
The Decembrist Revolt was a failed coup d'état led by liberal military and political dissidents against the Russian Empire. It took place in Saint Petersburg on 26 December [O.S. 14 December] 1825, following the sudden death of Emperor Alexander I.

The streltsy were the units of Russian firearm infantry from the 16th century to the early 18th century and also a social stratum, from which personnel for streltsy troops were traditionally recruited. They are also collectively known as streletskoye voysko. These infantry troops reinforced feudal levy horsemen or pomestnoye voysko.

Yemelyan Ivanovich Pugachev was an ataman of the Yaik Cossacks and the leader of the Pugachev's Rebellion, a major popular uprising in the Russian Empire during the reign of Catherine the Great.

Sloboda Ukraine, also known locally as Slobozhanshchyna or Slobozhanshchina, is a historical region in northeastern Ukraine and southwestern Russia. It developed and flourished in the 17th and 18th centuries on the southwestern frontier of the Tsardom of Russia. In 1765, it was converted into the Sloboda Ukraine Governorate.

The Left SR uprising, or Left SR revolt, was a rebellion against the Bolsheviks by the Left Socialist Revolutionary Party in Moscow, Soviet Russia, on 6–7 July 1918. It was one of a number of left-wing uprisings against the Bolsheviks that took place during the Russian Civil War.

Kondraty Fyodorovich Ryleyev was a Russian poet, publisher, and a leader of the Decembrist Revolt, which attempted to overthrow the Russian monarchy in 1825.

The Khotyn Uprising was a Ukrainian-led insurrection in the far-northern tip of Bessarabia region, nestled between Bukovina and Podolia. It occurred on January 7–February 1, 1919, less than a year after Bessarabia's integration into the Romanian Kingdom. The city it was centered on is now known as Khotyn (Хотин), and is located in Chernivtsi Oblast, Ukraine; in 1919, it was the capital of Hotin County, on the unofficial border between Romania and the Ukrainian People's Republic (UNR). The revolt was carried out by armed locals, mainly Ukrainian peasants, assisted by Cossack deserters from the Ukrainian People's Army and groups of Moldovans, with some support from local Bolsheviks and White Russians. It forms part of the Ukrainian War of Independence, though whether or not the UNR covertly supported it, beyond formally reneging it, is a matter of dispute. The role of Bolsheviks, which has been traditionally highlighted in Romanian and Soviet historiography alike, is similarly debated. The Khotyn Uprising is therefore ambiguously linked to the Russian Civil War and the Ukrainian–Soviet War.

Pugachev's Rebellion of 1773–1775 was the principal revolt in a series of popular rebellions that took place in the Russian Empire after Catherine II seized power in 1762. It began as an organized insurrection of Yaik Cossacks headed by Yemelyan Pugachev, a disaffected ex-lieutenant of the Imperial Russian Army, against a background of profound peasant unrest and war with the Ottoman Empire. After initial success, Pugachev assumed leadership of an alternative government in the name of the late Tsar Peter III and proclaimed an end to serfdom. This organized leadership presented a challenge to the imperial administration of Catherine II.

Military settlements represented a special organization of the Russian military forces in 1810–1857, which allowed the combination of military service and agricultural employment.

Chuhuiv or Chuguev is a city in Kharkiv Oblast, Ukraine. The city is the administrative center of Chuhuiv Raion (district). It hosts the administration of Chuhuiv urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: 31,018.

Zmiiv or Zmiyiv from 1976 to 1990, is a city in Chuhuiv Raion, Kharkiv, Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Zmiiv urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The population in 2001 was 17,063, falling to 13,737.

Stavyshche is a rural settlement in Bila Tserkva Raion, Kyiv Oblast (province) in northern Ukraine, on the Hnylyi Tikych river. It hosts the administration of Stavyshche settlement hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: 6,056 . In 2001, population was 7,929.

The Polubotok Club Affair was an important national civil affair and an armed revolt of the Kiev garrison troops that took place on July 17–18, 1917 in Kiev soon after the collapse of the Kerensky Offensive. It was part of a Ukrainian military movement, one of key roles played by the public organization Ukrainian Military Club of Pavlo Polubotok.

The Guo Huaiyi rebellion was a peasant revolt by Chinese farmers against Dutch rule in Taiwan in 1652. Sparked by dissatisfaction with heavy Dutch taxation on them but not the aborigines and extortion by low-ranking Dutch officials and servicemen, the rebellion initially gained ground before being crushed by a coalition of Dutch soldiers and their aboriginal allies. It is considered the most important uprising against the Dutch during the 37-year period of their colonisation of Taiwan.

The Chernigov Regiment revolt was the second and the last major armed conflict of the Decembrist revolt in the former Russian Empire. The revolt unfolded January 10 [O.S. December 29] – January 15 [O.S. January 3] 1826 in Ukraine between Kiev and Bila Tserkva.
Jančić's rebellion, also known as the First Mašići rebellion, was a rebellion led by ethnic Serbs in the Gradiška region against the Ottoman government in the Bosnia Eyalet. It broke out in September 1809 following a string of economical, national and religious deprivations of the rights of Serbs. Jančić's rebellion erupted immediately after the failed Yamaks revolt.

The Sheksna uprising was an anti-Bolshevik uprising in townships on the Sheksna River in the Vologda and Cherpovets provinces between 1–3 December 1918. The rebels seized the railway station Sheksna and broke railway communication on the Cherepovets-Vologda line, jeopardizing messages to Petrograd. The uprising was suppressed by Red Army troops arriving from Vologda and Cherpovets.
The Central Asian revolt of 1916, also known as the Semirechye Revolt and as Urkun in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan, was an anti-Russian uprising by the indigenous inhabitants of Russian Turkestan sparked by the conscription of Muslims into the Russian military for service on the Eastern Front during World War I. The rampant corruption of the Russian colonial regime and Tsarist colonialism with regards to its economic, political, religious, and national dimensions are all seen as contributing causes.
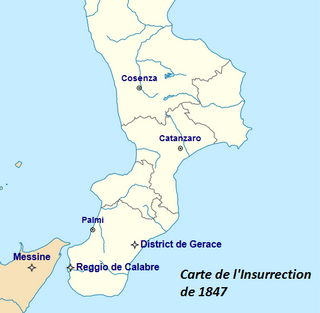
The Insurrection of 1847 in the Two Sicilies is a series of three revolts that happened in September 1847 in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. Its aim was the unification of Italy and the establishment of either a constitutional monarchy or a republic. The insurrection is often considered as a continuation of the Neapolitan revolution of 1820 and at the same time as a foretaste of the Sicilian revolution of 1848 and of the spring of nations.

The Chapan rebellion was one of the largest peasant uprising against the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War. Taking place in March-April 1919, the uprising covered the territory of Syzran, Sengileevsky, Karsunsky districts of Simbirsk and the Stavropol and Melekessky districts of Samara. It got its name from the clothes of the rebels: the chapan - a winter coat, made of sheepskin, a special robe belted with a sash, a popular clothing among the peasants of the region during cold weather. The uprising was brutally suppressed, and its participants, mostly peasants, were subjected to terror and mass repression.

















