
Bell Labs is an American industrial research and scientific development company credited with the development of radio astronomy, the transistor, the laser, the photovoltaic cell, the charge-coupled device (CCD), information theory, the Unix operating system, and the programming languages B, C, C++, S, SNOBOL, AWK, AMPL, and others. Ten Nobel Prizes and five Turing Awards have been awarded for work completed at Bell Laboratories.

Los Alamos National Laboratory is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, in the American southwest. Best known for its central role in helping develop the first atomic bomb, LANL is one of the world's largest and most advanced scientific institutions.

Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federally funded research and development center in Livermore, California, United States. Originally established in 1952, the laboratory now is sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administered privately by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC.

Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, Long Island, a hamlet of the Town of Brookhaven. It was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base. Located approximately 60 miles east of New York City, it is managed by Stony Brook University and Battelle Memorial Institute.

Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) is a federally funded research and development center in the hills of Berkeley, California, United States. Established in 1931 by the University of California (UC), the laboratory is sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administered by the UC system. Ernest Lawrence, who won the Nobel prize for inventing the cyclotron, founded the lab and served as its director until his death in 1958. Located in the Berkeley Hills, the lab overlooks the campus of the University of California, Berkeley.
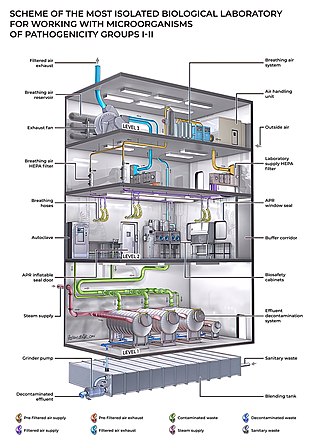
A biosafety level (BSL), or pathogen/protection level, is a set of biocontainment precautions required to isolate dangerous biological agents in an enclosed laboratory facility. The levels of containment range from the lowest biosafety level 1 (BSL-1) to the highest at level 4 (BSL-4). In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have specified these levels in a publication referred to as BMBL. In the European Union, the same biosafety levels are defined in a directive. In Canada the four levels are known as Containment Levels. Facilities with these designations are also sometimes given as P1 through P4, as in the term P3 laboratory.

A laboratory is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratories are found in a variety of settings such as schools, universities, privately owned research institutions, corporate research and testing facilities, government regulatory and forensic investigation centers, physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, regional and national referral centers, and even occasionally personal residences.

IBM Research is the research and development division for IBM, an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, with operations in over 170 countries. IBM Research is the largest industrial research organization in the world and has twelve labs on six continents.

The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH) is a public research university in Huntsville, Alabama. The university is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools and comprises eight colleges: arts, humanities & social sciences; business; education; engineering; honors; nursing; science; and graduate. The university's enrollment is approximately 10,000. It is part of the University of Alabama System and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities: Very High Research Activity".

The United States Department of Energy National Laboratories and Technology Centers is a system of laboratories overseen by the United States Department of Energy (DOE) for scientific and technological research. The primary mission of the DOE national laboratories is to conduct research and development (R&D) addressing national priorities: energy and climate, the environment, national security, and health. Sixteen of the seventeen DOE national laboratories are federally funded research and development centers administered, managed, operated and staffed by private-sector organizations under management and operating (M&O) contracts with the DOE. The National Laboratory system was established in the wake of World War II, during which the United States had quickly set-up and pursued advanced scientific research in the sprawling Manhattan Project.

The Thomas J. Watson Research Center is the headquarters for IBM Research. Its main laboratory is in Yorktown Heights, New York, 38 miles (61 km) north of New York City. It also operates facilities in Cambridge, Massachusetts and Albany, New York.

The U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command Army Research Laboratory is the U.S. Army's foundational research laboratory. ARL is headquartered at the Adelphi Laboratory Center (ALC) in Adelphi, Maryland. Its largest single site is at Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland. Other major ARL locations include Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico, Graces Quarters, Maryland, and NASA's Glenn Research Center, Ohio and Langley Research Center, Virginia. ARL also has regional sites in Playa Vista, California, Chicago, Austin, TX, and Boston.

Washington State University Tri-Cities is one of six campuses that make up Washington State University. It is located along the Columbia River in northern Richland, Washington. With upper division and graduate programs, WSU Tri-Cities offers 20 baccalaureate, 17 master's and 14 doctoral degree programs. The campus added freshman and sophomore courses in fall 2007 to become a true four-year public university. WSU Tri-Cities has strong community support and partnerships, particularly with the nearby Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.

The Coastal Science Campus of the University of California, Santa Cruz consists of five main institutions: UC Santa Cruz's Long Marine Laboratory, UC Santa Cruz's Coastal Biology Building, the NOAA Southwest Fisheries Science Center, the Seymour Marine Discovery Center, and the California Marine Wildlife Veterinary Care and Research Center.

United International University is a private research university in Dhaka, Bangladesh.

The Bell Labs Holmdel Complex, in Holmdel Township, Monmouth County, New Jersey, United States, functioned for 44 years as a research and development facility, initially for the Bell System and later Bell Labs. The centerpiece of the campus is an Eero Saarinen–designed structure that served as the home to over 6,000 engineers and researchers. This modernist building, dubbed "The Biggest Mirror Ever" by Architectural Forum, due to its mirror box exterior, was the site of a Nobel Prize discovery, the laser cooling work of Steven Chu.

IBM Yamato Facility is located in the city of Yamato, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan, is where IBM's research and development activities were done for IBM's worldwide and Asia-Pacific region market. Its buildings were designed by the architecture firm of Nikken Sekkei Ltd. and completed in 1985. In July 2012, all IBM research and development functions completed moving to IBM Toyosu Facility, Tokyo. The last IBM-related organizations left Yamato around September 2012, and the facility is no longer associated with IBM.
Living labs are open innovation ecosystems in real-life environments using iterative feedback processes throughout a lifecycle approach of an innovation to create sustainable impact. They focus on co-creation, rapid prototyping & testing and scaling-up innovations & businesses, providing joint-value to the involved stakeholders. In this context, living labs operate as intermediaries/orchestrators among citizens, research organisations, companies and government agencies/levels.

Flight Laboratory, IIT Kanpur is an airstrip/aerodrome located inside IIT Kanpur's campus at Kalyanpur 18 kilometres west of city of Kanpur, India. It is used by the Aerospace Engineering department of IIT Kanpur. Pawan Hans began a helicopter ferry service to Lucknow from June 2013, which later shut down silently.

The Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences is a research institute on virology administered by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), which reports to the State Council of the People's Republic of China. The institute is one of nine independent organisations in the Wuhan Branch of the CAS. Located in Jiangxia District, Wuhan, Hubei, it was founded in 1956 and opened mainland China's first biosafety level 4 (BSL-4) laboratory in 2018. The institute has collaborated with the Galveston National Laboratory in the United States, the Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie in France, and the National Microbiology Laboratory in Canada. The institute has been an active premier research center for the study of coronaviruses.

















