Chromium oxide may refer to:

Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the molecular species, H2CrO4 of which the trioxide is the anhydride. Chromic acid features chromium in an oxidation state of +6 (or VI). It is a strong and corrosive oxidising agent and a moderate carcinogen.

Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, CrO2−
4. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, Cr
2O2−
7. They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible.

Potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7, is a common inorganic chemical reagent, most commonly used as an oxidizing agent in various laboratory and industrial applications. As with all hexavalent chromium compounds, it is acutely and chronically harmful to health. It is a crystalline ionic solid with a very bright, red-orange color. The salt is popular in laboratories because it is not deliquescent, in contrast to the more industrially relevant salt sodium dichromate.
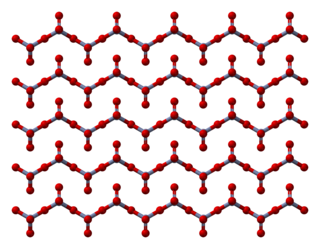
Chromium trioxide (also known as chromium(VI) oxide or chromic anhydride) is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO3. It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name. This compound is a dark-purple solid under anhydrous conditions, bright orange when wet and which dissolves in water concomitant with hydrolysis. Millions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly for electroplating. Chromium trioxide is a powerful oxidiser and a carcinogen.

Potassium chromate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2CrO4. This yellow solid is the potassium salt of the chromate anion. It is a common laboratory chemical, whereas sodium chromate is important industrially.

Sodium dichromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2Cr2O7. However, the salt is usually handled as its dihydrate Na2Cr2O7·2H2O. Virtually all chromium ore is processed via conversion to sodium dichromate and virtually all compounds and materials based on chromium are prepared from this salt. In terms of reactivity and appearance, sodium dichromate and potassium dichromate are very similar. The sodium salt is, however, around twenty times more soluble in water than the potassium salt (49 g/L at 0 °C) and its equivalent weight is also lower, which is often desirable.

Chromate conversion coating or alodine coating is a type of conversion coating used to passivate steel, aluminium, zinc, cadmium, copper, silver, titanium, magnesium, and tin alloys. The coating serves as a corrosion inhibitor, as a primer to improve the adherence of paints and adhesives, as a decorative finish, or to preserve electrical conductivity. It also provides some resistance to abrasion and light chemical attack on soft metals.

Chromium is a member of group 6, of the transition metals. The +3 and +6 states occur most commonly within chromium compounds, followed by +2; charges of +1, +4 and +5 for chromium are rare, but do nevertheless occasionally exist.

Chromium(III) sulfate usually refers to the inorganic compounds with the formula Cr2(SO4)3.x(H2O), where x can range from 0 to 18. Additionally, ill-defined but commercially important "basic chromium sulfates" are known. These salts are usually either violet or green solids that are soluble in water. It is commonly used in tanning leather.

Nickel(II) chromate (NiCrO4) is an acid-soluble compound, red-brown in color, with high tolerances for heat. It and the ions that compose it have been linked to tumor formation and gene mutation, particularly to wildlife.

Calcium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula CaCrO4, i.e. the chromate salt of calcium. It is a bright yellow solid which is normally found in the dihydrate form CaCrO4·2H2O. A very rare anhydrous mineral form exists in nature, which is known as chromatite.

Sodium chromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CrO4. It exists as a yellow hygroscopic solid, which can form tetra-, hexa-, and decahydrates. It is an intermediate in the extraction of chromium from its ores.

Chromium(VI) peroxide or chromium oxide peroxide is an unstable compound with the formula CrO5. This compound contains one oxo ligand and two peroxo ligands, making a total of five oxygen atoms per chromium atom.
Oxidation with chromium(VI) complexes involves the conversion of alcohols to carbonyl compounds or more highly oxidized products through the action of molecular chromium(VI) oxides and salts. The principal reagents are Collins reagent, PDC, and PCC. These reagents represent improvements over inorganic chromium(VI) reagents such as Jones reagent.

The Jones oxidation is an organic reaction for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carboxylic acids and ketones, respectively. It is named after its discoverer, Sir Ewart Jones. The reaction was an early method for the oxidation of alcohols. Its use has subsided because milder, more selective reagents have been developed, e.g. Collins reagent.
A chromate ester is a chemical structure that contains a chromium atom (symbol Cr) in a +6 oxidation state that is connected via an oxygen (O) linkage to a carbon (C) atom. The Cr itself is in its chromate form, with several oxygens attached, and the Cr–O–C attachment makes this chemical group structurally similar to other ester functional groups. They can be synthesized from various chromium(VI) metal compounds, such as CrO3, chromium chloride complexes, and aqueous chromate ions, and tend to react via redox reactions to liberate chromium(IV).

The chromium cycle is the biogeochemical cycle of chromium through the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere and lithosphere.
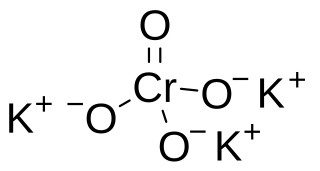
Potassium hypochromate is a chemical compound with the formula K3CrO4 with the unusual Cr5+ ion. This compound is unstable in water but stable in alkaline solution and was found to have a similar crystal structure to potassium hypomanganate.
Europium(III) chromate is a chemical compound composed of europium, chromium and oxygen with europium in the +3 oxidation state, chromium in the +5 oxidation state and oxygen in the -2 oxidation state. It has the chemical formula of EuCrO4.