Chiron is a centaur from Greek mythology.
Contents
Chiron may also refer to:
Chiron is a centaur from Greek mythology.
Chiron may also refer to:

Automobiles Ettore Bugatti was a German then French manufacturer of high-performance automobiles. The company was founded in 1909 in the then-German city of Molsheim, Alsace, by the Italian-born industrial designer Ettore Bugatti. The cars were known for their design beauty and numerous race victories. Famous Bugatti automobiles include the Type 35 Grand Prix cars, the Type 41 "Royale", the Type 57 "Atlantic" and the Type 55 sports car.

A ring system is a disc or torus orbiting an astronomical object that is composed of solid material such as gas, dust, meteoroids, planetoids or moonlets and stellar objects.

In Greek mythology, Chiron was held to be the superlative centaur amongst his brethren since he was called the "wisest and justest of all the centaurs".

2060 Chiron is a ringed small Solar System body in the outer Solar System, orbiting the Sun between Saturn and Uranus. Discovered in 1977 by Charles Kowal, it was the first-identified member of a new class of objects now known as centaurs—bodies orbiting between the asteroid belt and the Kuiper belt. Chiron is named after the centaur Chiron in Greek mythology.
Nessus may refer to:
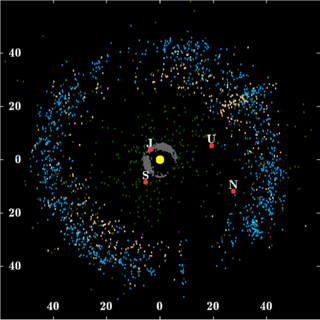
In planetary astronomy, a centaur is a small Solar System body that orbits the Sun between Jupiter and Neptune and crosses the orbits of one or more of the giant planets. Centaurs generally have unstable orbits because of this; almost all their orbits have dynamic lifetimes of only a few million years, but there is one known centaur, 514107 Kaʻepaokaʻawela, which may be in a stable orbit. Centaurs typically exhibit the characteristics of both asteroids and comets. They are named after the mythological centaurs that were a mixture of horse and human. Observational bias toward large objects makes determination of the total centaur population difficult. Estimates for the number of centaurs in the Solar System more than 1 km in diameter range from as low as 44,000 to more than 10,000,000.

Charles Thomas Kowal was an American astronomer known for his observations and discoveries in the Solar System. As a staff astronomer at Caltech's Mount Wilson and Palomar Mountain observatories between 1961 and 1984, he found the first of a new class of Solar System objects, the centaurs, discovered two moons of the planet Jupiter, and discovered or co-discovered a number of asteroids, comets and supernovae. He was awarded the James Craig Watson Medal for his contributions to astronomy in 1979.
8405 Asbolus is a centaur orbiting in the outer Solar System between the orbits of Jupiter and Neptune. It was discovered on 5 April 1995, by James Scotti and Robert Jedicke of Spacewatch (credited) at Kitt Peak Observatory in Arizona, United States. It is named after Asbolus, a centaur in Greek mythology and measures approximately 80 kilometers in diameter.
The apex is the highest point of something. The word may also refer to:
In Greek mythology, Asbolus was a centaur. He was a seer and Hesiod calls him an augur who read omens in the flight of birds.

Bugatti Automobiles S.A.S. is a French luxury sports car manufacturer. The company was founded in 1998 as a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group and is based in Molsheim, Alsace, France. The original Bugatti automobile brand was established by Ettore Bugatti (1881–1947) in 1909 at Molsheim and built sports, racing and luxury cars.
A trident is a three-pronged staff.
Chiron is the name given to a supposed moon of Saturn sighted by Hermann Goldschmidt in 1861. It has since been determined that no such moon exists.

7066 Nessus is a very red centaur on an eccentric orbit, located beyond Saturn in the outer Solar System. It was discovered on 26 April 1993, by astronomers of the Spacewatch program at the Kitt Peak National Observatory in Tucson, Arizona. The dark and reddish minor planet is likely elongated and measures approximately 60 kilometers in diameter. It was named after Nessus from Greek mythology.

10199 Chariklo is the largest confirmed centaur, a class of minor planet in the outer Solar System. It orbits the Sun between Saturn and Uranus, grazing the orbit of Uranus. On 26 March 2014, astronomers announced the discovery of two rings around Chariklo by observing a stellar occultation, making it the first minor planet known to have rings.
60558 Echeclus is a centaur, approximately 84 kilometers (52 miles) in diameter, located in the outer Solar System. It was discovered by Spacewatch in 2000 and initially classified as a minor planet with provisional designation 2000 EC98 (also written 2000 EC98). Research in 2001 by Rousselot and Petit at the Besançon observatory in France indicated that it was not a comet, but in December 2005 a cometary coma was detected. In early 2006 the Committee on Small Bodies Nomenclature (CSBN) gave it the cometary designation 174P/Echeclus. It last came to perihelion in April 2015, and was expected to reach about apparent magnitude 16.7 near opposition in September 2015.

Production vehicles or production cars are mass-produced models of automobiles offered for sale to the public and can be legally driven on public roads. Legislation and other industrial rules define the production vehicle within particular countries or uses. There is no single fixed global definition of the term.
Vulcan may refer to:

The Bugatti Chiron is a mid-engine two-seater sports car designed and developed in Germany by Bugatti Engineering GmbH and manufactured in Molsheim, France, by French automobile manufacturer Bugatti Automobiles S.A.S. The successor to the Bugatti Veyron, the Chiron was first shown at the Geneva Motor Show on 1 March 2016. The car's design was initially previewed with the Bugatti Vision Gran Turismo concept car unveiled at the 2015 Frankfurt Auto Show.