
The New Zealand foreshore and seabed controversy is a debate in the politics of New Zealand. It concerns the ownership of the country's foreshore and seabed, with many Māori groups claiming that Māori have a rightful claim to title. These claims are based around historical possession and the Treaty of Waitangi. On 18 November 2004, the New Zealand Parliament passed a law which deems the title to be held by the Crown. This law, the Foreshore and Seabed Act 2004, was enacted on 24 November 2004. Some sections of the act came into force on 17 January 2005. It was repealed and replaced by the Marine and Coastal Area Act 2011.
Sexual grooming is the action or behavior used to establish an emotional connection with a minor, and sometimes the child's family, to lower the child's inhibitions with the objective of sexual abuse. It can occur in various settings, including online, in person, and through other means of communication. Children who are groomed may experience mental health issues, including "anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress, and suicidal thoughts."

New Zealand lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights are some of the most extensive in the world. The protection of LGBT rights is advanced, relative to other countries in Oceania, and among the most liberal in the world, with the country being the first in the region to legalise same-sex marriage.
The ages of consent for sexual activity vary from age 15 to 18 across Australia, New Zealand and other parts of Oceania. The specific activity and the gender of its participants is also addressed by the law. The minimum age is the age at or above which an individual can engage in unfettered sexual relations with another person of minimum age. Close in age exceptions may exist and are noted where applicable. In Vanuatu the homosexual age of consent is set higher at 18, while the heterosexual age of consent is 15. Same sex sexual activity is illegal at any age for males in Papua New Guinea, Kiribati, Samoa, Niue, Tonga and Tuvalu; it is outlawed for both men and women in the Solomon Islands. In all other places the age of consent is independent of sexual orientation or gender.

Social welfare has long been an important part of New Zealand society and a significant political issue. It is concerned with the provision by the state of benefits and services. Together with fiscal welfare and occupational welfare, it makes up the social policy of New Zealand. Social welfare is mostly funded through general taxation. Since the 1980s welfare has been provided on the basis of need; the exception is universal superannuation.

The Liberal Government of New Zealand was the first responsible government in New Zealand politics organised along party lines. The government formed following the founding of the Liberal Party and took office on 24 January 1891, and governed New Zealand for over 21 years until 10 July 1912. To date, it is the longest-serving government in New Zealand's history. The government was also historically notable for enacting significant social and economic changes, such as the Old Age Pensions Act and women's suffrage. One historian described the policies of the government as "a revolution in the relationship between the government and the people".

The Crimes Amendment Act 2007 is an amendment to New Zealand's Crimes Act 1961 which removed the legal defence of "reasonable force" for parents prosecuted for assault on their children.

The Oranga Tamariki Act 1989 or Children's and Young People's Well-being Act 1989 is an Act of the New Zealand Parliament that was passed in 1989. The Act's main purpose is to "promote the well-being of children, young persons, and their families and family groups." In June 2017, the New Zealand Parliament passed amendment legislation renaming the bill the Oranga Tamariki Act 1989.

The Crimes Act 1961 is an act of New Zealand Parliament that forms a leading part of the criminal law in New Zealand. It repeals the Crimes Act 1908, itself a successor of the Criminal Code Act 1893. Most crimes in New Zealand are created by the Crimes Act, but some are created elsewhere. All common law offences are abolished by section 9, as are all offences against acts of the British Parliaments, but section 20 saves the old common law defences where they are not specifically altered.

The 2009 New Zealand Referendum on Child Discipline was held from 31 July to 21 August, and was a citizens-initiated referendum on parental corporal punishment. It asked:
Should a smack as part of good parental correction be a criminal offence in New Zealand?
The Elizabeth Morgan Act is an act of the 104th United States Congress that was declared unconstitutional in 2003 by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia as being a bill of attainder, because it was written to deny rights to a specific father based on his child's own assertion. It was originally introduced as H.R. 1855, by Rep. Thomas M. Davis. It was passed as a rider of the Department of Transportation and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, 1997.
Ian Robert Flockhart McKelvie is a New Zealand politician. He represented the National Party in the New Zealand House of Representatives from 2011 to 2023.
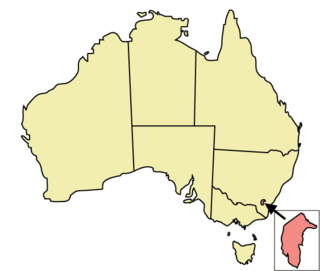
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT) is one of Australia's leading jurisdictions with respect to the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people. The ACT has made a number of reforms to territory law designed to prevent discrimination of LGBT people; it was the only state or territory jurisdiction in Australia to pass a law for same-sex marriage, which was later overturned by the High Court of Australia. The Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, New South Wales and Queensland are the only jurisdictions within Australia to legally ban conversion therapy on children. The ACT's laws also apply to the smaller Jervis Bay Territory.
New Zealand suffers from one of the highest rates of child poverty in the Western world. According to Statistics New Zealand, by the end of June 2022, 12% of all children were directly affected by poverty. Historically, child poverty has had, and continues to have a disproportionately high effect on in Māori and Pasifika households, with 14.5% of Māori children and 19.5% of Pacific children living in poverty. These two ethnic groups continue to experience lingering effects of forced land alienation and immigration discrimination.

Maria Josina Elisabeth "Marja" Lubeck is a New Zealand politician. She was a member of parliament in the House of Representatives for the Labour Party.

The Abortion Legislation Act 2020 is an Act of Parliament in New Zealand allowing unrestricted access to abortion within the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, and repealing sections of the Crimes Act 1961 related to unlawful abortion. After the 20-week period, women seeking an abortion must consult a qualified health practitioner who will assess their physical health, mental health, and well-being. The Act also provides provisions for conscientious objection rights for medical practitioners and exempts abortion services from certain Crimes Act provisions, while extending the definition of health services to include abortion services under the Health and Disability Commissioner Act 1994.

The Conversion Practices Prohibition Legislation Act 2022 is an Act of Parliament in New Zealand that bans conversion therapy practices that seek to change or suppress a person's sexual orientation, gender identity, or gender expression. The Bill passed its third and final reading on 15 February, receiving royal assent on 18 February 2022.







