
UST, formerly known as UST Global, is a provider of digital technology and transformation, information technology and services, headquartered in Aliso Viejo, California, United States. Stephen Ross founded UST in 1998 in Laguna Hills. The company has offices in the Americas, EMEA, APAC, and India.
Azure DevOps Server, formerly known as Team Foundation Server (TFS) and Visual Studio Team System (VSTS), is a Microsoft product that provides version control, reporting, requirements management, project management, automated builds, testing and release management capabilities. It covers the entire application lifecycle and enables DevOps capabilities. Azure DevOps can be used as a back-end to numerous integrated development environments (IDEs) but is tailored for Microsoft Visual Studio and Eclipse on all platforms.

Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to ISO.
Progress Chef is a configuration management tool written in Ruby and Erlang. It uses a pure-Ruby, domain-specific language (DSL) for writing system configuration "recipes". Chef is used to streamline the task of configuring and maintaining a company's servers, and can integrate with cloud-based platforms such as Amazon EC2, Google Cloud Platform, Oracle Cloud, OpenStack, IBM Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Rackspace to automatically provision and configure new machines. Chef contains solutions for both small and large scale systems.
DevOps is a methodology integrating and automating the work of software development (Dev) and information technology operations (Ops). It serves as a means for improving and shortening the systems development life cycle. DevOps is complementary to agile software development; several DevOps aspects came from the agile approach.
Continuous delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time. It aims at building, testing, and releasing software with greater speed and frequency. The approach helps reduce the cost, time, and risk of delivering changes by allowing for more incremental updates to applications in production. A straightforward and repeatable deployment process is important for continuous delivery.

OpenShift is a family of containerization software products developed by Red Hat. Its flagship product is the OpenShift Container Platform — a hybrid cloud platform as a service built around Linux containers orchestrated and managed by Kubernetes on a foundation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. The family's other products provide this platform through different environments: OKD serves as the community-driven upstream, Several deployment methods are available including self-managed, cloud native under ROSA, ARO and RHOIC on AWS, Azure, and IBM Cloud respectively, OpenShift Online as software as a service, and OpenShift Dedicated as a managed service.
Network functions virtualization (NFV) is a network architecture concept that leverages IT virtualization technologies to virtualize entire classes of network node functions into building blocks that may connect, or chain together, to create and deliver communication services.
Cloud management is the management of cloud computing products and services.
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management. Originally designed by Google, the project is now maintained by a worldwide community of contributors, and the trademark is held by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation.

Mirantis Inc. is a Campbell, California, based B2B open source cloud computing software and services company. Its primary container and cloud management products, part of the Mirantis Cloud Native Platform suite of products, are Mirantis Container Cloud and Mirantis Kubernetes Engine. The company focuses on the development and support of container and cloud infrastructure management platforms based on Kubernetes and OpenStack. The company was founded in 1999 by Alex Freedland and Boris Renski. It was one of the founding members of the OpenStack Foundation, a non-profit corporate entity established in September, 2012 to promote OpenStack software and its community. Mirantis has been an active member of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation since 2016.

Dynatrace, Inc. is a technology company that provides a software observability platform. Dynatrace technologies are used to monitor, analyze, and optimize application performance, software development and security practices, IT infrastructure, and user experience for businesses and government agencies throughout the world.
Infrastructure as code (IaC) is the process of managing and provisioning computer data center resources through machine-readable definition files, rather than physical hardware configuration or interactive configuration tools. The IT infrastructure managed by this process comprises both physical equipment, such as bare-metal servers, as well as virtual machines, and associated configuration resources. The definitions may be in a version control system, rather than maintaining the code through manual processes. The code in the definition files may use either scripts or declarative definitions, but IaC more often employs declarative approaches.
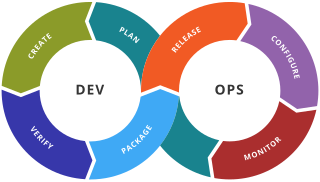
A DevOps toolchain is a set or combination of tools that aid in the delivery, development, and management of software applications throughout the systems development life cycle, as coordinated by an organisation that uses DevOps practices.
Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) is a discipline in the field of Software Engineering and IT infrastructure support that monitors and improves the availability and performance of deployed software systems and large software services. There is typically a focus on automation and an Infrastructure as Code methodology. SRE uses elements of software engineering, IT infrastructure, web development, and operations to assist with reliability. It is similar to DevOps as they both aim to improve the reliability and availability of deployed software systems.
Continuous configuration automation (CCA) is the methodology or process of automating the deployment and configuration of settings and software for both physical and virtual data center equipment.
Virtuozzo is a software company that develops virtualization and cloud management software for cloud computing providers, managed services providers and internet hosting service providers. The company's software enables service providers to offer Infrastructure as a service, Container-as-a-Service, Platform as a service, Kubernetes-as-a-Service, WordPress-as-a-Service and other solutions.

Oracle Cloud is a cloud computing service offered by Oracle Corporation providing servers, storage, network, applications and services through a global network of Oracle Corporation managed data centers. The company allows these services to be provisioned on demand over the Internet.
StackEngine was founded in Austin, Texas in 2014 to build enterprise-grade container management and automation products to help organizations simply deploy, manage, and scale resilient applications. It was designed as a Docker management software product to provide an integrated DevOps solution for end-to-end container application delivery and operations. StackEngine was acquired by Oracle in December 2015.
The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) is a Linux Foundation project that was started in 2015 to help advance container technology and align the tech industry around its evolution.






