Related Research Articles

Liechtenstein is a principality governed under a semi-constitutional monarchy. It has a form of mixed constitution in which political power is shared by the monarch and a democratically elected parliament. There is a two-party system and a form of representative democracy in which the prime minister and head of government is responsible to parliament. However the Prince of Liechtenstein is head of state and exercises considerable political powers.

The 1977 Irish general election to the 21st Dáil was held on Thursday, 16 June, following the dissolution of the 20th Dáil on 25 May by President Patrick Hillery on the request of Taoiseach Liam Cosgrave. The general election took place in 42 Dáil constituencies throughout Ireland for 148 seats in Dáil Éireann, the house of representatives of the Oireachtas, an increase of four seats with a significant revision of constituencies under the Electoral (Amendment) Act 1974. The election is regarded as a pivotal point in twentieth-century Irish politics. Jack Lynch led Fianna Fáil to a landslide election win, clearly defeating the outgoing Fine Gael–Labour government.
The Jamaica Labour Party is one of the two major political parties in Jamaica, the other being the People's National Party (PNP). While its name might suggest that it is a social democratic party, the JLP is actually a conservative party.

The Malaysian People's Party is a political party in Malaysia. Founded on 11 November 1955 as Partai Ra'ayat, it is one of the older political parties in Malaysia and traces its pedigree to the anti-colonial movements from the pre World War II period like the Kesatuan Melayu Muda.

The Patriotic Union is a liberal-conservative political party in Liechtenstein. The VU is one of the two major political parties in Liechtenstein, along with the monarchist conservative Progressive Citizens' Party (FBP). The VU is the relatively more liberal of the two parties, advocating constitutional monarchy and greater democracy. It is led by Thomas Zwiefelhofer and has ten members in the Landtag.
Historically in Quebec, Canada, there were a number of political parties that were part of the Canadian social credit movement. There were various parties at different times with different names at the provincial level, all broadly following the social credit philosophy; at various times they had varying degrees of affiliation with the Social Credit Party of Canada at the federal level.
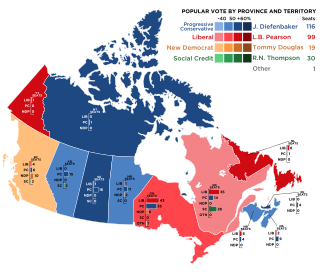
The 1962 Canadian federal election was held on June 18, 1962, to elect members of the House of Commons of Canada of the 25th Parliament of Canada. The governing Progressive Conservative (PC) Party won a plurality of seats in this election, and its majority government was reduced to a minority government.

The United Federal Party (UFP) was a political party in the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland.

Elections in Liechtenstein take place at a national level within a multi-party system, with two dominant political parties. The Landtag of Liechtenstein has 25 members, elected for a four-year term by proportional representation in two multi-seat constituencies.
The Union of Liberals and Leftists was a social-liberal political party in Iceland.

The Workers' and Peasants' Party was a political party in Liechtenstein. The party emerged from the trade union movement, as no workers had been elected in the 1949 elections. The party was founded as a delegates' assembly in 1953. It contested the February 1953 elections, it received 198 votes (6.9%) and but failed to win a seat due to the 18% electoral threshold. The party did not contest the June 1953 elections, and has not contested any since.
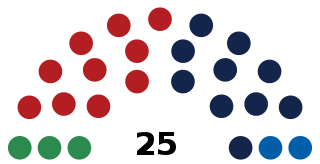
The Landtag of the Principality of Liechtenstein, commonly referred to as the Landtag of Liechtenstein, is the unicameral parliament of Liechtenstein.

Walter Kieber was a lawyer and political figure from Liechtenstein who served as Prime Minister of Liechtenstein from 1974 to 1978.

General elections were held in Pakistan on 7 December 1970 to elect members of the National Assembly. They were the first direct general elections since the independence of Pakistan and ultimately the only ones held prior to the independence of Bangladesh. Voting took place in 300 general constituencies, of which 162 were in East Pakistan and 138 in West Pakistan. A further thirteen seats were reserved for women, who were to be elected by members of the National Assembly.
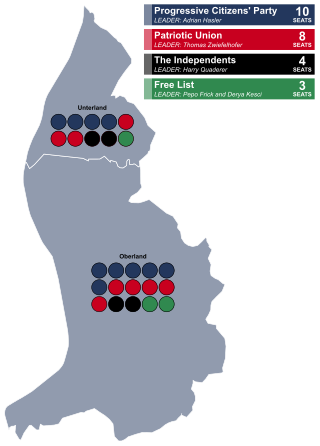
General elections were held in Liechtenstein on 3 February 2013, using a proportional representation system. Four parties contested the elections; the centre-right Patriotic Union (VU) and Progressive Citizens' Party (FBP), centre-left Free List (FL) and newly created populist alliance The Independents (DU).

The Progressive Constitutionalist Party (PCP) was a political party in Malta between 1953 and 1971.
The Liberal Party was a political party in Luxembourg in the 1930s and 1940s.

The Central Africa Party was a multi-racial political party in the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. The party organised separately in the three constituent part of the federation, Northern Rhodesia, Nyasaland and Southern Rhodesia.

The Sabah Chinese Association was a Chinese political party in the North Borneo and the Sabah state of Malaysia.

General elections were held in Liechtenstein on 7 February 2021 to elect the 25 members of the Landtag. The Patriotic Union (VU) and Progressive Citizens' Party (FBP) both won ten seats, with the VU receiving just 42 votes more than the FBP. The Independents (DU), which finished third in the 2017 elections but then suffered a split in 2018 when three of its five MPs broke away to form Democrats for Liechtenstein (DpL), failed to win a seat, while DpL won two. The Free List retained its three seats, becoming the third-largest party in the Landtag.
References
- ↑ Principality of Liechtenstein A documentary account Archived 2011-06-07 at the Wayback Machine Press and Information Office
- ↑ Vincent E McHale (1983) Political parties of Europe, Greenwood Press, p608 ISBN 0-313-23804-9