
Danish is a North Germanic language spoken by around six million people, principally in Denmark and in the region of Southern Schleswig in northern Germany, where it has minority language status. Also, minor Danish-speaking communities are found in Norway, Sweden, Spain, the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina. Due to immigration and language shift in urban areas, around 15–20% of the population of Greenland speak Danish as their first language.

The Kalmar Union was a personal union in Scandinavia that from 1397 to 1523 joined under a single monarch of the three kingdoms of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway, together with Norway's overseas dependencies. The union was not quite continuous; there were several short interruptions. Legally, the countries remained separate sovereign states, but with their domestic and foreign policies being directed by a common monarch.

Scandinavia is a region in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties. The term Scandinavia in local usage covers the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. The majority national languages of these three, belong to the Scandinavian dialect continuum, and are mutually intelligible North Germanic languages. In English usage, Scandinavia also sometimes refers to the Scandinavian Peninsula, or to the broader region including Finland and Iceland, which is always known locally as the Nordic countries.

Zealand, at 7,031 km2, is the largest and most populous island in Denmark proper. Zealand has a population of 2,302,074.

The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony–Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and of Brunswick-Lüneburg (Hanover) joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715.

The Øresund or Öresund Bridge is a combined railway and motorway bridge across the Øresund strait between Sweden and Denmark. The bridge runs nearly 8 kilometres from the Swedish coast to the artificial island Peberholm in the middle of the strait. The crossing is completed by the 4-kilometre (2.5 mi) Drogden Tunnel from Peberholm to the Danish island of Amager.

The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages, a sub-family of the Indo-European languages, along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is sometimes referred to as the "Nordic languages", a direct translation of the most common term used among Danish, Faroese, Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish scholars and laypeople.

Christian I was a Scandinavian monarch under the Kalmar Union. He was king of Denmark (1448–1481), Norway (1450–1481) and Sweden (1457–1464). From 1460 to 1481, he was also duke of Schleswig and count of Holstein. He was the first king of the House of Oldenburg.

Sweden and Norway or Sweden–Norway, officially the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway, or as the United Kingdoms, was a personal union of the separate kingdoms of Sweden and Norway under a common monarch and common foreign policy that lasted from 1814 until its peaceful dissolution in 1905.

The House of Oldenburg is a European dynasty of North German origin. It is one of Europe's most influential royal houses, with branches that rule or have ruled in Denmark, Iceland, Greece, Norway, Russia, Sweden, Schleswig, Holstein, and Oldenburg. The current Queen of Denmark and King of Norway, the former King of Greece, the consort of the monarch of the United Kingdom, as well as the first fourteen persons in the line of succession to the British throne, are all patrilineal members of the Glücksburg branch of this house.

The Treaty of Kiel or Peace of Kiel was concluded between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the Kingdom of Sweden on one side and the Kingdoms of Denmark and Norway on the other side on 14 January 1814 in Kiel. It ended the hostilities between the parties in the ongoing Napoleonic Wars, where the United Kingdom and Sweden were part of the anti-French camp while Denmark–Norway was allied to Napoleon Bonaparte.

The Sweden national football team represents Sweden in international football and is controlled by the Swedish Football Association, the governing body of football in Sweden. Sweden's home ground is Friends Arena in Solna and the team is coached by Janne Andersson. From 1945 to late 1950s, they were considered one of the greatest teams in Europe.

Scanian is a closely related group of South Swedish dialects spoken in the province of Scania in southern Sweden. Scanian formed part of the old Scandinavian dialect continuum and are by most historical linguists considered to be an East Danish dialect group, but due to the modern-era influence from Standard Swedish in the region and because traditional dialectology in the Scandinavian countries normally has not considered isoglosses that cut across state borders, the Scanian dialects have normally been treated as a South Swedish dialect group in Swedish dialect research. However, many of the early Scandinavian linguists, including Adolf Noreen and G. Sjöstedt, classified it as "South Scandinavian", and some linguists, such as Elias Wessén, also considered Old Scanian a separate language, classified apart from both Old Danish and Old Swedish.

The rescue of the Danish Jews occurred during Nazi Germany's occupation of Denmark during World War II. On October 1, 1943, Nazi leader Adolf Hitler ordered Danish Jews to be arrested and deported. The Danish resistance movement, with the assistance of many Danish citizens, managed to evacuate 7,220 of Denmark's 7,800 Jews, plus 686 non-Jewish spouses, by sea to nearby neutral Sweden.

Helsingborg is a town and the seat of Helsingborg Municipality, Scania, Sweden. It had 108,334 inhabitants in 2017. Helsingborg is the centre of the northern part of western Scania. There is no formal metropolitan area, but the municipality of Helsingborg City and its neighbouring five municipalities had in spring of 2013 a population of 269 489 inhabitants at an area of 1,353 square kilometres, a population density of 200 people/km2. This makes Helsingborg the fourth largest population area in Sweden. The city is also Sweden's closest point to Denmark, with the Danish city Helsingør clearly visible on the other side of the Øresund about 4 km (2 mi) to the west, closer than to the city's own remoter areas. If including all population around the northern part of Øresund, as a Helsingborg-Helsingør metropolitan area, its population increases to 732 450 at an area of 2,802 square kilometres. The busy ferry route known as the HH Ferry route has through history been operated by several shipping lines. As of 2014 more than 70 car ferries departures from each harbour every day.
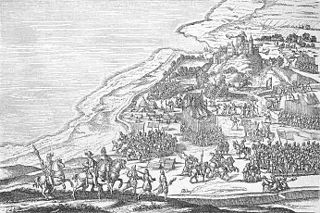
The Northern Seven Years' War was fought between the Kingdom of Sweden and a coalition of Denmark–Norway, Lübeck and Polish-Lithuanian commonwealth between 1563 and 1570. The war was motivated by the dissatisfaction of King Frederick II of Denmark with the dissolution of the Kalmar Union, and the will of King Eric XIV of Sweden to break Denmark's dominating position. The fighting continued until both armies had been exhausted, and many men died. The resulting Treaty of Stettin was a stalemate, with neither party gaining any new territory.

Denmark–Norway, also known as the Dano–Norwegian Realm, the Oldenburg Monarchy, or the Oldenburg realms, was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real union consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway, the Duchy of Schleswig, and the Duchy of Holstein. The state also claimed sovereignty over two historical peoples: Wends and Gutes. Denmark–Norway had several colonies, namely the Danish Gold Coast, the Nicobar Islands, Serampore, Tharangambadi, and the Danish West Indies.

The Nordic countries, or the Nordics, are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic, where they are most commonly known as Norden. The term includes Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, as well as Greenland and the Faroe Islands—which are both part of the Kingdom of Denmark—and the Åland Islands and Svalbard archipelagos that belong to Finland and Norway respectively, whereas the Norwegian Antarctic territories are often not considered a part of the Nordic countries, due to their geographical location. Several regions in Europe, such as the Northern Isles of Scotland, share cultural or ethnic ties with Nordic nations, but are not considered to be Nordic countries. Scandinavians, who comprise over three quarters of the region's population, are the largest group, followed by Finns, who comprise the majority in Finland; other ethnic groups are the Greenlandic Inuit, the Sami people, and recent immigrants and their descendants. The native languages Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, Icelandic, and Faroese are all North Germanic languages rooted in Old Norse. Native non-Germanic languages are Finnish, Greenlandic and several Sami languages. The main religion is Lutheran Christianity.



















