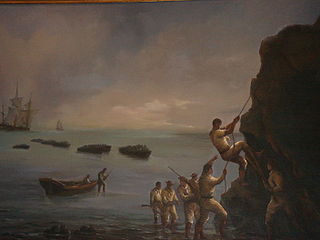Eight ships of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Challenger, most famously the fifth, the survey vessel Challenger that carried the Challenger expedition from 1872 to 1876.
Eighteen ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Eagle, after the eagle.
Six ships of the French navy have borne the name Annibal in honour of Hannibal

Valdivia is a city and commune in southern Chile, administered by the Municipality of Valdivia. The city is named after its founder Pedro de Valdivia and is located at the confluence of the Calle-Calle, Valdivia, and Cau-Cau Rivers, approximately 15 km (9 mi) east of the coastal towns of Corral and Niebla. Since October 2007, Valdivia has been the capital of Los Ríos Region and is also the capital of Valdivia Province. The national census of 2017 recorded the commune of Valdivia as having 166,080 inhabitants (Valdivianos), of whom 150,048 were living in the city. The main economic activities of Valdivia include tourism, wood pulp manufacturing, forestry, metallurgy, and beer production. The city is also the home of the Austral University of Chile, founded in 1954 and the Centro de Estudios Científicos.
Thirteen ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Vigilant:

Sharpe's Devil is the twenty-fifth historical novel in the Richard Sharpe series written by Bernard Cornwell and published in 1993. The story is set in 1820, with Sharpe and Harper en route to Chile to find their old friend Blas Vivar. Along the way they encounter the exiled Napoleon Bonaparte and the Scottish former Royal Navy officer Lord Cochrane.
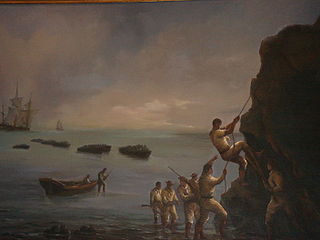
The Capture of Valdivia was a battle in the Chilean War of Independence between Royalist forces commanded by Colonel Manuel Montoya and Fausto del Hoyo and the Patriot forces under the command of Thomas Cochrane and Jorge Beauchef, held on 3 and 4 February 1820. The battle was fought over the control of the city Valdivia and its strategic and heavily fortified harbour. In the battle Patriots gained control of the southwestern part of the Valdivian Fort System after an audacious assault aided by deception and the darkness of the night. The following day the demoralised Spanish evacuated the remaining forts, looted local Patriot property in Valdivia and withdrew to Osorno and Chiloé. Thereafter, Patriot mobs looted the property of local Royalists until the Patriot army arrived to the city restoring order.
Almirante Williams is the name that has been given to several ships belonging to the Chilean Navy. They are named after Chilean Admiral Juan Williams Rebolledo (1825–1910).

The Chilean submarine O'Brien was an Oberon-class submarine in the Chilean Navy.
Foudre may refer to one of the following ships of the French Navy:
A number of ships of the Spanish Navy have borne the name San José in honour of Saint Joseph

The maritime history of Chile begins with the independence of Chile, but traces it origin in the colonial era and has ultimately origin in the seafaring tradition of the Iberian Peninsula, Europe and the Mediterranean as well as from indigenous peoples of Chile.

The Battle of Mocopulli was fought on April 1 of 1824 as the culmination of a Chilean patriots invasion plan against royalist Chiloé. The battle concluded in a royalist victory that delayed the incorporation of Chiloé into Chile to 1826 when a new invasion was launched.

Esmeralda was a 44-gun frigate built in Port Mahón, Balearic Islands in 1791 for the Spanish Navy. The First Chilean Navy Squadron, under the command of Thomas Cochrane, captured her on the night of 5 November 1820. She was renamed Valdivia in Chilean service. She was beached at Valparaíso in June 1825.

The First Chilean Navy Squadron was the heterogeneous naval force that temporarily terminated Spanish colonial rule in the Pacific and protagonized the most important naval actions of in the Latin American wars of independence. The Chilean revolutionary government organized the squadron in order to carry the war to the Viceroyalty of Perú, then the center of Spanish power in South America, and thus secure the independence of Chile and Argentina.
Independencia was a 26-gun corvette of the First Chilean Navy Squadron.
Several ships of the Chilean Navy have been named Esmeralda
Several vessels have been named Cumberland for the county of Cumberland:
Several ships of the Chilean Navy have been named Almirante Simpson after Admiral Robert Winthrop Simpson (1799–1877), a Chilean of British origin who fought in the Chilean War of Independence and War of the Confederation. It may also refer to his son, Admiral Enrique Simpson (1835–1901), who fought in the War of the Pacific.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.