Cobalt nitrate can refer to:
- Cobalt(II) nitrate and its several hydrates
- Cobalt(III) nitrate, a diamagnetic volatile compound
Cobalt nitrate can refer to:
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions.
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.

Cobalt(II) chloride is an inorganic compound of cobalt and chlorine, with the formula CoCl
2. The compound forms several hydrates CoCl
2•nH
2O, for n = 1, 2, 6, and 9. Claims of the formation of tri- and tetrahydrates have not been confirmed. The anhydrous form is a blue crystalline solid; the dihydrate is purple and the hexahydrate is pink. Commercial samples are usually the hexahydrate, which is one of the most commonly used cobalt compounds in the lab.
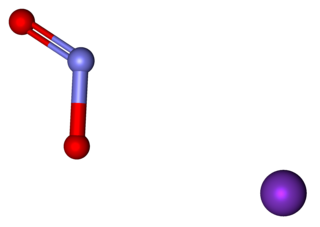
Potassium nitrite (distinct from potassium nitrate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula KNO2. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrite ions NO2−, which forms a white or slightly yellow, hygroscopic crystalline powder that is soluble in water.

Manganese carbonate is a compound with the chemical formula MnCO3. Manganese carbonate occurs naturally as the mineral rhodochrosite but it is typically produced industrially. It is a pale pink, water-insoluble solid. Approximately 20,000 metric tonnes were produced in 2005.
Cobalt oxide is a family of chemical compounds consisting of cobalt and oxygen atoms.
Cobalt(II) oxide is an inorganic compound that has been described as an olive-green or gray solid. It is used extensively in the ceramics industry as an additive to create blue colored glazes and enamels as well as in the chemical industry for producing cobalt(II) salts. A related material is cobalt(II,III) oxide, a black solid with the formula Co3O4.

Cobalt nitrate is the inorganic compound with the formula Co(NO3)2.xH2O. It is cobalt(II)'s salt. The most common form is the hexahydrate Co(NO3)2·6H2O, which is a red-brown deliquescent salt that is soluble in water and other polar solvents.

Tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula [Co(en)3]Cl3 (where "en" is the abbreviation for ethylenediamine). It is the chloride salt of the coordination complex [Co(en)3]3+. This trication was important in the history of coordination chemistry because of its stability and its stereochemistry. Many different salts have been described. The complex was first described by Alfred Werner who isolated this salt as yellow-gold needle-like crystals.

Cobalt(II,III) oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Co3O4. It is one of two well characterized cobalt oxides. It is a black antiferromagnetic solid. As a mixed valence compound, its formula is sometimes written as CoIICoIII2O4 and sometimes as CoO•Co2O3.

Cobalt(II) hydroxide or cobaltous hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Co(OH)
2, consisting of divalent cobalt cations Co2+
and hydroxide anions HO−
. The pure compound, often called the "beta form" is a pink solid insoluble in water.

Chloropentamminecobalt chloride is the dichloride salt of the coordination complex [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+. It is a red-violet, diamagnetic, water-soluble salt. The compound has been of academic and historical interest.

Bromopentaamminecobalt(III) bromide is the dibromide salt of the cobalt coordination compound with the formula [Co(NH3)5Br]2+. It is a purple, water-soluble solid. The analogous chloropentaamminecobalt(III) chloride is also well known.
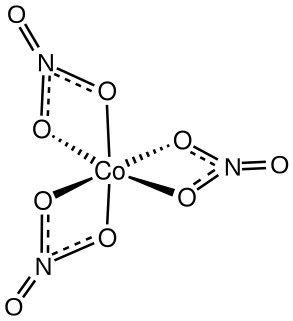
Cobalt(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Co(NO3)3. It is a green, diamagnetic solid that sublimes at ambient temperature.
The sulfate nitrates are a family of double salts that contain both sulfate and nitrate ions (NO3−, SO42−). They are in the class of mixed anion compounds. A few rare minerals are in this class. Two sulfate nitrates are in the class of anthropogenic compounds, accidentally made as a result of human activities in fertilizers that are a mix of ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate, and also in the atmosphere as polluting ammonia, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide react with the oxygen and water there to form solid particles. The nitro group (NO3−) can act as a ligand, and complexes containing it can form salts with sulfate.
Cobalt silicide may refer to the following chemical compounds:

Samarium(III) nitrate is a odorless white-colored chemical compound with the formula Sm(NO3)3. It forms the hexahydrate, which decomposes at 50°C to the anhydrous form. When further heated to 420°C, it is converted to the oxynitrate, and at 680°C it decomposes to form samarium(III) oxide.
A nitrate nitrite is a chemical compound or salt that contains nitrite and nitrate anions (NO3− and NO2−). These are mixed anion compounds. Some have third anions. Many nitrite nitrate compounds are actually coordination complexes of cobalt. Such a substance was discovered by Wolcott Gibbs and Frederick Genth in 1857.